Provide a definition of a commodity product. What role does speculation and hedging play in the commodities market?
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Commodity Products and the Role of Speculation & Hedging in the Commodities Market
1. Definition of a Commodity Product
Acommodity productis araw material or primary agricultural productthat isuniform in quality and interchangeable with other products of the same type, regardless of the producer.
✅Key Characteristics:
Standardized and homogeneous– Little differentiation between producers.
Traded on global markets– Bought and sold on commodity exchanges.
Price determined by supply & demand– Subject to market fluctuations.
💡Examples of Commodity Products:
Agricultural Commodities– Wheat, corn, coffee, cotton.
Energy Commodities– Crude oil, natural gas, coal.
Metals & Minerals– Gold, silver, copper, aluminum.
📌Key Takeaway:Commodities areessential goods used in global trade, where price is the primary competitive factor.
2. The Role of Speculation in the Commodities Market📈
Definition
Speculationinvolves buying and selling commoditiesfor profit rather than for actual use, based on price predictions.
✅How Speculation Works:
Traders and investorsbuy commodities expecting price increases(long positions).
Theysell commodities expecting price declines(short positions).
No physical exchange of goods—transactions are purely financial.
💡Example:
A trader buyscrude oil futures at $70 per barrel, expecting prices to rise. If oil reaches$80 per barrel, the trader sells for profit.
Advantages of Speculation
✔Increases market liquidity– More buyers and sellers improve trading efficiency.✔Enhances price discovery– Helps determine fair market value.✔Absorbs market risk– Speculators take risks that producers or consumers avoid.
Disadvantages of Speculation
âŒCreates excessive volatility– Large speculative trades can cause price spikes or crashes.âŒDetaches prices from real supply and demand– Can inflate bubbles or cause artificial declines.âŒMarket manipulation risks– Speculators with large holdings can distort prices.
📌Key Takeaway:Speculationadds liquidity and helps price discovery, butcan lead to extreme volatilityif unchecked.
3. The Role of Hedging in the Commodities Market🔄
Definition
Hedgingis arisk management strategyused by commodity producers and consumers toprotect against price fluctuations.
✅How Hedging Works:
Producers (e.g., farmers, oil companies)use futures contracts tolock in a pricefor future sales, reducing the risk of price drops.
Consumers (e.g., airlines, food manufacturers)hedge tosecure stable input costs, avoiding sudden price surges.
💡Example:
An airline hedges against rising fuel costsby buying fuel futures at a fixed price for the next 12 months. If fuel prices rise, the airline is protected from increased expenses.
Advantages of Hedging
✔Stabilizes revenue and costs– Helps businesses plan with certainty.✔Protects against price swings– Reduces exposure to unpredictable market conditions.✔Encourages long-term investment– Producers and buyers operate with confidence.
Disadvantages of Hedging
âŒReduces potential profits– If prices move favorably, hedgers miss out on gains.âŒContract obligations– Hedgers must honor contract terms, even if market prices improve.âŒHedging costs– Fees and contract costs can be high.
📌Key Takeaway:Hedgingprotects businesses from commodity price risk, ensuringstable revenue and cost control.
4. Speculation vs. Hedging: Key Differences
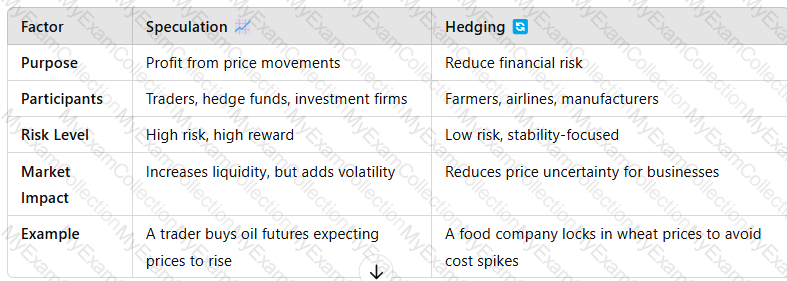
Key Takeaway:Speculationseeks profit from price changes, while hedgingminimizes risk from price fluctuations.
5. Conclusion
✅Commodity productsarestandardized raw materialstraded globally, with prices driven bysupply and demand dynamics.✅Speculationbrings liquidity and price discovery butcan increase volatility.✅Hedginghelpsbusinesses stabilize costs and revenues, ensuring financial predictability.✅Both strategies play essential rolesin ensuring abalanced, functional commodities market.
