A small deaning services organisation is about to start work on a hospital dleaning contract for the local Health Trust. You, as auditor, are conducting a Stage 2 audit to ISO 9001 and review the contract with the Service Manager. The contract requires that a cleaning plan is produced. You: "How was the cleaning plan for the contract developed?" Service Manager: "We have a basic template that covers the materials, labour requirements and cleaning methods to be employed. Some of that is specified by the customer." You: "How does the plan deal with locations like the intensive care wards and the operating theatres, which are included in the contract?" Service Manager: "The basic plan covers general wards, but we will do more frequent cleaning in those areas if the hospital requests it." You: "Are you aware of the regulatory requirements for cleaning standards in hospitals?" Service Manager: "No. We depend on the hospital to look after that side of things in the contract." You decide to raise a non-conformity against section 8.2.2.a.1 of ISO 9001. You decide to raise another non-conformity against section 8.2.4 of ISO 9001 when finding that the cleaning plan was amended without the agreement of the Health Trust. A different cleaning chemical was substituted to that specified in the contract. At the follow- up audit, the corrective action proposed was to "obtain a concession from the Health Trust for use of the new chemical." Which one of the following options is the reason why you did not accept this action taken?
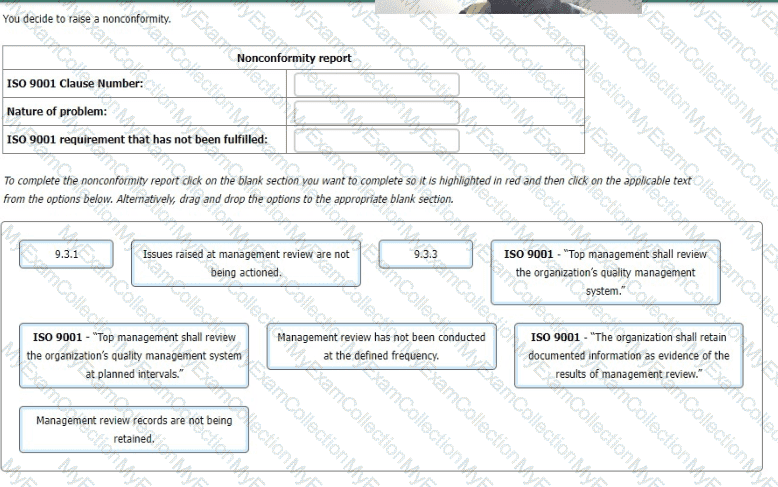
You are carrying out an annual audit at an organisation that offers home security services. You are interviewing the Quality Manager (QM)
You: "Would you tell me about your management review process?"
QM: "The senior management team plans to review the management system every six months. The review follows a set agenda and records are maintained."
You: "May I see the records from the last two management reviews?"
Narrative: The Quality Manager gives you the latest record, which shows the last management review took place nine months ago.
The Quality Manager then gives you the previous management review record, which took place one year before the latest review.
You: "Are there any other review reports in the last two years?
QM: "No, these are the only ones."
For each of the following scenarios, select four that are corrective actions.
You work for organisation A. You are asked to lead an internal audit of A's quality management system. It has a head office in Plant A1 and a second Plant A2 nearby. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, production in A2 was discontinued and it was rented to a logistics organisation B, not related to A. There are no A employees working in A2. Organisation A expects to reassume production in A2 as soon as possible.
Which of the following actions would you consider appropriate when planning the internal audit of A's quality management system?
Scenario 5: Mechanical-Electro (ME) Audit Stages
Mechanical-Electro, better known as ME, is an American company that provides mechanical and electrical services in China. Their services range from air-conditioning systems, ventilation systems, plumbing, to installation of electrical equipment in automobile plants, electronic manufacturing facilities, and food processing plants.
Due to the fierce competition from local Chinese companies and failing to meet customer requirements, ME's revenue dropped significantly. In addition, customers' trust and confidence in the company decreased, and the reputation of the company was damaged.
In light of these developments, the top management of ME decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After having an effective QMS in place for over a year, they applied for a certification audit.
A team of four auditors was appointed for the audit, including Li Na as the audit team leader. Initially, the audit team conducted a general review of ME's documents, including the quality policy, operational procedures, inventory lists, QMS scope, process documentation, training records, and previous audit reports.
Li Na stated that this would allow the team to maintain a systematic and structured approach to gathering documents for all audit stages. While reviewing the documented information, the team observed some minor issues but did not identify any major nonconformities. Therefore, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to prepare a report or conduct a meeting with ME's representatives at that stage of the audit. She stated that all areas of concern would be discussed in the next phase of the audit.
Following the on-site activities and the opening meeting with ME's top management, the audit team structured an audit test plan to verify whether ME’s QMS conformed to Clause 8.2.1 (Customer Communication) of ISO 9001.
