Business management is seeking assurance from the CIO that IT has a plan in place for early identification of potential issues that could impact the delivery of a new application Which of the following is the BEST way to increase the chances of a successful delivery'?
Implement a release and deployment plan
Conduct comprehensive regression testing.
Develop enterprise-wide key risk indicators (KRls)
Include business management on a weekly risk and issues report
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to increase the chances of a successful delivery of a new application and to assure the business management that IT has a plan in place for early identification of potential issues is to include business management on a weekly risk and issues report. A risk and issues report is a document that summarizes the current status, progress, and challenges of the IT project, as well as the actions and resources needed to address them. A risk and issues report helps to communicate and align the expectations and objectives of the IT and business stakeholders, and to facilitate timely and effective decision-making and problem-solving. A risk and issues report also helps to monitor and control the project scope, schedule, budget, and quality, and to ensure that the project delivers the desired value and benefits to the organization. The other options are not as effective as including business management on a weekly risk and issues report, althoughthey may be part of the IT project management process or outcomes. Implementing a release and deployment plan, conducting comprehensive regression testing, and developing enterprise-wide key risk indicators (KRIs) are all activities that can help to ensure the quality and reliability of the new application, but they do not necessarily involve the business management or provide assurance for the early identification of potential issues. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5, Section 5.4.1, page 5-32.
Which of the following would BEST enable a risk-based decision when considering the use of an emerging technology for data processing?
Gap analysis
Threat assessment
Resource skills matrix
Data quality assurance plan
Answer:
Explanation:
 The best way to enable a risk-based decision when considering the use of an emerging technology for data processing is to perform a gap analysis. A gap analysis is a technique that compares the current state and the desired state of a process, system, or capability, and identifies the gaps or differences between them. A gap analysis can help to evaluate the benefits, costs, risks, and opportunities of using an emerging technology for data processing, and to determine the feasibility, suitability, and readiness of adopting the emerging technology. The other options are not as helpful as a gap analysis, as they are related to the specific aspects or components ofthe data processing, not the overall assessment and comparison of the current and desired state of the data processing. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.2: IT Risk Identification Methods, page 19.
Recovery the objectives (RTOs) should be based on
minimum tolerable downtime
minimum tolerable loss of data.
maximum tolerable downtime.
maximum tolerable loss of data
Answer:
Explanation:
Recovery time objectives (RTOs) are the acceptable timeframes within which business processes must be restored after a disruption. RTOs should be based on the maximum tolerable downtime (MTD), which is the longest time that a business process can be inoperable without causing irreparable harm to the organization. The other options are not directly related to RTOs, as they refer to the amount of data loss or corruption that can be tolerated, not the time to restore the business processes. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.3: Key Risk Indicators, page 197.
Which of the following is the MOST effective way to help ensure future risk levels do not exceed the organization's risk appetite?
Developing contingency plans for key processes
Implementing key performance indicators (KPIs)
Adding risk triggers to entries in the risk register
Establishing a series of key risk indicators (KRIs)
Answer:
Explanation:
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)are metrics used to monitor changes in risk exposure, enabling proactive adjustments to keep risks within appetite. They provide early warnings of potential breaches in risk thresholds.
An engineer has been assigned to conduct data restoration after a server storage failure. However, the procedure was not successful. Which of the following is the MOST probable cause of this situation?
Failure to test the disaster recovery plan (DRP)
Failure to prepare a business continuity plan (BCP)
Insufficient data captured in the business impact analysis (BIA)
Insufficient definition of the recovery point objective (RPO)
Answer:
Explanation:
The RPO defines how much data loss is acceptable during system failure. If not clearly defined, restoration may skip key data, leading to incomplete recovery. ISACA guidelines highlight that alignment of RPO/RTO with business objectives is critical for viable DR planning
Which of the following is the BEST indication of a mature organizational risk culture?
Corporate risk appetite is communicated to staff members.
Risk owners understand and accept accountability for risk.
Risk policy has been published and acknowledged by employees.
Management encourages the reporting of policy breaches.
Answer:
Explanation:
Organizational risk culture is the term describing the values, beliefs, knowledge, attitudes and understanding about risk shared by a group of people with a common purpose. Organizationalrisk culture influences how the organization identifies, assesses, and manages risks, and how it aligns its risk appetite and tolerance with its objectives and strategies1.
The best indication of a mature organizational risk culture is that risk owners understand and accept accountability for risk, because it means that the organization:
Clearly defines and assigns the roles and responsibilities of the risk owners, who are the individuals or groups who have the authority and ability to manage the risks within their scope or domain
Empowers and supports the risk owners to perform their risk management duties, such as identifying, assessing, responding, monitoring, and reporting the risks
Holds the risk owners accountable for the outcomes and consequences of the risks, and evaluates their performance and compliance with the risk policies, standards, and procedures
Encourages and rewards the risk owners for demonstrating risk awareness and competence, and for contributing to the risk management improvement and learning23
The other options are not the best indications of a mature organizational risk culture, but rather some of the elements or aspects of it. Corporate risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept in order to achieve its objectives. Corporate risk appetite is communicated to staff members to guide their risk decision making and behavior, and to ensure the consistency and alignment of the risk taking and tolerance across the organization. Risk policy is the document that establishes the principles, framework, and process for managing the risks within the organization. Risk policy is published and acknowledged by employees to ensure their awareness and compliance with the risk management expectations and requirements. Management is the group of individuals who have the authority and responsibility to direct and control the organization’s activities and resources. Management encourages the reporting of policy breaches to ensure the transparency and accountability of the risk management performance and outcomes, and to identify and address the risk management issues and gaps4. References =
Risk culture - Institute of Risk Management
Risk Owner - ISACA
Taking control of organizational risk culture | McKinsey
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of the following provides a risk practitioner with the MOST reliable evidence of a third party's ability to protect the confidentiality of sensitive corporate information?