XYZ is a manufacturing company based in the UK. It has a large complex supply chain and imports raw materials from Argentina and South Africa. It sells completed products internationally via their website. Evaluate the role of licencing and taxation on XYZ’s operations.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of the Role of Licensing and Taxation on XYZ’s Operations
Introduction
Licensing and taxation play acritical role in international trade, supply chain management, and overall financial performance. For XYZ, aUK-based manufacturing companythat importsraw materials from Argentina and South Africaand sellsinternationally via an e-commerce platform, compliance with licensing and taxation regulations is essential to ensuresmooth operations, cost efficiency, and legal compliance.
This evaluation will assess theimpact of licensing and taxation on XYZ’s global supply chain, import/export activities, and financial performance.
1. The Role of Licensing in XYZ’s Operations
1.1 Import and Export Licensing Regulations
As XYZ importsraw materials from Argentina and South Africa, it must comply with theUK’s import licensing requirementsand trade agreements with these countries.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Import licensesmay be required for certain restricted raw materials (e.g.,metals, chemicals, agricultural products).
Export control lawsmay apply, depending on thedestination of final products.
Delays or finesmay occur if licenses are not properly managed.
💡Example:If XYZ importsmetal componentssubject to UK trade restrictions, it mustsecure import licensesbefore shipment clearance.
1.2 Industry-Specific Licensing Requirements
Some industries requirespecial licensesto manufacture and sell products globally.
✅Impact on XYZ:
If XYZ manufactureselectronics or chemical-based products, it may need compliance certifications (e.g.,CE marking in the EU, FDA approval in the US).
Failure to meet licensing requirements canblock international sales.
💡Example:A UK manufacturer sellingmedical devicesmust obtainMHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency) approvalbefore distributing products.
1.3 E-Commerce & Digital Sales Licensing
As XYZ sells its products internationally via itswebsite, it must comply with:✅Consumer Protection Laws(e.g., GDPR for EU customers).✅E-commerce business registrationand online sales regulations.
💡Example:XYZ may need aVAT number in the EUif it sells products to European customers via its website.
2. The Role of Taxation in XYZ’s Operations
2.1 Import Duties and Tariffs
XYZ’s supply chain involvesimporting raw materials from Argentina and South Africa, which may attractimport duties and tariffs.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Higherimport duties increase raw material costsand impact profitability.
Tariff-free trade agreements(e.g., UK-South Africa trade deal)may reduce costs.
Post-Brexit UK-EU trade regulationsmay affect supply chain tax structures.
💡Example:If theUK imposes high tariffs on South African goods, XYZ may need tofind alternative suppliers or negotiate better deals.
2.2 Corporate Tax & International Tax Compliance
XYZ must comply withUK corporate tax lawsand international taxation regulations.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Payingcorporate tax in the UKbased onglobal sales revenue.
Managinginternational tax obligationswhen selling in multiple countries.
Risk of double taxationif the same income is taxed in multiple jurisdictions.
💡Example:If XYZ sells products inGermany and the US, it may need toregister for tax in those countriesand comply withlocal VAT/GST requirements.
2.3 Value Added Tax (VAT) & Sales Tax
Since XYZsells internationally via its website, it must adhere toglobal VAT and sales tax rules.
✅Impact on XYZ:
In theEU, VAT registration is required for online sales above a certain threshold.
In theUS, sales tax regulations varyby state.
Compliance withUK VAT laws (e.g., 20% standard rate)on domestic sales.
💡Example:A UK company sellingonline to EU customersmust comply with theEU One-Stop-Shop (OSS) VAT scheme.
2.4 Transfer Pricing & Tax Efficiency
If XYZhas international subsidiaries or supply chain partners, it must managetransfer pricing regulations.
✅Impact on XYZ:
Ensuringfair pricing between UK operations and overseas supplierstoavoid tax penalties.
Optimizingtax-efficient supply chain structurestominimize tax burdens.
💡Example:Multinational companies likeApple and Amazonusetax-efficient structuresto reduce liabilities.
3. Strategic Actions for XYZ to Manage Licensing and Taxation Effectively
XYZ can take several steps tooptimize tax compliance and licensing efficiency:
 A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer screen
Description automatically generated
Conclusion
Licensing and taxation have amajor impact on XYZ’s international manufacturing and e-commerce operations. To maintain profitability andregulatory compliance, XYZ must:
✅Ensureimport/export licensingaligns with UK and international trade laws.✅Manageimport duties, VAT, and corporate tax obligationseffectively.✅Optimize itssupply chain and tax planningto reduce costs.
By proactively managing these areas, XYZ canenhance its global competitiveness while minimizing risks.
