A network administrator configures this policy:
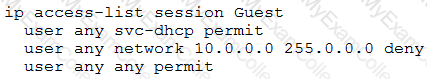
Users to which this policy applies are unable to receive IP addresses with DHCP. How should the administrator fix the issue?
Refer to the exhibit.
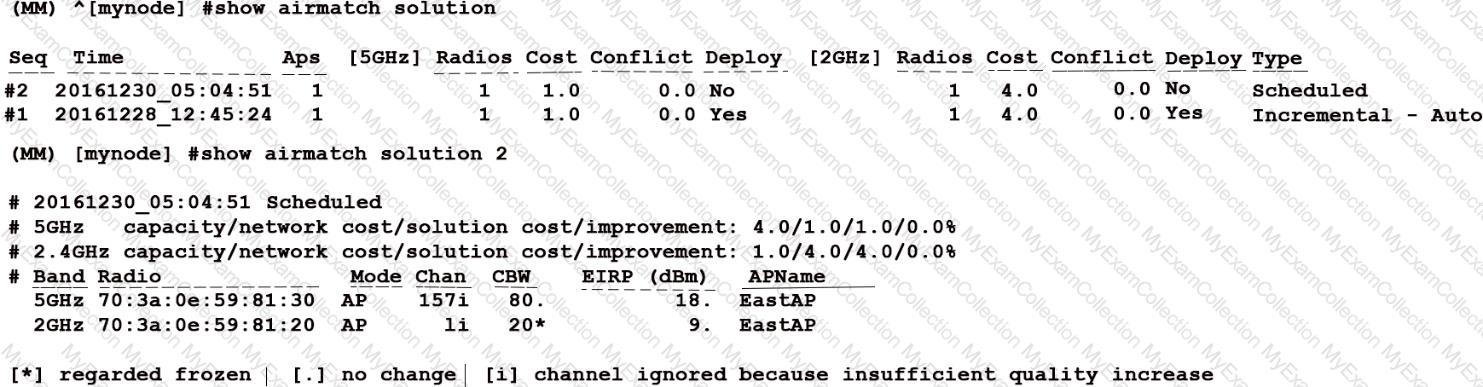
An Aruba solution uses AirMatch with the default AirMatch profile settings. A network administrator sees that a scheduled optimization was completed, but a plan was not deployed.
Based on the exhibit, why did this occur?
Assume that administrators accept the default forwarding mode for WLANs. How does wireless user traffic flow in a master-local architecture, and how does it flow in a Mobility Master (MM) architecture?
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1

Exhibit 2

A company has an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution and needs a new WLAN for the corporate campus. A network administrator completes the creation of this WLAN, as shown in Exhibit 1. When the administrator tries to test a connection to the WLAN in various locations, the WLAN sometimes shows up in the list of WLANs on the client but sometimes does not. The administrator can see the WLAN in the list, as shown in Exhibit 2.
What is the error?
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit 1

Exhibit 2

Exhibit 3

A network administrator creates a guest WLAN on an Aruba Mobility Manager (MM). The exhibits show some of the settings for the WLAN. The administrator does not change the policies for those roles.
How does the firewall control guest clients when they first connect to the WLAN?
A network administrator monitors an Aruba Mobility Controller with Aruba AirWave and sees the configuration status is Error. What should the administrator conclude?
How can network administrators upgrade AirMatch on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
A company has an Aruba solution. The company wants to support a guest WLAN with the internal captive portal, but the company also wants to develop their own custom portal pages.
What correctly describes the level of customization that the internal captive portal supports?
A company wants to provide wireless access for visitors with their Aruba solution. Which configuration feature enables the guest to access the wireless network without authentication?
A WLAN in an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution uses WPA2-Enterprise security. This WLAN currently authenticates users to Active Directory (AD), and users log in with their Windows domain credentials. Network administrators now want to authenticate the Windows clients as well, based on the client Computer Names.
What should the administrators do on MM to achieve this goal?
A Mobility Controller (MC) runs ArubaOS 8. What is a valid reason for an administrator to set the MC to master-local mode?
A network administrator needs to create an Aruba firewall rule that permits wireless users to receive DHCP settings when they first connect to the Aruba solution. What are the correct source and destination aliases for the rule?
Refer to the exhibit.
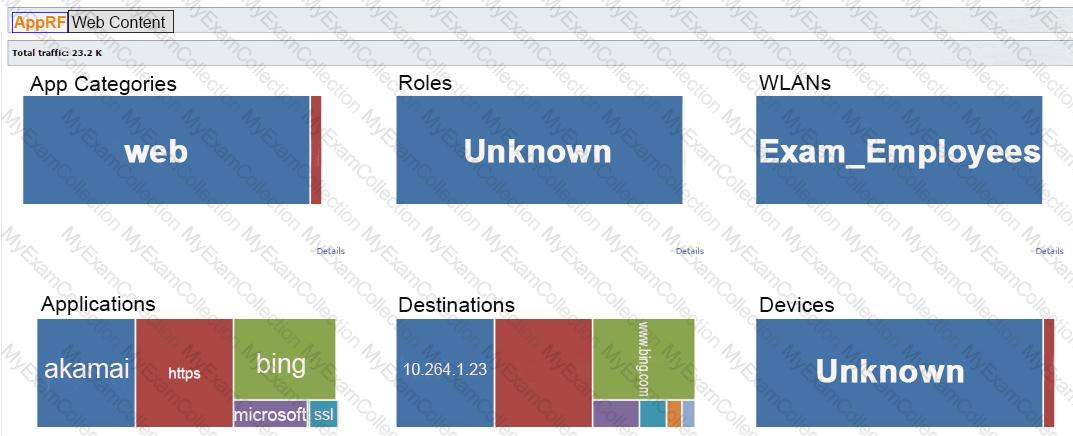
The exhibit shows output from a Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. What is a valid reason for the administrator to click the akamai square under applications?
Which settings can a Mobility Master (MM) deploy to Mobility Controllers (MCs) but master controllers CANNOT deploy to local controllers?