To do so, they gathered information through group interviews and sampling. Li Na conducted interviews with departmental managers in the first group and then with top management. In addition, she chose a sampling method that sufficiently represented customer complaints from both areas of ME's operations.
The team members were responsible for the sampling procedure. They selected a sample size of 4 out of 45 customer complaints received weekly for electrical services and 2 out of 10 complaints for mechanical services.
Afterward, the audit team evaluated the evidence against the audit criteria and generated the audit findings.
After reviewing the documented information, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to report the minor nonconformities that were identified; instead, they would be discussed in the next audit phase. Is this acceptable?
Which of the following subjects should an auditor discuss when communicating with the auditee’s top management?
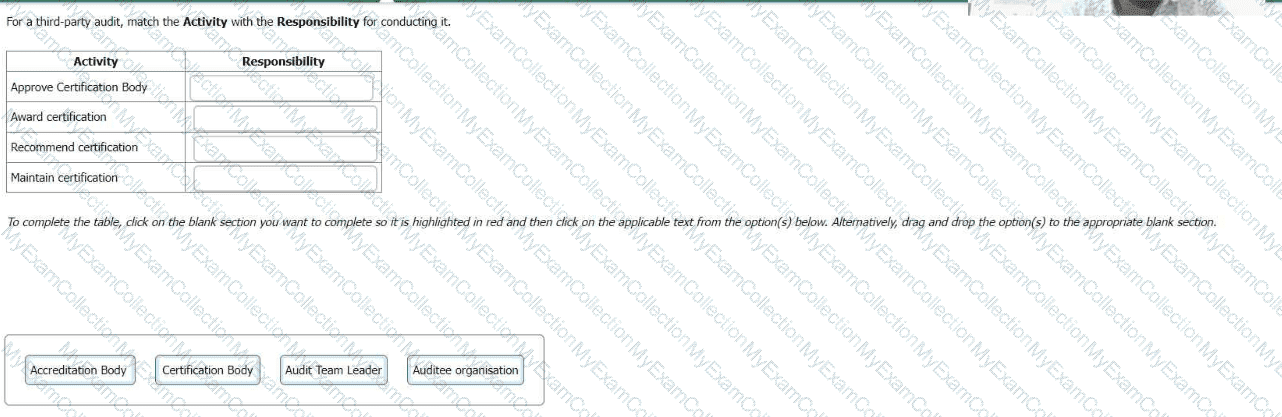
For a third-party, match the Activity with the Responsibility for conducting it.
Select the term that best describes the purpose of retaining documented information in a quality management system to ISO 9001.
Whistlekleen is a national dry cleaning and laundry organization with 50 shops. You are conducting a surveillance audit of the Head Office and are sampling customer complaints. You find that 80% of complaints originate from five shops in the same region. Most of these complaints relate to damage to customer laundry. The Quality Manager tells you that those are the oldest shops in the organization. The cleaning equipment needs replacing, but the organization cannot afford it now. Complaining customers are offered a financial incentive to close the complaint.
On raising the matter with senior management, you are told that there are plans to replace the equipment in these shops over the next five years.
Select the one option which correctly describes the non-conformity to be raised against ISO 9001.
Select the term which best describes the quality management system process of modifying a non-conforming product to bring it within acceptance criteria.
Audit criteria are a set of requirements used as a reference against which objective evidence is compared.
Which two of the following are not potential audit criteria?
An audit team of three people is conducting a Stage 2 audit to ISO 9001 of an engineering organisation which manufactures sacrificial anodes for the
oil and gas industry in marine environments. These are aluminium products designed to prevent corrosion of submerged steel structures. As one of
the auditors, you find that the organisation has shipped anodes for Project DK in the Gulf of Mexico before the galvanic efficiency test results for the
anodes have been fully analysed and reported as required by the customer. The Quality Manager explains that the Managing Director authorised the
release of the anodes to avoid late delivery as penalties would be imposed. The customer was not informed since the tests rarely fall below the
required efficiency. You raise a nonconformity against clause 8.6 of ISO 9001.
During the audit team meeting in preparation for the Closing meeting, the second auditor disagreed with the clause of ISO 9001 selected for the
above nonconformity. He thinks it should be clause 9.1.1.
Choose three options for how the audit team leader should best respond to the situation:
Scenario 4:
TD Advertising is a print management company based in Chicago. The company offers design services, digital printing, storage, and distribution. As TD expanded, its management recognized that success depended on adopting new technologies and improving quality.
To ensure customer satisfaction and quality improvement, the company decided to pursue ISO 9001 certification.
After implementing the QMS, TD hired a well-known certification body for an audit. Anne Key was appointed as the audit team leader. She received a document listing the audit team members, audit scope, criteria, duration, and audit engagement limits.
Anne reviewed the document and approved the audit mandate. The certification body and TD’s top management signed the certification agreement.