Currency Options and Currency Swaps are instruments used in foreign exchange. Explain the advantages of using these derivatives compared to the use of spot transactions
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Comparison of Currency Options, Currency Swaps, and Spot Transactions in Foreign Exchange
Introduction
In international trade and finance, companies dealing withforeign currenciesuse various financial instruments tomanage exchange rate risks. The three main instruments are:
Currency Options– Provide the right (but not obligation) to exchange currency at a fixed rate in the future.
Currency Swaps– A contract to exchange currency flows over a set period.
Spot Transactions– A simpleimmediate currency exchangebased on the current market rate.
While spot transactions offer simplicity,currency options and swaps provide better risk management and flexibility.
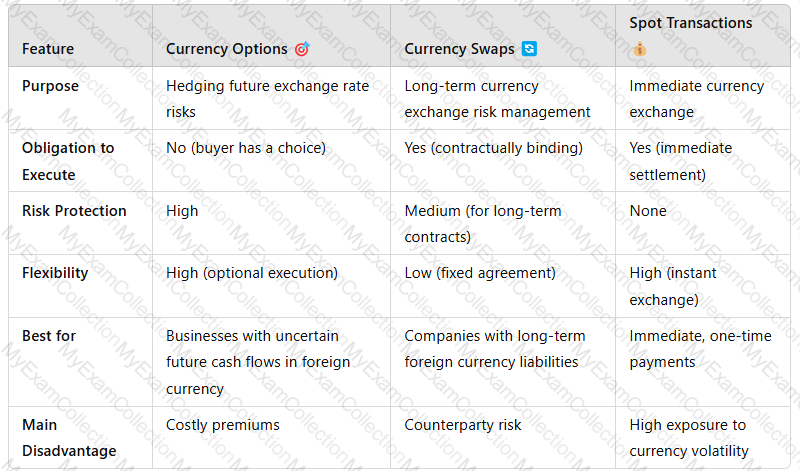
1. Currency Options🎯(Flexible Risk Management Tool)
Definition
Acurrency optiongives the holder theright, but not the obligation, to exchange a currency at a predetermined rate on or before a specific date.
✅Types of Options:
Call Option– Right tobuya currency at a fixed rate.
Put Option– Right tosella currency at a fixed rate.
💡Example:A UK importer buying goods from the US purchases aGBP/USD call optionto protect against an increase in the exchange rate.
Advantages of Currency Options Over Spot Transactions
✔Risk Protection– Protects against adverse currency movements while maintaining upside potential.✔Flexibility– No obligation to execute the transaction if the exchange rate is favorable.✔Ideal for Hedging Future Payments– Useful for businesses withuncertain future cash flows in foreign currencies.
âŒDisadvantages✖Premium Costs– Buying options requires upfront payment.✖Complexity– More sophisticated than spot transactions.
📌Best for:Businesses managing currency risk with unpredictable payment schedules.
2. Currency Swaps🔄(Long-Term Hedging Solution)
Definition
Acurrency swapis a contract between two parties toexchange currency flowsover a set period at a predetermined rate.
✅How It Works:
Companies exchangeprincipal and interest paymentsin different currencies.
Used tosecure long-term financingin foreign markets.
💡Example:AUK company with a loan in USDenters aGBP/USD swapwith a US firm to exchange interest payments, reducing exchange rate risk.
Advantages of Currency Swaps Over Spot Transactions
✔Long-Term Stability– Protects businesses from long-term exchange rate fluctuations.✔Cost Efficiency– Often cheaper than converting currency via spot transactions repeatedly.✔Reduces Interest Rate Risk– Useful for companies withforeign currency debt obligations.
âŒDisadvantages✖Less Flexible Than Options– The swap contract must be followed as agreed.✖Counterparty Risk– Dependent on the financial stability of the other party.
📌Best for:Companies with long-term foreign currency liabilities (e.g., loans, international contracts).
3. Spot Transactions💰(Immediate Currency Exchange, No Hedging)
Definition
Aspot transactionis a straightforward exchange of currency at thecurrent market rateforimmediate settlement(usually within two days).
💡Example:A European exporter receiving USD payment converts itimmediately into EURusing a spot transaction.
Limitations Compared to Derivatives (Options & Swaps)
âŒNo Risk Protection– Subject to daily exchange rate volatility.âŒNot Suitable for Future Obligations– Cannot hedge againstexpected payments or receipts.âŒHigher Costs for Frequent Transactions– Repeated spot trades incur forex fees and spread costs.
📌Best for:Small businesses or one-time transactions with no currency risk concerns.
4. Comparison Table: Currency Options, Swaps, and Spot Transactions
 A screenshot of a white and black chart
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a white and black chart
Description automatically generated
Key Takeaway:
Currency options offer flexibility and protectionbut come at a cost.