A signed nondisclosure agreement (NDA)
Control self-assessment (CSA) results
External audit reports
Internal audit reports
Answer:
Explanation:
External audit reports are independent and objective, typically conducted under standard frameworks (e.g., SOC 2). They assess the third party’s controls in a structured and verifiable manner, offering the highest assurance of confidentiality protections.
Who should be responsible for determining which stakeholders need to be involved in the development of a risk scenario?
Risk owner
Risk practitioner
Compliance manager
Control owner
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner is responsible for determining which stakeholders need to be involved in the development of a risk scenario, as they have the knowledge and skills to facilitate the process and ensure that the relevant perspectives and information are considered. The risk owner, the compliance manager, and the control owner are examples of stakeholders who may participate in the risk scenario development, but they are not responsible for determining who should be involved. References = Risk Scenarios Toolkit, page 9; CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 101.
Which of the following practices MOST effectively safeguards the processing of personal data?
Personal data attributed to a specific data subject is tokenized.
Data protection impact assessments are performed on a regular basis.
Personal data certifications are performed to prevent excessive data collection.
Data retention guidelines are documented, established, and enforced.
Answer:
Explanation:
Personal data is any information that relates to an identified or identifiable individual, such as name, address, email, phone number, etc. Processing personal data involves collecting, storing, using, disclosing, or deleting it. Processing personal data poses various risks to the privacy and security of the data subjects,such as unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or loss. Therefore, processing personal data requires appropriate technical and organizational measures to safeguard the data and to comply with the relevant laws and regulations. One of the most effective practices to safeguard the processing of personal data is to use tokenization. Tokenization is a technique that replaces sensitive data elements with non-sensitive equivalents, called tokens, that have no meaning or value outside of a specific system or context. Tokenization reduces the risk of exposing personal data to unauthorized parties, as the tokens cannot be reversed or linked back to the original data without the proper key or algorithm. Tokenization also helps to minimize the amount of personal data that is stored or transmitted, and to limit the scope of compliance requirements. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.2.2, p. 196-197
Management has determined that it will take significant time to remediate exposures in the current IT control environment. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
Implement control monitoring.
Improve project management methodology.
Reassess the risk periodically.
Identify compensating controls.
Answer:
Explanation:
When remediation is delayed, compensating controls provide interim protection by reducing risk to acceptable levels.
Which of the following presents the GREATEST concern associated with the
use of artificial intelligence (Al) systems?
Al systems need to be available continuously.
Al systems can be affected by bias.
Al systems are expensive to maintain.
Al systems can provide false positives.
Answer:
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY focus of an independent review of a risk management process?
Accuracy of risk tolerance levels
Consistency of risk process results
Participation of stakeholders
Maturity of the process
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary focus of an independent review of a risk management process is to evaluate the maturity of the process, which means the extent to which the process is aligned with the organization’s objectives, culture, and governance, and how well it is integrated, implemented, and monitored across the organization. A mature risk management process is one that is consistent, effective, efficient, and adaptable to changing circumstances and environments. A maturity assessment can help to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the risk management process, as well as the opportunities and challenges for improvement. The other options are not the primary focus, but they may be secondary or tertiary aspects of the review. Accuracy of risk tolerance levels is a measure of how well the organization defines and communicates its risk appetite and risk limits, which are important inputs for the risk management process, but not the main outcome. Consistency of risk process results is a measure of how reliable and repeatable the risk management process is, which reflects the quality and validity of the data, assumptions, methods, and tools used in the process, but not the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the process. Participation of stakeholders is a measure of how well the organization engages and involves its internal and external stakeholders in the risk management process, which enhancesthe awareness, ownership, andaccountability of the process, but not the alignment and integration of the process. References = Assessing the Risk Management Process, p. 9-10.
When reporting risk assessment results to senior management, which of the following is MOST important to include to enable risk-based decision making?
Risk action plans and associated owners
Recent audit and self-assessment results
Potential losses compared to treatment cost
A list of assets exposed to the highest risk
Answer:
Explanation:
 When reporting risk assessment results to senior management, the most important information to include to enable risk-based decision making is the potential losses compared to treatment cost. This information helps to quantify the impact and likelihood of the risks, and to evaluate the cost and benefit of the risk responses. This information also helps to prioritize and allocate resources for the risk management program, and to align the risk management program with the enterprise’s objectives, strategy, and risk appetite. The other options are not as important as the potential losses compared to treatment cost, as they provide different types of information for the risk management process:
Risk action plans and associated owners are the documents that specify the actions to be taken to address the identified risks, the resources required, the timelines, the owners, and the expected outcomes. This information helps to implement and monitor the risk management program, and to assign the authority and accountability for the risk management activities.
Recent audit and self-assessment results are the outcomes of the independent and objective examination of the risk management program, such as by internal or external auditors, or by the risk owners or practitioners themselves. This information helps to provide assurance and feedback on the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk management program, and to identify the gaps or weaknesses that need to be addressed.
A list of assets exposed to the highest risk are the resources that have the most value for the enterprise, such as hardware, software, data, or services, and that are affected by or contribute to the highest risks. This information helps to identify and protect the critical assets of theenterprise, and to reduce the exposure and impact of the risks to the assets. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.3.1.1, pp. 58-59.
In the three lines of defense model, a PRIMARY objective of the second line is to:
Review and evaluate the risk management program.
Ensure risks and controls are effectively managed.
Implement risk management policies regarding roles and responsibilities.