Before contacting TD, Anne reviewed the audit scope and noticed that TD made changes to it due to the adoption of new printing equipment. However, Anne disagreed with the changes, stating they would affect the audit timeline. She considered withdrawing from the audit.
In scenario 4, the audit team determined the audit feasibility by considering only the resources available for the audit. Is this acceptable?
Which action indicates that an organization is meeting the requirements of ISO 9001 regarding nonconforming outputs?
Scenario 3:
Fin-Pro is a financial institution in Austria offering commercial banking, wealth management, and investment services. The company faced a significant loss of customers due to failing to improve service quality as they expanded.
To regain customer confidence, top management implemented a QMS based on ISO 9001. After a year, they contacted ACB, a local certification body, to pursue ISO 9001 certification.
The audit team was led by Emilia, an experienced lead auditor, and included three auditors. After an agreement was reached, ACB sent the audit objectives to the audit team.
The audit team began by gathering information about Fin-Pro’s understanding of ISO 9001 requirements. While reviewing documented information, they noticed missing records of training and awareness sessions. They conducted employee interviews to verify attendance.
The team also reviewed the organizational chart and job descriptions to confirm employee competence. They observed the company’s working environment (social, psychological, and physical conditions).
The audit team analyzed the evidence and prepared an audit report with findings and conclusions.
Which statement below represents the level of responsibility demonstrated by the audit team in scenario 3?
You are conducting a third-party audit to ISO 9001 and the next item on your audit plan is 'internal auditing'.
When reviewing a sample of audit records up to 5 years previously, you find that many contain non-conformance reports and no actions have been taken. You interview the Quality Manager.
You: "I have noted that many of the older files contain non-conformances that have not had any corrective action taken."
Quality Manager: "Because the business is always changing, the departmental managers tell me that the non-conformances are no longer applicable. I made a decision that any non-conformance over 3 years old is automatically closed"
You: "Do you obtain any confirmation beforehand from the appropriate departments that the non-conformances are no longer applicable."
Quality Manager: " No, because they are so old I consider that they are no longer appropriate. Please remember that we take a risk-based approach which means we audit where and when it is considered important to do so.
Select one course of action you would now take from the options.
Scenario 3:
Fin-Pro is a financial institution in Austria offering commercial banking, wealth management, and investment services. The company faced a significant loss of customers due to failing to improve service quality as they expanded.
To regain customer confidence, top management implemented a QMS based on ISO 9001. After a year, they contacted ACB, a local certification body, to pursue ISO 9001 certification.
The audit team was led by Emilia, an experienced lead auditor, and included three auditors. After an agreement was reached, ACB sent the audit objectives to the audit team.
The audit team began by gathering information about Fin-Pro’s understanding of ISO 9001 requirements. While reviewing documented information, they noticed missing records of training and awareness sessions. They conducted employee interviews to verify attendance.
The team also reviewed the organizational chart and job descriptions to confirm employee competence. They observed the company’s working environment (social, psychological, and physical conditions).
The audit team analyzed the evidence and prepared an audit report with findings and conclusions.
ACB sent the audit objectives to the audit team after an agreement was reached. Is this acceptable?
The ISO 9001 clause 5.1.1 states top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to the quality management system.
In the context of the ISO 9001 management system certification, select the one correct description of top management's responsibilities.
During a second-party audit of a dairy farm (by a potential customer) complying with ISO 9001:2015, the auditor verifies that there is large variability in the daily production of the milking yard. The current agreement with their only customer is to provide 2,000 litres per day. However, in the last two years, they have noticed an increasing variability in daily production.
If they produce less than 2,000 litres, they are penalised with a fine of 1.5 pesos for every litre that they do not provide. If they produce more than 2,000 litres, they use the extra milk to feed the pigs.
This process has been in operation for decades. The dairy farm was founded by the grandfather of the current owners, who did not want to alter the established practices.
The auditor raises a nonconformity on the basis that the process is not under control (Clause 8.1).
If you had been the auditor, which one of the following actions would you have accepted?