Currency swaps provide long-term stabilityfor large corporations.
Spot transactions are simplebut expose businesses to market fluctuations.
5. Conclusion & Best Recommendation
For businesses engaged ininternational trade, investments, or loans, usingcurrency options and swapsis superior tospot transactions, as they provide:
✅Protection from exchange rate volatility.✅Cost efficiency for large or recurring transactions.✅Better financial planning and risk management.
Best Choice Based on Business Needs:
For short-term flexibility → Currency Options🎯
For long-term contracts or loans → Currency Swaps🔄
For one-time currency exchange → Spot Transactions💰
By selecting the right derivative instrument, businesses canreduce foreign exchange risk and improve financial stability.
Discuss how the following can impact upon supply chain operations and business strategy:
1) Discrimination, equality and diversity
2) Redundancy and dismissal
3) Working time and payment
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Impact of Employment Policies on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Introduction
Employment policies such asdiscrimination, equality and diversity, redundancy and dismissal, and working time and paymenthave a significant impact onsupply chain operations and business strategy. These factors influenceemployee productivity, legal compliance, reputation, and operational efficiency.
For businesses operating inglobal supply chains, ensuring compliance withemployment laws and ethical workforce practicesis crucial to maintainingsustainability, cost efficiency, and risk management.
1. Impact of Discrimination, Equality, and Diversity on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Discrimination laws anddiversity and inclusion (D&I) policiesensure fair treatment in the workplace.
✅Impact on Supply Chain Operations
Companies mustprevent workplace discriminationacross hiring, promotions, and supplier engagement.
Non-compliance withequality lawscan lead tolegal penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Supply chain leaders mustpromote diverse supplier partnershipsand inclusive hiring practices.
💡Example:Many multinational corporations, such asUnilever and IBM, havesupplier diversity programsthat prioritize working withminority-owned and women-owned businesses.
✅Impact on Business Strategy
Encouragesinnovation and diverse perspectivesin problem-solving.
Enhancesbrand reputation and customer loyaltythrough ethical business practices.
Helps businesses attracttop global talentby fostering an inclusive workplace.
📌Strategic Action:Businesses should implementanti-discrimination traininganddiversity recruitment strategiesto create a fair and inclusive work environment.
2. Impact of Redundancy and Dismissal on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Redundancy and dismissal policies regulate how companiesterminate employment due to economic downturns, automation, or restructuring.
✅Impact on Supply Chain Operations
Workforcereductions can disrupt production schedules and supplier relationships.
Companies must ensurefair redundancy policiesto prevent legal claims or industrial action.
Automation may lead toworker displacement, requiringretraining programs.
💡Example:Ford’s decision to restructure operations in the UKresulted in job losses, requiring compliance withUK redundancy lawsand union negotiations.
✅Impact on Business Strategy
Must balancecost-cutting measureswith employee morale and brand reputation.
Need to comply withnational and international labor lawsto avoid legal action.
Investing inemployee retraining and redeploymentcan reduce negative effects of redundancy.
📌Strategic Action:Businesses should establishclear redundancy frameworks, provideseverance packages, and offeroutplacement supportfor affected employees.
3. Impact of Working Time and Payment on Supply Chain Operations and Business Strategy
Working time regulations and fair wage policiesimpact labor costs, productivity, and compliance.
✅Impact on Supply Chain Operations
Ensuring compliance withworking time laws (e.g., UK Working Time Regulations 1998)prevents overworking employees.
Failure to meetminimum wage and overtime regulationscan lead to legal disputes.
Supply chains must ensurefair pay for workers in offshore factoriesto meetethical sourcing standards.
💡Example:TheUK National Minimum Wage Actensures fair wages, while theModern Slavery Act (2015)prevents exploitation in global supply chains.
✅Impact on Business Strategy
Fair wages enhanceemployee motivation and reduce turnover.
Complying withwage and hour lawsprevents reputational risks and fines.
Ethical pay practices attractconscious consumers and investors.
📌Strategic Action:Businesses should conductregular wage auditsand ensureglobal supplier compliance with fair labor laws.
Conclusion
Employment policies related todiscrimination, redundancy, and working time/paysignificantly impactsupply chain operations and business strategy. Companies must ensure:
✅Diversity and equality policiesto foster innovation and enhance reputation.✅Ethical redundancy and dismissal processesto maintain legal compliance.✅Fair wages and working hoursto improve productivity and worker well-being.
By aligning HR policies with supply chain strategy, businesses canenhance efficiency, reduce risks, and build a sustainable competitive advantage.
Evaluate diversification as a growth strategy. What are the main drivers and risks?