Act as the owner for any operational risk identified as part of the risk program.
Answer:
Explanation:
The second line of defense provides oversight to ensure risks and controls are effectively managed. This includes compliance, risk management policies, and performance monitoring, aligning withRisk Governanceframeworks and enhancing the organization’s risk resilience.
Several network user accounts were recently created without the required management approvals. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner's BEST recommendation to address this situation?
Conduct a comprehensive compliance review.
Develop incident response procedures for noncompliance.
Investigate the root cause of noncompliance.
Declare a security breach and Inform management.
Answer:
Explanation:
Several network user accounts were recently created without the required management approvals. This indicates that there is a risk of unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction of the network resources or data, which may affect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the network.
The best recommendation to address this situation is to investigate the root cause of noncompliance. This means that the risk practitioner should analyze the factors or reasons that led to the creation of the network user accounts without the required management approvals, such as human error, negligence, malice, system failure, process flaw, etc.
Investigating the root cause of noncompliance helps to identify and correct the source of the problem, prevent or reduce the recurrence of the problem, and improve the compliance and security of the network user accounts.
The other options are not the best recommendations to address this situation. They are either secondary or not effective for noncompliance.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 31
Information Technology & Security, page 25
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 23
An organization is planning to move its application infrastructure from on-premises to the cloud. Which of the following is the BEST course of the actin to address the risk associated with data transfer if the relationship is terminated with the vendor?
Meet with the business leaders to ensure the classification of their transferred data is in place
Ensure the language in the contract explicitly states who is accountable for each step of the data transfer process
Collect requirements for the environment to ensure the infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is configured appropriately.
Work closely with the information security officer to ensure the company has the proper security controls in place.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action to address the risk associated with data transfer if the relationship is terminated with the vendor is to ensure the language in the contract explicitly states who is accountable for each step of the data transfer process. This can help to avoid ambiguity, confusion, or disputes over the ownership, responsibility, and liability of the data and the data transfer process. Meeting with the business leaders, collecting requirements, and working with the information security officer are important activities, but they are not as effective as ensuring the contractual agreement is clear and enforceable. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 4; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 153.
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when determining a recovery time objective (RTO)?
Time between backups for critical data
Sensitivity of business data involved
Cost of downtime due to a disaster
Maximum tolerable data loss after an incident
Answer:
Explanation:
The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable length of time that a system can be down after a failure or disaster. Determining the RTO involves assessing the cost of downtime and its impact on business operations to ensure that recovery strategies are cost-effective and aligned with business needs.
Which of the following approaches will BEST help to ensure the effectiveness of risk awareness training?
Piloting courses with focus groups
Using reputable third-party training programs
Reviewing content with senior management
Creating modules for targeted audiences
Answer:
Explanation:
The best approach to ensure the effectiveness of risk awareness training is to create modules for targeted audiences. This means that the risk awareness training should be customized and tailored to the specific needs, roles, and responsibilities of different groups of staff, such as business owners, process owners, IT staff, or external parties. Creating modules for targeted audiences helps to ensure that the risk awareness training is relevant, engaging, and applicable to the participants, and that it covers the appropriate level of detail and complexity. It also helps to enhance the learning outcomes and retention of the risk awareness training, and to foster aculture of risk awareness and responsibility within the enterprise. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.4.1, page 2491
Which of the following is MOST critical when designing controls?
Involvement of internal audit
Involvement of process owner
Quantitative impact of the risk
Identification of key risk indicators
Answer:
Explanation:
The most critical factor when designing controls is the involvement of the process owner, who is the person responsible for the performance and outcomes of a business process. The process owner has the best knowledge and understanding of the process objectives, activities, inputs,outputs, resources, and risks. The process owner can provide valuable input and feedback on the design of controls that are relevant, effective, efficient, and aligned with the process goals. The process owner can also ensure that the controls are implemented, monitored, and improved as needed. The involvement of the process owner can also increase the acceptance and ownership of the controls by the process participants and stakeholders. The other options are less critical when designing controls. The involvement of internal audit can provide assurance and advice on the adequacy and effectiveness of the controls, but internal audit is not responsible for the design or implementation of the controls. The quantitative impact of the risk can help to prioritize and justify the controls, but it is not sufficient to determine the appropriate type and level of controls. The identification of key risk indicators can help to monitor and measure the risk and the performance of the controls, but it is not the main driver of the control design. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 181
A management team is on an aggressive mission to launch a new product to penetrate new markets and overlooks IT risk factors, threats, and vulnerabilities. This scenario BEST demonstrates an organization's risk:
management.
tolerance.
culture.
analysis.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Risk culture is the system of values and behaviors present in an organization that shapes risk decisions of management and employees1. Risk culture influences how the organization perceives, responds to, and manages the risks that may affect its objectives, operations, or assets2.
The scenario described in the question best demonstrates an organization’s risk culture, because it shows how the management team’s attitude and actions towards risk are driven by the organization’s values and goals. In this case, the organization’s risk culture is characterized by:
A high risk appetite and tolerance, which means that the organization is willing to take and accept significant risks in order to achieve its strategic objectives of launching a new product and penetrating new markets
A low risk awareness and sensitivity, which means that the organization does not pay enough attention or consideration to the potential IT risk factors, threats, and vulnerabilities that may affect its product development and market entry
A weak risk governance and control, which means that the organization does not have adequate or effective policies, procedures, or mechanisms to identify, assess, respond, or monitor the IT risks and their impacts
References = Risk Culture of Companies | ERM - Enterprise Risk Management Initiative …, Taking control of organizational risk culture | McKinsey
Who is PRIMARILY accountable for risk treatment decisions?