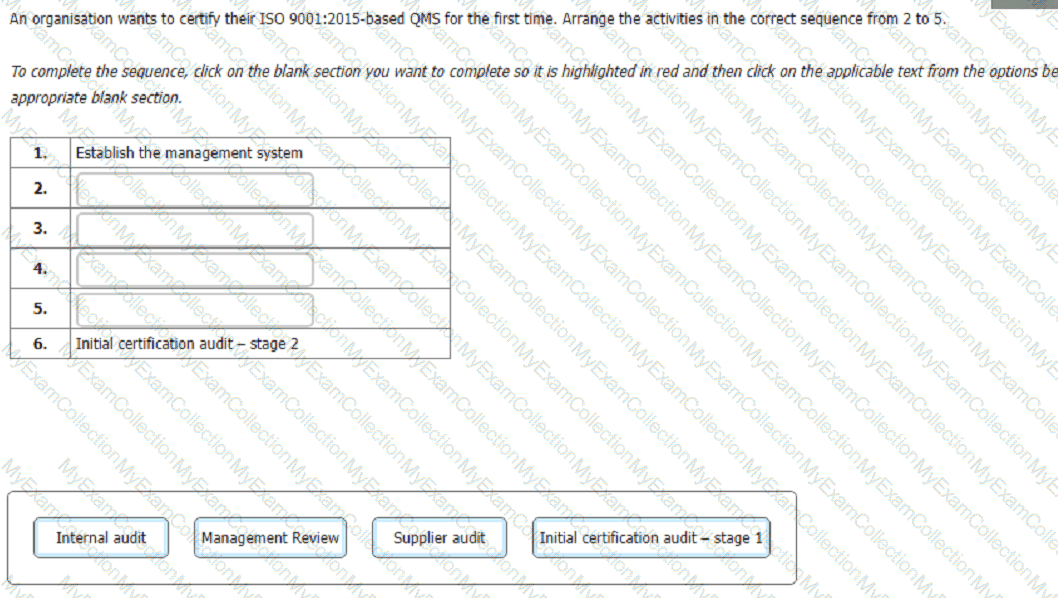
An organisation wants to certify their ISO 9001:2015-based QMS for the first time. Arrange the activities in the correct sequence from 2 to 5.
To complete the sequence, click on the blank section you want to complete so it is highlighted in red and then click on the applicable text from the options below. Alternatively, drag and drop the
options to the appropriate blank section.
Whistlekleen is a national dry cleaning and laundry company with 50 shops. You are conducting a surveillance audit of the Head Office and are sampling customer complaints. You find that 80% of complaints originate from five shops in the same region. Most of these complaints relate to damage to customer laundry. The Quality Manager tells you that these are the oldest shops in the company. The cleaning equipment needs replacing but the company cannot afford it at the moment. You learn
that the shop managers were told to dismiss most of the claims on the basis of the poor quality of the laundered materials.
On raising the matter with senior management, you are told that there are plans to replace the equipment in these shops over the next five years.
When reviewing the customer complaint file, you find that the organisation is facing a legal dispute with a customer over damage to an expensive cashmere coat.
Select the best option for how this should be handled by the Quality Management System.
You are conducting an audit at a single-site organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organisation manufactures cosmetics for major retailers and the name of the retailer supplied appears on the product packaging. Sales turnover has increased significantly over the past five years.
You are interviewing the new Product Development Manager. You note that a software application called SWIFT is used to help control the product development process.
You have gathered audit evidence as outlined in the table. Match the ISO 9001 clause 8.3 extracts to the audit evidence.
During an ISO 9001 audit of an electric cable manufacturer, you are reviewing the customer file for XYZ Construction in the Sales Department. This contract specifies that the installation configuration of the cable runs should meet national fire safety standards for Category A.
You discover that the customer later agreed to the approval of a less stringent Category B configuration instead.
The organization has the following quality policy document displayed in the reception area.
"This organization is committed to providing electric cables to customers' requirements, in accordance with statutory regulations for their use. Continual improvement is a permanent objective of the organization. This policy shall be communicated to all employees and, where required, to all interested parties."
Referring to the scenario, select the two options for which the organization is meeting its policy commitments.
Scenario 7: POLKA is a car manufacturing company based in Stockholm, Sweden. The company has around 14,000 employees working in different sectors which help with the design, painting, assembling, and test drives of the final product. The company is widely known for its qualitative products and affordable prices. In order to retain their reputation, POLKA implemented a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001.
Before applying for certification, the company decided to conduct an internal audit to check whether there are any nonconformities in their QMS and if the requirements of ISO 9001 are being fulfilled. The top management appointed Sean, the internal auditor, as the team leader of the internal audit team. Sean required from the top management to have unrestricted access to the employees and executives of POLKA and to the documented information. Furthermore, Sean required to establish a team with a large number of auditors, considering the size and the complexity of the organization. The top management of POLKA agreed with Sean's requirements.
The top management, in cooperation with Sean, assigned 10 more employees to the audit team. Following that. Sean planned the audit activities and assigned the roles and responsibilities to each auditor. They began by interviewing employees of different manufacturing departments to check whether they are aware of the process of the QMS implementation. While conducting these activities, one of the auditors asked Sean for permission to audit the department in which he worked on a daily basis, as he was very familiar with the processes of the department.
Along the way, the teams findings showed that the staff were trained, documented information was updated, and the QMS fulfilled the requirements of ISO 9001. The internal audit took three weeks to complete, and on the last week the audit team held a final meeting
The team shared their results and together drafted the audit report This report was submitted to the top management of the company. The report was maintained as documented information, and was available to the relevant interested parties.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
According to Scenario 7, one of the auditors requested permission from Sean to audit the department in which he worked on a daily basis. Should Sean grant the auditor permission?