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of Diversification as a Growth Strategy
Introduction
Diversification is agrowth strategywhere a company expands intonew markets or develops new productsthat are different from its existing offerings. It is theriskiest strategyinAnsoff’s Growth Matrix, but it can provide significant opportunities forbusiness expansion, revenue diversification, and risk mitigation.
Diversification is driven by factors such asmarket saturation, competitive pressure, and technological advancementsbut also carries risks related tohigh investment costs and operational complexity.
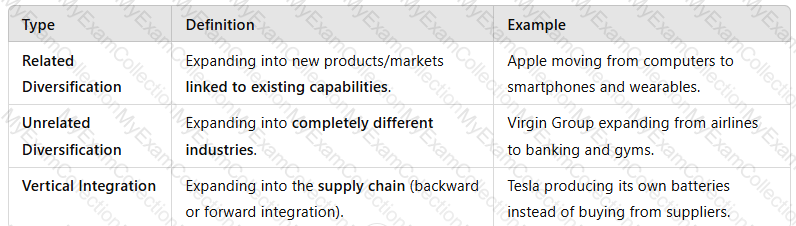
1. Types of Diversification
 A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
Description automatically generated
2. Main Drivers of Diversification🚀
1. Market Saturation and Competitive Pressure
When a businessreaches peak growthin its existing market, diversification helpsfind new revenue streams.
Competition forces businessesto explore new industries for continued growth.
💡Example:Amazonexpanded from anonline bookstore to cloud computing (AWS)due to competition and limited retail growth.
2. Risk Reduction and Business Sustainability
Diversifying reducesdependence on a single market or product.
Protects the business againsteconomic downturns and industry-specific risks.
💡Example:Samsung operates in electronics, shipbuilding, and insurance, reducing reliance on one sector.
3. Leveraging Core Competencies and Brand Strength
Companies useexisting expertise, technology, or brand reputationto enter new markets.
💡Example:Nike expanded from sportswear to fitness apps and wearable technology.
4. Technological Advancements & Market Opportunities
Digital transformation and innovationcreate opportunities for diversification.
Companies invest innew technologies, AI, and automationto expand their offerings.
💡Example:Google diversified into AI, smart home devices, and autonomous vehicles (Waymo).
3. Risks of Diversificationâš ï¸
1. High Investment Costs & Uncertain Returns
Diversification requiressignificant R&D, marketing, and infrastructure investment.
ROI is uncertain, andfailure can result in financial losses.
💡Example:Coca-Cola's failed diversification into the wine industryresulted in losses due to brand mismatch.
2. Lack of Expertise & Operational Challenges
Expanding intounfamiliar industriesincreasesoperational complexity and risks.
Companies maylack the expertiserequired for success.
💡Example:Tesco’s expansion into the US market (Fresh & Easy) faileddue to a lack of understanding of American consumer behavior.
3. Dilution of Brand Identity
Expanding into unrelated sectors canconfuse customersandweaken brand strength.
💡Example:Harley-Davidson’s attempt to enter the perfume marketdamaged its brand credibility.
4. Regulatory and Legal Barriers
Compliance with different industry regulationscan be complex and costly.
💡Example:Facebook faced regulatory scrutinywhen diversifying into financial services withLibra cryptocurrency.
4. Conclusion
Diversification can be ahigh-reward growth strategy, but it requires carefulplanning, market research, and strategic alignment.
✅Main driversincludemarket saturation, risk reduction, leveraging expertise, and technology opportunities.âŒKey risksincludehigh costs, operational challenges, brand dilution, and regulatory barriers.
Companies mustevaluate diversification carefullyand ensurestrategic fit, financial feasibility, and market demandbefore expanding into new industries.
Evaluate the role of strategic human management in creating competitive advantage for an organisation
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of the Role of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) in Creating Competitive Advantage
Introduction
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is theproactive alignment of HR policies withbusiness strategyto achieve long-term success. It focuses on developingtalent, leadership, culture, and employee engagementto enhanceorganizational performance and competitiveness.
By implementingeffective SHRM practices, companies can create asustainable competitive advantagethrough a highly skilled and motivated workforce.
1. The Role of SHRM in Creating Competitive Advantage
1.1 Talent Acquisition and Workforce Planning
✅Why it matters?
Recruiting and retaininghighly skilled employeesis essential for innovation and efficiency.
Workforce planning ensuresthe right people are in the right rolesat the right time.
💡Example:Google’s strategic hiring approachfocuses on attractingtop AI and engineering talent, driving innovation in tech.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Builds anexpert workforcethat competitors cannot easily replicate.✔Reducesturnover costsby ensuring long-term retention.