Risk owner
Business manager
Data owner
Risk manager
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk owner is primarily accountable for risk treatment decisions, as they are the person or entity with the authority and responsibility to manage a particular risk. The risk owner shouldevaluate the available risk response options, select the most appropriate one, implement the chosen response, and monitor its effectiveness. The risk owner should also communicate and report on the risk status and any issues or changes. The business manager, data owner, and risk manager are not primarily accountable for risk treatment decisions, although they may be involved in the risk management process. The business manager is responsible for the overall performance and objectives of a business unit or function. The data owner is responsible for the security and quality of a specific data asset. The risk manager is responsible for facilitating and coordinating the risk management activities across the organization. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Identification, page 47.
Which of the following is the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) for determining how well an IT policy is aligned to business requirements?
Total cost to support the policy
Number of exceptions to the policy
Total cost of policy breaches
Number of inquiries regarding the policy
Answer:
Explanation:
An IT policy is a document that defines the rules, standards, and procedures for the use, management, and security of IT resources within an organization. An IT policy should be aligned to the business requirements, which are the needs, expectations, and objectives of the business stakeholders, such as customers, employees, managers, partners, regulators, etc. An IT policy that is aligned to the business requirements can help support the business strategy, improve the business performance, and enhance the business value. A key performance indicator (KPI) is a metric that measures the achievement of a specific goal or objective. A KPI should be relevant, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound. The best KPI for determining how well an IT policy is aligned to the business requirements is the number of exceptions to the policy. An exception to the policy is a deviation or violation of the policy rules, standards, or procedures, which may be intentional or unintentional, authorized or unauthorized, justified or unjustified. The number of exceptions to the policy can indicate how well the policy is understood, communicated, implemented, and enforced within the organization. The number of exceptions to the policy can also indicate how well the policy reflects the current and future business needs and expectations, and how flexible and adaptable the policy is to the changing business environment. A low number of exceptions to the policy can suggest that the policy is well aligned to the business requirements, while a high number of exceptions to the policy can suggest that the policy is misaligned or outdated, and may need to be reviewed or revised. References = Key Performance Indicator (KPI): Definition, Types, andExamples, Business KPIs: 5 important characteristics to be effective, What is a KPI? How To Choose the Best KPIs for Your Business - HubSpot Blog.
Which of the following methods is the BEST way to measure the effectiveness of automated information security controls prior to going live?
Testing in a non-production environment
Performing a security control review
Reviewing the security audit report
Conducting a risk assessment
Answer:
Explanation:
Automated information security controls are controls that are implemented or executed by software or hardware, without human intervention, to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and systems1. Examples of automated information security controls include firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, authentication, and logging2. The effectiveness of automated information security controls refers to how well they achieve their intended objectives and outcomes, such as preventing, detecting, or responding to security threats or incidents3. The best way to measure the effectiveness of automatedinformation security controls prior to going live is to test them in a non-production environment, which is an environment thatsimulates the production environment, but does not contain real or sensitive data orsystems4. Testing in a non-production environment allows the organization to verify the proper and consistent configuration, functionality, and performance of the automated information security controls, without affecting the normal operations or risking the exposure of the data or systems5. Testing in a non-production environment also enables the organization to identify andresolve any issues or gaps in the automated information security controls, and to evaluate their compatibility and interoperability with other systems or controls6. Performing a security control review, reviewing the security audit report, and conducting a risk assessment are not the best ways to measure the effectiveness of automated information security controls prior to going live, as they do not provide direct and timely information on the configuration, functionality, and performance of the automated information security controls. Performing a security control review is a process that involves checking and verifying that the organization’s security controls are up to date, relevant, and effective7. A security control review can help to identify and address any issues or gaps in the security controls, but it does not show the actual behavior and results of the automated information security controls in a realistic environment. Reviewing the security audit report is a process that involves reading and analyzing the findings and recommendations of an independent examination and evaluation of the organization’s security controls8. A security audit report can help to provide assurance and advice on the adequacy and effectiveness of the security controls, but it does not show the current and dynamic status and performance of the automated information security controls in a changing environment. Conducting a risk assessment is a process that involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks and their potential impacts on the organization’s objectives and performance. A risk assessment can help to anticipate and prepare for the risks that may affect the organization’s security, but it does not show the actual impact and outcome of the automated information security controls in a specific scenario. References = 1: Automation Support for Security Control Assessments - NIST2: Automated Security Control Assessment: When Self-Awareness Matters3: Technology Control Automation: Improving Efficiency, Reducing … - ISACA4: [What is a Non-Production Environment? | Definition and FAQs] 5: [Why You Need a Non-Production Environment - Plutora] 6: [Testing Automated Security Controls - SANS Institute] 7: A brief guide to assessing risks and controls | ACCA Global8: IT Risk Resources | ISACA : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.1: Risk Identification, pp. 57-59.]
Which of the following describes the relationship between Key risk indicators (KRIs) and key control indicators (KCIS)?
KCIs are independent from KRIs KRIs.
KCIs and KRIs help in determining risk appetite.
KCIs are defined using data from KRIs.
KCIs provide input for KRIs
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that provide information on the level of exposure to a given risk. Key control indicators (KCIs) are metrics that measure the performance or effectiveness of a control in mitigating a risk. KCIs provide input for KRIs, because they help to assess the residual risk after applying the control. For example, if the KRI is the number of security incidents, and the KCI is the percentage of incidents detected by the intrusion prevention system (IPS), then the KCI provides input for the KRI by showing how well the IPS is reducing the risk of security breaches. References = CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions
Which of the following would cause the GREATEST concern for a risk practitioner reviewing the IT risk scenarios recorded in an organization’s IT risk register?