Scenario 6: Davis Clinic (DC) is an American medical center focused on integrated health care. Since its establishment DC was committed to providing qualitative services for its clients, which is the reason why the company decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After a year of having an active QMS in place, DC applied for a certification audit.
A team of five auditors, from a well-known certification body, was selected to conduct the audit. Eva was appointed as the audit team leader. After three days of auditing, the team gathered to review and examine their findings. They also discussed the audit findings with DC's top management and then drafted the audit conclusions.
In the closing meeting, which was held between the audit team and the top management of DC. Eva presented two nonconformities that were detected during the audit. Eva stated that the company did not retain documented information regarding its outsourced services for an analysis laboratory and regarding the conducted management reviews. During the closing meeting, the audit team required from DCs top management to come up with corrective action plans within two weeks. Although the top management did not agree with the audit findings, the audit team insisted that the auditee must submit corrective actions within the given time frame in order for the audit activities to continue.
Once the action plans were evaluated, the audit team began preparing the audit report. Eva required from the team to provide accurate descriptions of the audit findings and the audit conclusions. The report was then distributed to all the interested parties involved in the audit, including the certification body Based on the report, the certification body together with Eva, as the audit team leader, made the certification decision.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Why is it important to discuss the audit findings with DC’s top management prior to the closing meeting and the submission of the final audit report?
Which of the following is a principle of maintaining audit work documents?
State the correct sequence of events in the certification process for an organisation to obtain third-party accredited certification to ISO 9001.

You have been nominated audit team leader of a third-party audit. Which of the following could be the two most relevant objectives of this audit?
Which type of audit risk is the risk that a significant defect may occur in the QMS, although the organization has internal control mechanisms in place?
Scenario 2:
Bell is a Canadian food manufacturing company that operates globally. Their main products include nuts, dried fruits, and confections. Bell has always prioritized product quality and has maintained a good reputation for many years. However, the company's production error rate increased significantly, leading to more customer complaints.
To increase efficiency and customer satisfaction, Bell implemented a Quality Management System (QMS) based on ISO 9001. The top management established a QMS implementation team comprising five middle managers from various departments, including Leslie, the quality manager.
Leslie was responsible for assigning responsibilities and authorities for QMS-related roles. He also suggested including a top management representative in the QMS team, but top management declined due to other priorities.
The team defined the QMS scope as:
"The scope of the QMS includes all activities related to food processing."
Leslie established a quality policy and presented it to the team for review before top management approval. Top management also proposed a new strategy for handling customer complaints, requiring biweekly customer surveys to monitor customer perceptions.
The quality policy was established by Leslie and approved by top management. Is this acceptable? Please refer to scenario 2.
Whistiekleen is a national dry cleaning and laundry organisation with 50 shops. You are conducting a surveillance audit of the Head Office and are sampling customer complaints. You find that 80% of complaints originate from five shops in the same region. Most of these complaints relate to damage to customer laundry. The Quality Manager tells you that these are the oldest shops in the organisation. The deaning equipment needs replacing but the organisation cannot afford it now. You learn that the shop managers were told to dismiss most of the claims based on the poor quality of the laundered materials.
On raising the matter with senior management, you are told that there are plans to replace the equipment in these shops over the next five years.
Match the ISO 9001 Clauses to the statements.

"A set of interrelated or interlacing elements of an organization to establish policies and objectives, and processes to achieve those objectives" is the definition of a/an:
Which two of the following aspects of a quality management system must the organisation continually improve?
An ISO 9001 certified organization sells packaged food. To maximize the benefits of third-party certification to the organization and stakeholders, the organization has labelled their product 'ISO 9001 certified product' and is selling it as 'quality food'.
Which TWO of the following describes this situation in the context of the purpose and benefits of third-party ISO 9001 certification?
Confidence in the audit process and its ability to achieve its objectives depends on the competence of those involved in performing audits:
According to ISO 19011, select the two participants who need to be competent in performing audits.
During a second-party audit, the auditor examines the records that are available for the external provider, ABC Forgings, to whom manufacturing has recently been outsourced.
There are standard external provider checklists for three competitors for the contract and there are inspection records from the trial manufacturing batches produced by ABC Forgings. There is no documented evidence of the criteria used to confirm the appointment of ABC Forgings, and no contract or terms and conditions. Ongoing monitoring indicates that external provider performance is satisfactory, but no documented information has been retained.
Select two options for the evidence which demonstrates a nonconformity with clause 8.4 of ISO 9001.
XYZ Corporation is an organisation that employs 100 people. As audit team leader, you are conducting a
certification audit at Stage 1. When reviewing the quality management system (QMS) documentation, you
find that quality objectives have been set for every employee in the organisation except top management.