1.2 Employee Development and Training
✅Why it matters?
Continuous learning and skills development enhanceemployee productivity and innovation.
Upskilling employees keeps companies ahead infast-changing industries.
💡Example:Amazon’s Career Choice Programinvests in employee training to develop future leaders and improve workforce capabilities.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Enhances organizational agilityby equipping employees withemerging skills.✔Creates a culture ofcontinuous improvement and innovation.
1.3 Performance Management and Employee Engagement
✅Why it matters?
Effective performance management systemsensure employees align with business goals.
Engaged employees aremore productive, motivated, and committedto company success.
💡Example:Salesforce’s focus on employee engagementthrough leadership development and internal career growth has resulted in high retention and innovation.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Driveshigh workforce productivityand efficiency.✔Reduces costs related topoor performance and disengagement.
1.4 HR Technology and Data-Driven Decision-Making
✅Why it matters?
Digital HR tools (e.g.,AI-driven recruitment, performance analytics, HR automation) optimize talent management.
Data-driven HR strategies help predictworkforce trends and talent gaps.
💡Example:Unilever uses AI-driven HR analyticsto identify high-potential employees and enhance leadership succession planning.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Enablesdata-driven workforce planningfor future growth.✔Increasesefficiency and reduces hiring biases.
1.5 Employee Well-being and Diversity & Inclusion
✅Why it matters?
Work-life balance policies, mental health support, and DEI (Diversity, Equity, Inclusion) programsimprove workplace culture.
Diverse teamsenhance creativity, problem-solving, and innovation.
💡Example:Microsoft’s Diversity & Inclusion programshave strengthened its brand and innovation by fostering amore inclusive workforce.
✅Competitive Advantage Created:✔Attractstop global talentwho seek inclusive workplaces.✔Strengthensbrand reputation and employee loyalty.
2. Advantages of Strategic HRM in Competitive Positioning
✅Develops Unique Talent & Expertise– Hard for competitors to replicate.✅Enhances Productivity & Efficiency– Skilled, engaged employees drive better results.✅Supports Business Agility & Innovation– Workforce is adaptable to market changes.✅Builds Strong Employer Brand– Attracts and retains high-quality talent.
📌Key Takeaway:SHRM transformsHR from an administrative function to a strategic assetthat creates long-term value.
3. Challenges & Risks of SHRM
âŒImplementation Costs– Advanced HR technology and training require investment.âŒResistance to Change– Employees may resist new HR policies.âŒMeasuring ROI Can Be Complex– Talent development impacts long-term but ishard to quantify.âŒLegal & Compliance Risks– Global HR policies mustalign with labor lawsacross different countries.
📌Solution:Businesses must integrateHR analytics, leadership buy-in, and cultural change strategiesto overcome these challenges.
4. Conclusion
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) isa key driver of sustainable competitive advantageby:
✅Attracting and retaining top talent.✅Developing a highly skilled, engaged, and innovative workforce.✅Leveraging HR technology and data-driven insights.✅Promoting employee well-being, diversity, and inclusion.
Companies thatprioritize SHRMcreate adynamic, future-ready workforce, ensuring long-term success in competitive markets.
Evaluate the following approaches to supply chain management: the Business Excellence Model, Top-Down Management Approach and Six Sigma
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Evaluation of Approaches to Supply Chain Management
Introduction
Effectivesupply chain management (SCM)is critical for organizations to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Various management approaches help organizations optimize their supply chain performance. Three widely recognized approaches include:
Business Excellence Model (BEM)– A framework for continuous improvement.
Top-Down Management Approach– A hierarchical decision-making structure.
Six Sigma– A data-driven methodology for process improvement.
Each approach has strengths and limitations when applied to supply chain management.
1. Business Excellence Model (BEM) in Supply Chain Management
Explanation
TheBusiness Excellence Model (BEM)is a holistic framework used to assess and improve business performance. TheEuropean Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) Excellence Modelis one of the most common BEM frameworks.
It focuses on9 key criteria:Leadership, Strategy, People, Partnerships & Resources, Processes, Customer Results, People Results, Society Results, and Business Performance.
Application in Supply Chain Management
✅Encouragescontinuous improvementin supplier relationships and logistics.✅Focuses oncustomer-centric supply chainstrategies.✅Promotescollaboration with suppliers and stakeholdersto optimize efficiency.
💡Example:Toyota’s Lean Supply ChainfollowsBEM principlesto maintainsupplier partnerships and quality improvement.
Evaluation
✅Advantages
Provides astructured frameworkfor evaluating supply chain performance.
Enhancescollaboration between internal teams and external suppliers.