Some IT risk scenarios have multi-year risk action plans.
Several IT risk scenarios are missing assigned owners.
Numerous IT risk scenarios have been granted risk acceptances.
Many IT risk scenarios are categorized as avoided.
Answer:
Explanation:
Assigning ownership to each risk scenario is fundamental in risk management. Without designated owners, there is a lack of accountability, which can lead to risks not being adequately managed or mitigated. The absence of assigned owners means that no one is responsible for monitoring, reporting, or addressing the risk, increasing the likelihood of adverse outcomes.
Which of the following will be the GREATEST concern when assessing the risk profile of an organization?
The risk profile was not updated after a recent incident
The risk profile was developed without using industry standards.
The risk profile was last reviewed two years ago.
The risk profile does not contain historical loss data.
Answer:
Explanation:
The greatest concern when assessing the risk profile of an organization is that the risk profile was last reviewed two years ago. A risk profile is a snapshot of the current risk exposure and appetite of the organization, based on the identification, analysis, and evaluation of the risks that could affect the achievement of the organization’s objectives. A risk profile should be reviewed and updated regularly, atleast annually, or whenever there are significant changes in the internal or external environment, such as new projects, strategies, regulations, or incidents. A risk profile that was last reviewed two years ago may not reflect the current risk situation and status of the organization, and may lead to inaccurate or incomplete risk assessment and response. The risk profile not being updated after a recent incident, the risk profile being developed without using industry standards, and the risk profile not containing historical loss data are also concerns, but they are not as critical as the risk profile being outdated. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 48.
Which of the following is the BEST success criterion for control implementation?
Adequate resources are allocated to perform the control.
Responsibilities for control execution are properly defined.
Risk is at an acceptable level after the control is in place.
Key risk indicators (KRIs) for the control are properly defined.
Answer:
The number of tickets to rework application code has significantly exceeded the established threshold. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner s BEST recommendation?
Perform a root cause analysis
Perform a code review
Implement version control software.
Implement training on coding best practices
Answer:
Explanation:
A root cause analysis is a process of identifying and understanding the underlying or fundamental causes or factors that contribute to or result in a problem or incident that has occurred or may occur in the organization. A root cause analysis can provide useful insights and solutions on the origin and nature of the problem or incident, and prevent or reduce its recurrence or impact.
Performing a root cause analysis is the risk practitioner’s best recommendation when the number of tickets to rework application code has significantly exceeded the established threshold, because it can help the organization to address the following questions:
Why did the application code require rework?
What were the errors or defects in the application code?
How did the errors or defects affect the functionality or usability of the application?
Who was responsible or accountable for the application code development and testing?
When and how were the errors or defects detected and reported?
What were the costs or consequences of the rework for the organization and its stakeholders?
How can the errors or defects be prevented or minimized in the future?
Performing a root cause analysis can help the organization to improve and optimize the application code quality and performance, and to reduce or eliminate the need for rework. It can also help the organization to align the application code development and testing with the organization’s objectives and requirements, and to comply with the organization’s policies and standards.
The other options are not the risk practitioner’s best recommendations when the number of tickets to rework application code has significantly exceeded the established threshold, because they do not address the main purpose and benefit of performing a root cause analysis, which is to identify and understand the underlying or fundamental causes or factors that contribute to or result in the problem or incident.
Performing a code review is a process of examining and evaluating the application code for its quality, functionality, and security, using the input and feedback from the peers, experts, or tools. Performing a code review can help the organization to identify and resolve the errors or defects in the application code, but it is not the risk practitioner’s best recommendation, because it doesnot indicate why the application code required rework, and how the errors or defects affected the organization and its stakeholders.
Implementing version control software is a process of using a software tool to manage and track the changes and modifications to the application code, and to ensure the consistency and integrity of the application code. Implementing version control software can help theorganization to control and monitor the application code development and testing, but it is not the risk practitioner’s best recommendation, because it does not indicate why the application code required rework, and how the errors or defects affected the organization and its stakeholders.
Implementing training on coding best practices is a process of providing and facilitating the learning and development of the skills and knowledge on the principles, guidelines, and standards for the application code development and testing. Implementing training on coding best practices can help the organization to enhance the competence and performance of the application code developers and testers, but it is not the risk practitioner’s best recommendation, because it does not indicate why the application code required rework, and how the errors or defects affected the organization and its stakeholders. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 189
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Which of the following is the BEST key control indicator (KCI) for risk related to IT infrastructure failure?
Number of times the recovery plan is reviewed
Number of successful recovery plan tests
Percentage of systems with outdated virus protection
Percentage of employees who can work remotely
Answer:
Explanation:
A key control indicator (KCI) is a metric that provides information on the extent to which a given control is meeting its intended objectives in terms of loss prevention, reduction, etc. A KCI should have an explicit relationship to both the specific control and the specific risk against which the control has been implemented. For risk related to IT infrastructure failure, a possible control is to have a recovery plan that can restore the critical IT services and minimize the impact of the failure. A KCI that can measure the effectiveness of this control is the number of successful recovery plan tests, which indicates how well the recovery plan can be executed in a real scenario. The higher the number of successful tests, the lower the risk of IT infrastructure failure. Therefore, this is the best KCI among the given options. References =
Integrating KRIs and KPIs for Effective Technology Risk Management
Key Control Indicator (KCI) - CIO Wiki
Infrastructure Issues: Understanding and Mitigating Risks
Which of the following MUST be captured in a risk treatment plan?
Risk owner
Senior management
Risk register details
Risk financial impact
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk treatment plan (sometimes called a risk response plan) describes how selected risk treatments will be implemented, by whom, and by when. For the plan to be actionable and enforceable, every significant risk and its treatment must have a clearly assigned risk owner.