The Quality Manager complains that this has created a lot of resistance to the QMS, and the Chief Executive
is asking questions about how much it will cost. He asks for your opinion on whether this is the correct
method of setting objectives.
Three months after Stage 1, you return to XYZ Corporation to conduct a Stage 2 certification audit as Audit
Team Leader with one other auditor. You find that the Quality Manager has cancelled the previous quality
objectives for all employees and replaced them with a single objective for himself. This states that "The
Quality Manager will drive multiple improvements in the QMS in the next year". The Quality Manager indicates
that this gives him the authority to issue instructions to department managers when quality improvement is
needed. He says that this approach has the full backing of senior management. He shows you the latest
Quality Improvement Request that was included in the last management review.

After further auditing, the issues below were found. Select three statements that apply to the term 'audit trail'
Noitol is an organisation specialising in the design and production of e-learning training materials for the insurance market. During an ISO 9001 audit
of the development department, the auditor asks the Head of Development about the process used for validation of the final course design. She states that they usually ask customers to validate the product with volunteers. She says that the feedback received often leads to key improvements.
The auditor samples the design records for a recently completed course for the 247 Insurance organisation. Design verification was carried out but there was no validation report. The Head of Development advises that this customer required the product on an urgent basis, so the validation stage
was omitted. When asked, the Head estimates that this occurs about 50% of the time. She confirms that they always ask for feedback and often make changes. There is no record of feedback in the design file for the course.
The auditor raises a nonconformity against ISO 9001. Which one of the following options is the basis for the nonconformity?
In the context of a third-party management system certification audit, which two of the following statements are correct?
Scenario 6: Davis Clinic (DC) is an American medical center focused on integrated health care. Since its establishment DC was committed to providing qualitative services for its clients, which is the reason why the company decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After a year of having an active QMS in place, DC applied for a certification audit.
A team of five auditors, from a well-known certification body, was selected to conduct the audit. Eva was appointed as the audit team leader. After three days of auditing, the team gathered to review and examine their findings. They also discussed the audit findings with DC's top management and then drafted the audit conclusions.
In the closing meeting, which was held between the audit team and the top management of DC. Eva presented two nonconformities that were detected during the audit. Eva stated that the company did not retain documented information regarding its outsourced services for an analysis laboratory and regarding the conducted management reviews. During the closing meeting, the audit team required from DCs top management to come up with corrective action plans within two weeks. Although the top management did not agree with the audit findings, the audit team insisted that the auditee must submit corrective actions within the given time frame in order for the audit activities to continue.
Once the action plans were evaluated, the audit team began preparing the audit report. Eva required from the team to provide accurate descriptions of the audit findings and the audit conclusions. The report was then distributed to all the interested parties involved in the audit, including the certification body Based on the report, the certification body together with Eva, as the audit team leader, made the certification decision.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Is it acceptable for the certification body and Eva to make the certification decision together?
Scenario 7: POLKA is a car manufacturing company based in Stockholm, Sweden. The company has around 14,000 employees working in different sectors which help with the design, painting, assembling, and test drives of the final product. The company is widely known for its qualitative products and affordable prices. In order to retain their reputation, POLKA implemented a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001.
Before applying for certification, the company decided to conduct an internal audit to check whether there are any nonconformities in their QMS and if the requirements of ISO 9001 are being fulfilled. The top management appointed Sean, the internal auditor, as the team leader of the internal audit team. Sean required from the top management to have unrestricted access to the employees and executives of POLKA and to the documented information. Furthermore, Sean required to establish a team with a large number of auditors, considering the size and the complexity of the organization. The top management of POLKA agreed with Sean's requirements.
The top management, in cooperation with Sean, assigned 10 more employees to the audit team. Following that. Sean planned the audit activities and assigned the roles and responsibilities to each auditor. They began by interviewing employees of different manufacturing departments to check whether they are aware of the process of the QMS implementation. While conducting these activities, one of the auditors asked Sean for permission to audit the department in which he worked on a daily basis, as he was very familiar with the processes of the department.
Along the way, the teams findings showed that the staff were trained, documented information was updated, and the QMS fulfilled the requirements of ISO 9001. The internal audit took three weeks to complete, and on the last week the audit team held a final meeting
The team shared their results and together drafted the audit report This report was submitted to the top management of the company. The report was maintained as documented information, and was available to the relevant interested parties.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Scenario 7 states that Sean planned audit activities on his own. Is this acceptable?
An organisation decides to purchase products and services only from ISO 9001 certified suppliers.
Match the four organisational functions to a potential benefit.

Scenario 1: AL-TAX is a company located in California which provides financial and accounting services. The company manages the finances of 17 companies and now is seeking to expand their business even more The CEO of AL-TAX, Liam Durham, claims that the company seeks to provide top-notch services to their clients Recently, there were a number of new companies interested in the services provided by AL-TAX.