Focuses onquality management and customer satisfaction.
âŒLimitations
Can becomplex and resource-intensiveto implement.
Requirescultural changeand strong leadership commitment.
2. Top-Down Management Approach in Supply Chain Management
Explanation
TheTop-Down Management Approachfollows ahierarchical structurewhere decisions are made by senior management and communicated downward. This approach ensurescentralized decision-makingandstrong leadership control.
Application in Supply Chain Management
✅Ensuresconsistency in supply chain policiesand strategic direction.✅Facilitatesquick decision-makingin procurement and logistics.✅Helps maintaincompliance with regulatory standardsand corporate policies.
💡Example:Amazon’s Supply Chain Strategyis largelytop-down, with executives making key strategic decisions on warehousing, delivery, and automation.
Evaluation
✅Advantages
Ensuresstrong leadership directionin supply chain management.
Reducesconfusion in decision-makingby maintaining clear authority.
Useful forlarge-scale global supply chainsthat need standardization.
âŒLimitations
Can berigid and slow to adaptto changing supply chain disruptions.
Mayreduce innovationand employee engagement in problem-solving.
Less effective indynamic, fast-changing industries.
3. Six Sigma in Supply Chain Management
Explanation
Six Sigmais adata-driven methodologyaimed at reducing defects and improving quality. Itfollows theDMAIC cycle(Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to enhanceprocess efficiency and minimize errors.
Application in Supply Chain Management
✅Helps identifywaste and inefficienciesin supply chain processes.✅Reducesdefects and errors in procurement, logistics, and inventory management.✅Enhancessupplier performance evaluationthrough data analysis.
💡Example:General Electric (GE) used Six Sigmato improvesupply chain efficiency, reducing defects and operational costs.
Evaluation
✅Advantages
Reducessupply chain disruptions by improving process reliability.
Usesdata-driven decision-makingfor procurement and logistics.
Improvessupplier quality management.
âŒLimitations
Requiresintensive training and certification (Black Belt, Green Belt, etc.).
Can betoo rigid for industries requiring flexibility and innovation.
Implementation may becostly and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Each approach offers unique benefits for supply chain management:
BEMensures aholistic, continuous improvement frameworkfor supply chains.
Top-Down Managementprovidesstrong leadership direction and centralized decision-making.
Six Sigmaimprovesprocess quality and operational efficiency.
Organizations shouldcombine these approachesbased on theirbusiness model, industry requirements, and strategic goalsto optimize supply chain performance.
Explain how culture and historic influences can impact upon a business’s strategic decisions and positioning within the marketplace
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
How Culture and Historic Influences Impact Strategic Decisions and Market Positioning
A business’sstrategic decisionsandpositioning within the marketplaceare shaped by bothorganizational cultureandhistorical influences. These factors affect how a companydevelops strategy, interacts with customers, manages employees, and competes globally.
1. The Role of Organizational Culture in Strategic Decisions
Organizational culture is theshared values, beliefs, and behaviorswithin a company. It influencesdecision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage.
🔹How Culture Affects Strategy
✅Risk Appetite– A culture that embraces innovation (e.g., Google) will invest in R&D, while risk-averse cultures (e.g., traditional banks) focus on stability.✅Decision-Making Speed– Hierarchical cultures (e.g., Japanese firms) rely on consensus, while Western firms (e.g., Apple) may have centralized decision-making.✅Customer Engagement– Acustomer-centric culture(e.g., Amazon) leads to investment in personalization and AI-driven recommendations.
💡Example:
Toyota’s Kaizen Culture (Continuous Improvement)has shaped itslean manufacturing strategy, giving it a competitive advantage in cost efficiency.
2. How Historic Influences Shape Business Strategy
Historical events,past business performance, economic trends, and industry evolutionshape how businessesposition themselves in the marketplace.
🔹How History Affects Strategy
✅Legacy of Innovation or Conservatism– Companies with a history ofinnovation(e.g., IBM, Tesla) continuously push boundaries, while firms with traditional roots (e.g., British banks) focus on risk management.✅Economic Crises and Financial Stability– Businesses that survived financial crises (e.g., 2008 recession) tend to developrisk-averse financial strategies.✅Market Reputation and Consumer Perception– A stronghistorical reputationcan be leveraged for branding (e.g., Rolls-Royce’s luxury image).
💡Example:
Legonearly went bankrupt in the early 2000s, leading it toredefine its strategy, focus ondigital gaming partnerships, and revive its brand.
3. The Influence of National and Corporate Culture on Global Positioning
When expanding globally, businesses mustalign their strategies with different cultural expectations.