CRISC guidance emphasizes that:
Accountability for risk treatment lies with the risk owner.
A risk treatment plan primarily provides treatment for identified risk that exceeds risk tolerance and should specify responsibility for implementing the chosen risk treatment.
Ensuring accountability and ownership is critical for the effectiveness of the risk management program.
While items such as financial impact and risk register references are useful supporting information, the one element that must be present for each treated risk is the person or role responsible for making sure the treatment is implemented and monitored.
Therefore:
A. Risk owner — REQUIRED in every risk treatment plan entry.
B. “Senior management†is too generic; they may approve the plan but are not always the specific treatment owners.
C. “Risk register details†are normally linked to or referenced, but they are not the key must-have field for effective execution.
D. “Risk financial impact†is important for prioritization and cost–benefit analysis, but without an owner, nothing guarantees action.
This is consistent with CRISC’s treatment-plan guidance that risk treatment plans “primarily specify the responsibility for implementing the chosen risk treatment and provide treatment for identified risk that exceeds risk tolerance.â€
An updated report from a trusted research organization shows that attacks have increased in the organization's industry segment. What should be done FIRST to integrate this data into risk assessments?
Average the ransomware attack frequencies together
Revise the threat frequency for ransomware attack types
Adjust impact amounts based on the average ransom
Use the new frequency as the maximum value in a Monte Carlo simulation
Answer:
Explanation:
New threat intelligence primarily impacts the frequency component of risk calculations.
CRISC states:
“When new information about threats is available, it must be incorporated into risk assessment by adjusting threat event frequencies in related scenarios.â€
A and D are statistical manipulations, not practical first steps.
C addresses impact, not likelihood.
Hence, B. Revise the threat frequency is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 2 – IT Risk Assessment, Topic: Incorporating Threat Intelligence.
Which of the following provides the MOST mitigation value for an organization implementing new Internet of Things (loT) devices?
Performing a vulnerability assessment on the loT devices
Designing loT architecture with IT security controls from the start
Implementing key risk indicators (KRIs) for loT devices
To ensure risk trend data is collected and reported
Answer:
A recent regulatory requirement has the potential to affect an organization’s use of a third party to supply outsourced business services. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
Conduct a gap analysis
Transfer risk to the third party
Terminate the outsourcing agreement
Identify compensating controls
Answer:
Explanation:
When a new regulation affects outsourcing arrangements, the first and best response is to perform a gap analysis.
“Upon regulatory change, the risk practitioner should perform a gap analysis to determine areas of noncompliance and required updates in contracts or controls.â€
Transferring or terminating agreements may follow depending on results.
Hence, A is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 3 – Risk Response and Mitigation, Topic: Third-Party Risk and Compliance Management.
Which of the following would be MOST useful to senior management when determining an appropriate risk response?
A comparison of current risk levels with established tolerance
A comparison of cost variance with defined response strategies
A comparison of current risk levels with estimated inherent risk levels
A comparison of accepted risk scenarios associated with regulatory compliance
Answer:
Explanation:
A comparison of current risk levels with established tolerance is the most useful information for senior management when determining an appropriate risk response, as it shows the gap between the actual risk exposure and the desired risk exposure of the enterprise. This gap indicates the need and urgency for risk response actions, and helps senior management to prioritize and allocate resources for risk mitigation. A comparison of current risk levels with established tolerance also reflects the effectiveness of the existing risk management process and controls, and enables senior management to monitor and adjust the risk strategy and objectives accordingly. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, Question 234. CRISC by Isaca Actual Free Exam Q&As, Question 9. CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, Question 234. CRISC Sample Questions 2024, Question 234.
Which of the following is the FIRST step when developing a business case to drive the adoption of a risk remediation project by senior management?
Calculating the cost
Analyzing cost-effectiveness
Determining the stakeholders
Identifying the objectives
Answer:
Explanation:
 The first step when developing a business case to drive the adoption of a risk remediation project by senior management is to identify the objectives of the project. The objectives are the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that the project aims to accomplish. The objectives should be aligned with the organization’s vision, mission, and strategy, as well as the identified business problem or opportunity. The objectives should also reflect the expected benefits and outcomes of the project, such as reducing the risk exposure, enhancing the security posture, or improving the business performance. Identifying the objectives is the first step because it provides the direction, scope, and justification for the project, and it serves as the basis for evaluating the alternative solutions, estimating the costs and benefits, and communicating the value proposition to the senior management and other stakeholders. The other options are not the first step, although they may be subsequent or concurrent steps in the business case development process. Calculating the cost is a part of the financial analysis, which estimates the total expenditure and funding sources of the project, but it does not define the purpose or the scope of the project. Analyzing cost-effectiveness is a part of the economic analysis, which compares the costs and benefits of the alternative solutions and recommends the optimal one, but it does not specify the goals or the criteria of the project. Determining the stakeholders is a part of the stakeholder analysis, which identifies and assesses the interests, expectations, and influence of the parties involved in or affected by the project, but it does not establish the objectives or the rationale of the project. References = Business case: 7 key steps to build it and use it - Twproject: project …, Guide to developing the Project Business Case - GOV.UK, How to Write a Business Case: Template & Examples | Adobe Workfront
Senior management has asked a risk practitioner to develop technical risk scenarios related to a recently developed enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. These scenarios will be owned by the system manager. Which of the following would be the BEST method to use when developing the scenarios?