In order to fulfill the requirements of new clients and further improve quality, Liam discussed with other top management members the idea of implementing a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. During the discussion, one of the members of the top management claimed that the size of the company was not large enough to implement a QMS. In addition, another member claimed that a QMS is not applicable for the industry in which AL TAX operates. However, as the majority of the members voted for implementing the QMS. Liam initiated the project.
Initially, Liam hired an experienced consultant to help AL-TAX with the implementation of the QMS. They started by planning and developing processes and methods for the establishment of a QMS based on ISO 9001. Furthermore, they ensured that the quality policy is appropriate to the purpose and context of AL TAX and communicated to all employees. In addition, they also tried to follow a process that enables the company to ensure that its processes are adequately resourced and managed, and that improvement opportunities are determined.
During the implementation process, Liam and the consultant focused on determining the factors that could hinder their processes from achieving the planned results and implemented some preventive actions in order to avoid potential nonconformities Six months after the implementation of the QMS. AL-TAX conducted an internal audit. The results of the internal audit revealed that the QMS was not fulfilling all requirements of ISO 9001. A serious issue was that the QMS was not fulfilling the requirements of clause 5.1.2 Customer focus and had also not ensured clear and open communication channels with suppliers.
Throughout the next three years, the company worked on improving its QMS through the PDCA cycle in the respective areas. To assess the effectiveness of the intended actions while causing minimal disruptions, they tested changes that need to be made on a smaller scale. After taking necessary actions, AL-TAX decided to apply for certification against ISO 9001.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Scenario 1 indicates that AL-TAX did not ensure clear and open communication channels with interested parties. Which quality management principle did the organization not follow in this case?
The following list gives examples of records that may be evidence of how an organisation has fulfilled the requirements of clause 8.4 of ISO 9001. Match the records to the appropriate requirement of clause 8.4.

Which of the following is a record related to the audit program that should be managed and maintained?
You are carrying out an audit at an organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organisation offers regulatory consultancy services to manufacturers of cosmetics. The business operates from ten regional offices.
You are nearing the end of the audit and need to decide if sufficient evidence of top management leadership and commitment with respect to the quality management system has been gathered.
Which four of the following would demonstrate top management leadership and commitment with respect to the quality management system?
You have been just hired as the Internal Lead Auditor of a large organisation, responsible for internal audits. Your first job is to analyse the answers to nonconformities included in the report of a recent internal audit to Top Management.
The report contained one nonconformity as follows:
There is no evidence of Top Management ensuring the availability of resources to operate the QMS, the establishment of objectives, the promotion of continual improvement, and the promoting of the process approach.
Which four of the following Top Management actions can be considered 'corrections to the nonconformity'?
Scenario 2:
Bell is a Canadian food manufacturing company that operates globally. Their main products include nuts, dried fruits, and confections. Bell has always prioritized product quality and has maintained a good reputation for many years. However, the company's production error rate increased significantly, leading to more customer complaints.
To increase efficiency and customer satisfaction, Bell implemented a Quality Management System (QMS) based on ISO 9001. The top management established a QMS implementation team comprising five middle managers from various departments, including Leslie, the quality manager.
Leslie was responsible for assigning responsibilities and authorities for QMS-related roles. He also suggested including a top management representative in the QMS team, but top management declined due to other priorities.
The team defined the QMS scope as:
"The scope of the QMS includes all activities related to food processing."
Leslie established a quality policy and presented it to the team for review before top management approval. Top management also proposed a new strategy for handling customer complaints, requiring biweekly customer surveys to monitor customer perceptions.
Which of the following indicates that Bell has defined its quality objectives?
You are conducting an audit at an organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organisation offers health and safety training to customers. Training courses are offered either as open courses, delivered at a public venue, or online, or as courses that are tailored to meet specific requirements. The business operates from a single office and those who deliver the training are either full-time employees or subcontractors.
You have gathered audit evidence as outlined below. Match the ISO 9001 Clause 8 extract to the audit evidence.

You are carrying out an audit at a single-site organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The
organisation manufactures cosmetics for major retailers and the name of the retailer supplied appears on the product
packaging. Sales turnover has increased significantly over the past five years. The organisation uses a software programme called SWIFT, which is used to record sales, plan production, purchase supplies, print despatch notes, track new product development, perform traceability exercises, carry out mass balance checks, raise invoices, create budgets, and support financial control.
You are nearing the end of the audit and you are reviewing your audit notes. You notice a recurring trend concerning the SWIFT database as shown below:

You ask the Quality Manager to explain how the SWIFT database is controlled. You learn that the Operations Director is
responsible for determining and progressing SWIFT software updates. You decide to meet the Operations Director (OD).
You: "Good afternoon."
OD: "Good afternoon."
You: "What responsibility do you have concerning the SWIFT database?"