🔹How Culture Affects Global Market Entry
✅Consumer Preferences– Fast food chainsadapt menusfor local cultures (e.g., McDonald's in India offers vegetarian options).✅Negotiation & Communication Styles– Business negotiations inChinaemphasize relationships ("Guanxi"), whileWestern firmsprioritize efficiency.✅Leadership and Management Approaches–German firmsemphasize engineering precision, whileSilicon Valley firmsprioritize agility and experimentation.
💡Example:
IKEAmodifies store layouts in different countries—small apartments in Japan vs. large home spaces in the U.S.
4. Strategic Positioning Based on Cultural & Historic Factors
A company’s historical and cultural influences define itspositioning strategy:
 A screenshot of a white box
Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a white box
Description automatically generated
Conclusion
A business’sstrategic decisions and market positioningare deeply influenced byorganizational culture, national culture, and historical performance. Companies thatleverage their cultural strengths and adapt to market historycan achievelong-term competitive advantage.
Discuss how XYZ, a global beverage manufacturing organisation, could use the Boston Consultancy Group Framework to impact upon strategic decision making
Introduction
TheBoston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrixis a strategic tool used by organizations to analyze their product portfolio and allocate resources effectively. It classifies products intofour categories—Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs—based onmarket growth rateandmarket share.
As aglobal beverage manufacturing organization, XYZ can use theBCG Matrixto evaluate its product range, identify growth opportunities, and make informed strategic decisions.
1. Explanation of the BCG Matrix
TheBCG Matrixis divided into four quadrants:
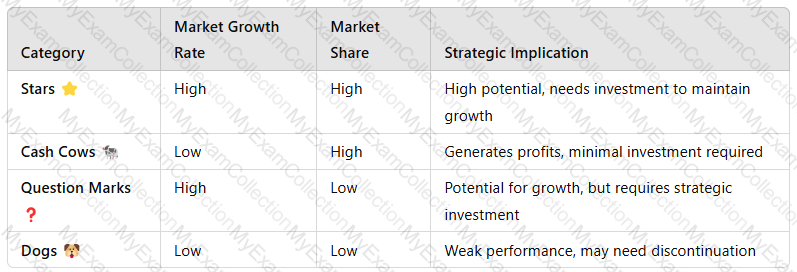
Example for XYZ:
Star:A fast-growingenergy drinkbrand in emerging markets.
Cash Cow:A flagshipcola productwith stable market demand.
Question Mark:A newfunctional health drinkwith uncertain market acceptance.
Dog:An underperformingdiet soda variantwith declining sales.
2. How XYZ Can Use the BCG Matrix for Strategic Decision-Making
XYZ can use the BCG Matrix to makeresource allocation and investment decisionsbased on product performance.
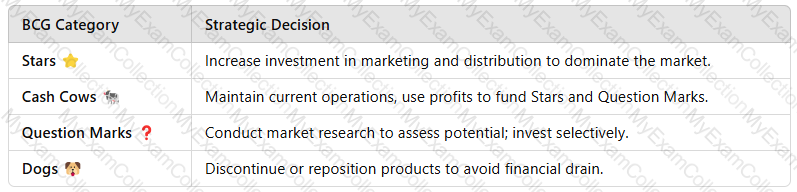
3. Advantages of Using the BCG Matrix for XYZ
✅Resource Allocation– Helps prioritize investment in high-growth products.
✅Strategic Focus– Identifies which products to grow, maintain, or phase out.
✅Market Adaptation– Helps XYZ adjust its beverage portfolio based on changing consumer trends.
💡Example:IfXYZ’s energy drink(a Star) is experiencing high growth, more marketing and production investment may be justified.
4. Limitations of the BCG Matrix
âŒIgnores Market Competition– A product may have a high market share, but competition could still impact profitability.
âŒSimplistic Assumptions– Not all products neatly fit into one category; market dynamics are complex.
âŒFocuses on Growth and Share Only– It does not consider external factors likeprofit margins, customer loyalty, or brand strength.
💡Example:AQuestion Mark productmight have potential, but if consumer preferences shift, it may never become a Star.
5. Application of the BCG Matrix in the Beverage Industry
XYZ can apply theBCG Matrixby reviewing itsentire product portfolioacross different geographic markets.

Conclusion
TheBCG Matrixis a valuable strategic tool for XYZ to analyze itsproduct portfolio, prioritize investments, and make informedmarket-based decisions. However, it should be used alongside otherstrategic models(e.g.,PESTLE, VRIO) to ensure acomprehensive business strategy.
Answer:
See the complete answer below in Explanation.
Explanation:
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix and Strategic Decision-Making for XYZ