Cause-and-effect diagram
Delphi technique
Bottom-up approach
Top-down approach
Answer:
Explanation:
A cause-and-effect diagram, also known as a fishbone diagram or an Ishikawa diagram, is a graphical tool that helps to identify and analyze the potential causes and effects of a problem or an event. A cause-and-effect diagram can be used to develop technical risk scenarios related to a recently developed ERP system, because it can help to:
Break down the complex problem or event into manageable and measurable categories and subcategories of causes and effects
Visualize the relationships and interactions among the various factors that contribute to the problem or event
Identify the root causes and the most significant effects of the problem or event
Generate ideas and hypotheses for testing and validating the problem or event
Communicate and present the problem or event clearly and logically to the stakeholders1
A cause-and-effect diagram can be constructed by following these steps:
Define the problem or event and write it in a box on the right side of the diagram
Draw a horizontal line from the box to the left side of the diagram, representing the main spine of the fishbone
Identify the major categories of causes that affect the problem or event, such as people, process, technology, environment, etc., and write them on the branches of the spine
For each category, brainstorm and list the possible subcategories and specific causes that influence the problem or event, and write them on the sub-branches of the spine
For each cause, identify and list the possible effects or consequences that result from the problem or event, and write them on the sub-sub-branches of the spine
Analyze the diagram and prioritize the causes and effects based on their frequency, severity, and controllability
Develop technical risk scenarios based on the most critical causes and effects, and describe how they could affect the ERP system and the organization1
What should be the PRIMARY objective of updating a risk awareness program in response to a steady rise in cybersecurity threats across the industry?
To increase familiarity and understanding of potential security incidents
To ensure compliance with risk management policies and procedures
To reduce the risk of insider threats that could compromise security practices
To lower the organization's risk appetite and tolerance levels
Answer:
Explanation:
The main goal of updating a risk awareness program in response to rising threats is to ensure employees understand new risks and how to respond to them, thereby enhancing overall security posture.
A risk practitioner has recently become aware of unauthorized use of confidential personal information within the organization. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
Establish database activity monitoring
Report the incident to the chief privacy officer (CPO)
Invoke the incident response plan
Escalate the issue to the data owner
Answer:
Explanation:
In the event of a data breach or misuse of confidential information, the first step is to activate the incident response plan. This ensures immediate containment, impact analysis, and communication protocols are followed.
What is the BEST recommendation to reduce the risk associated with potential system compromise when a vendor stops releasing security patches and updates for a business-critical legacy system?
Segment the system on its own network.
Ensure regular backups take place.
Virtualize the system in the cloud.
Install antivirus software on the system.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best recommendation to reduce the risk associated with potential system compromise when a vendor stops releasing security patches and updates for a business-critical legacy system is to segment the system on its own network. Network segmentation is the process of dividing a network into smaller subnetworks or segments, based on different criteria, such as function, location, or security level. Network segmentation helps to isolate the system from the rest of the network, and limit the exposure and access to the system. Network segmentation also helps to improve the performance and security of the network, by reducing the network traffic and congestion, and enhancing the monitoring and control capabilities. The other options are not as effective as segmenting the system on its own network, although they may provide some additional protection or recovery options. Ensuring regular backups take place, virtualizing the system in the cloud, and installing antivirus software on the system are all measures that can helpto reduce the risk of data loss or system damage, but they do not address the root cause of the risk, which is the lack of security patches and updates for the system. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.1, page 3-11.
Which of the following risk activities is BEST facilitated by enterprise architecture (EA)?
Aligning business unit risk responses to organizational priorities
Determining attack likelihood per business unit
Adjusting business unit risk tolerances
Customizing incident response plans for each business unit
Answer:
An IT risk practitioner has been asked to regularly report on the overall status and effectiveness of the IT risk management program. Which of the following is MOST useful for this purpose?
Balanced scorecard
Capability maturity level
Internal audit plan
Control self-assessment (CSA)
Answer:
Explanation:
A balanced scorecard is a strategic management tool that helps to measure and communicate the performance of an organization or a program against its goals and objectives. A balanced scorecard typicallyconsists of four perspectives: financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth. Each perspective has a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect the critical success factors and desired outcomes of the organization or the program1.
A balanced scorecard is most useful for reporting on the overall status and effectiveness of the IT risk management program, because it can provide a comprehensive and balanced view of the program’s performance across multiple dimensions. A balanced scorecard can help to align the IT risk management program with the business strategy and vision, and to demonstrate the value and impact of the program to the stakeholders. A balanced scorecard can also help to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the IT risk management program, and to monitor and improve the program’s processes and outcomes2.
The other options are not as useful as a balanced scorecard for reporting on the overall status and effectiveness of the IT risk management program. A capability maturity level is a measure of the maturity and quality of a process or a practice, based on a predefined set of criteria andstandards. A capability maturity level can help to assess and benchmark the IT risk management program’s processes and practices, but it does not provide a holistic view of the program’s performance and results3. An internal audit plan is a document that outlines the scope, objectives, and methodology of an internal audit activity. An internal audit plan can help to evaluate and verify the IT risk management program’s controls and compliance, but it does not provide a strategic view of the program’s goals and outcomes4. A control self-assessment (CSA) is a technique that involves the participation of the process owners and the staff in assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of their own controls. A CSA can help to enhance the awareness and ownership of the IT risk management program’s controls, but it does not provide an objective and independent view of the program’s performance and impact. References =
Balanced Scorecard Basics - Balanced Scorecard Institute
Using the Balanced Scorecard to Measure and Manage IT Risk
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) Overview
Internal Audit Planning: The Basics - The IIA
[Control Self-Assessment - ISACA]
Which of the following would MOST likely drive the need to review and update key performance indicators (KPIs) for critical IT assets?