OD: "I maintain it. If anyone wishes to propose an update to the database, they send me an email with
details of their proposal. I then either process the database update myself, or I send the request to the
consultant who designed the database 20 years ago. The necessary software changes are made, and the
amended software is immediately released to users."
You: "Would you explain how the software amendments are controlled?"
OD: "Of course. I personally update every computer myself."
You: "Do you inform the database users of the changes?"
OD: "No I don't. They find out for themselves by using the software, or they come to see me if they have
any questions."
You: "How do you ensure that the database users use the latest version?"
OD: "That's easy, I update every computer myself."
You: "During the audit, I noted there were several versions of SWIFT in use (you refer to your audit
notes)."
OD: "I know. That's because some versions work better than others, and depending on user needs and
experiences, we allow users to revert to using an earlier version if they find it works better for them."
Based on the scenario, which two of the following statements are true? There is evidence of
nonconformity with a requirement defined in ...
ABC is a service organisation that cleans and irons bed and table linen for four large hospitals in the city centre. It claims to meet ISO 9001:2015 requirements. During an internal audit, an auditor observes that
machine No. 4 is being operated with the three variables outside the limits established in the applicable documented procedure SP-701. The auditor has decided to raise a nonconformity.
Which six elements should be included in the nonconformity report?
Scenario 7: POLKA is a car manufacturing company based in Stockholm, Sweden. The company has around 14,000 employees working in different sectors which help with the design, painting, assembling, and test drives of the final product. The company is widely known for its qualitative products and affordable prices. In order to retain their reputation, POLKA implemented a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001.
Before applying for certification, the company decided to conduct an internal audit to check whether there are any nonconformities in their QMS and if the requirements of ISO 9001 are being fulfilled. The top management appointed Sean, the internal auditor, as the team leader of the internal audit team. Sean required from the top management to have unrestricted access to the employees and executives of POLKA and to the documented information. Furthermore, Sean required to establish a team with a large number of auditors, considering the size and the complexity of the organization. The top management of POLKA agreed with Sean's requirements.
The top management, in cooperation with Sean, assigned 10 more employees to the audit team. Following that. Sean planned the audit activities and assigned the roles and responsibilities to each auditor. They began by interviewing employees of different manufacturing departments to check whether they are aware of the process of the QMS implementation. While conducting these activities, one of the auditors asked Sean for permission to audit the department in which he worked on a daily basis, as he was very familiar with the processes of the department.
Along the way, the teams findings showed that the staff were trained, documented information was updated, and the QMS fulfilled the requirements of ISO 9001. The internal audit took three weeks to complete, and on the last week the audit team held a final meeting
The team shared their results and together drafted the audit report This report was submitted to the top management of the company. The report was maintained as documented information, and was available to the relevant interested parties.
Based on the scenario above, answer the following question:
Sean requested unrestricted access to the employees, executives, and documented information of POLKA. Is this in accordance with audit best practices?
Scenario 5: Mechanical-Electro (ME) Audit Stages
Mechanical-Electro, better known as ME, is an American company that provides mechanical and electrical services in China. Their services range from air-conditioning systems, ventilation systems, plumbing, to installation of electrical equipment in automobile plants, electronic manufacturing facilities, and food processing plants.
Due to the fierce competition from local Chinese companies and failing to meet customer requirements, ME's revenue dropped significantly. In addition, customers' trust and confidence in the company decreased, and the reputation of the company was damaged.
In light of these developments, the top management of ME decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After having an effective QMS in place for over a year, they applied for a certification audit.
A team of four auditors was appointed for the audit, including Li Na as the audit team leader. Initially, the audit team conducted a general review of ME's documents, including the quality policy, operational procedures, inventory lists, QMS scope, process documentation, training records, and previous audit reports.
Li Na stated that this would allow the team to maintain a systematic and structured approach to gathering documents for all audit stages. While reviewing the documented information, the team observed some minor issues but did not identify any major nonconformities. Therefore, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to prepare a report or conduct a meeting with ME's representatives at that stage of the audit. She stated that all areas of concern would be discussed in the next phase of the audit.
Following the on-site activities and the opening meeting with ME's top management, the audit team structured an audit test plan to verify whether ME’s QMS conformed to Clause 8.2.1 (Customer Communication) of ISO 9001.
To do so, they gathered information through group interviews and sampling. Li Na conducted interviews with departmental managers in the first group and then with top management. In addition, she chose a sampling method that sufficiently represented customer complaints from both areas of ME's operations.
The team members were responsible for the sampling procedure. They selected a sample size of 4 out of 45 customer complaints received weekly for electrical services and 2 out of 10 complaints for mechanical services.
Afterward, the audit team evaluated the evidence against the audit criteria and generated the audit findings.
According to general principles of sampling procedure, did the audit team select a valid sample for electrical services?







 A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.

 A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a computer AI-generated content may be incorrect.