The outsourcing of related IT processes
Outcomes of periodic risk assessments
Changes in service level objectives
Findings from continuous monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are metrics used to measure and evaluate the achievement of the organization’s objectives and strategies1. KPIs for critical IT assets are KPIs that focus onthe performance and value of the IT assets that are essential for the organization’s operations and functions2. KPIs for critical IT assets may include metrics such as availability, reliability, utilization, cost, and security of the IT assets3. The need to review and update KPIs for critical IT assets may be driven by various factors, such as changes in the business environment, customer expectations, or regulatory requirements. However, the most likely factor that would drive the need to review and update KPIs for critical IT assets is the outcomes of periodic risk assessments. A risk assessment is a process that involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks and their potential impacts on the organization’s objectives and performance4. A periodic risk assessment is a risk assessment that is performed at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, to capture the changes and updates in the risk environment and the risk profile5. The outcomes of periodic risk assessments would most likely drive the need to review and update KPIs for critical IT assets, as they would provide insights into the current and emerging risks that may affect the performance and value of the critical IT assets, as well as the effectiveness and efficiency of the existingand planned controls and responses. By reviewing and updating the KPIs for critical IT assets based on the outcomes of periodic risk assessments, the organization can ensure that the KPIs are relevant, realistic, and aligned with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance, and that they provide accurate and timely information for decision making and reporting. The outsourcing of related IT processes, changes in service level objectives, and findings from continuous monitoring are not the most likely factors that would drive the need to review and update KPIs for critical IT assets, as they do not provide the same level of information and impact as the outcomes of periodic risk assessments. The outsourcing of related IT processes is a decision that involves transferring some or all of the IT processes that support or enable the critical IT assets to an external service provider. The outsourcing of related IT processes may affect the performance and value of the critical IT assets, but it does not necessarily require a review and update of the KPIs for critical IT assets, as the KPIs may still be valid and applicable for the outsourced IT processes. Changes in service level objectives are changes in the expected or agreed level of quality or performance of the IT services that support or enable the critical IT assets. Changes in service level objectives may affect the performance and value of the critical IT assets, but they do not necessarily require a review and update of theKPIs for critical IT assets, as the KPIs may still be consistent and compatible with the changed service level objectives. Findings from continuous monitoring are the results or outcomes of the ongoing observation and measurement of the performance and compliance of the IT processes and systems that support or enable the critical IT assets. Findings from continuous monitoring may affect the performance and value of the critical IT assets, but they do not necessarily require a review and update of the KPIs for critical IT assets, as the KPIs may still be relevant and reliable for the continuously monitored IT processes and systems. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: Risk Monitoring, pp. 189-191.
Which of the following BEST enables risk-based decision making in support of a business continuity plan (BCP)?
Impact analysis
Control analysis
Root cause analysis
Threat analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
The best tool to enable risk-based decision making in support of a business continuity plan (BCP) is an impact analysis. An impact analysis is a process of identifying and evaluating the potential effects of an interruption or disruption of business operations on the organization’scritical functions, processes, and resources. An impact analysis can help to determine the recovery priorities, objectives, and strategies forthe BCP. Control analysis, root cause analysis, and threat analysis are other possible tools, but they are not as effective as an impact analysis. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 12; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 215.
The PRIMARY purpose of IT control status reporting is to:
ensure compliance with IT governance strategy.
assist internal audit in evaluating and initiating remediation efforts.
benchmark IT controls with Industry standards.
facilitate the comparison of the current and desired states.
Answer:
Explanation:
IT control status reporting is the process of collecting and analyzing data about the effectiveness and efficiency of IT controls. IT controls are the policies, procedures, and practices that ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT resources and information. IT control status reporting helps to monitor the performance of IT controls against the predefined objectives and criteria, and to identify any gaps or issues that need to be addressed. IT control status reporting also provides information to the stakeholders about the current status and progress of IT control implementation and improvement.
The primary purpose of IT control status reporting is to facilitate the comparison of the current and desired states of IT controls. This means that IT control status reporting helps to evaluate the gap between the actual and expected performance of IT controls, and to determine the actions and resources needed to close the gap. IT control status reporting also helps to align the IT controls with the business goals and strategies, and to ensure that the IT controls are delivering value to the organization. By comparing the current and desired states of IT controls, IT control status reporting enables continuous improvement and optimization of IT control processes and outcomes.
The other options are not the primary purpose of IT control status reporting, but rather some of the benefits or outcomes of it. IT control status reporting can help to ensure compliance with IT governance strategy,but it is not the main reason for doing it. IT governance is the framework that defines the roles, responsibilities, and relationships among the stakeholders involved in ITdecision making and oversight. IT control status reporting can support IT governance by providing relevant and reliable information to the stakeholders, and by demonstrating the accountability and transparency of IT control activities. However, IT control status reporting is not the same as IT governance, and it is not the only way to ensure compliance with IT governance strategy.
IT control status reporting can also assist internal audit in evaluating and initiating remediation efforts, but it is not the main objective of it. Internal audit is an independent and objective assurance and consulting activity that evaluates the adequacy and effectiveness of IT controls, and provides recommendations for improvement. IT control status reporting can provide input and evidence to the internal audit process, and help to identify the areas of IT control that need further review or testing. IT control status reporting can also help to monitor and track the implementation of the audit findings and recommendations, and to verify the results of the remediation efforts. However, IT control status reporting is not the same as internal audit, and it is not the only source of information for internal audit.
Finally, IT control status reporting can benchmark IT controls with industry standards, but it is not the main goal of it. Industry standards are the best practices or guidelines that define the minimum requirements or expectations for IT control performance and quality. IT control status reporting can help to compare the IT controls with the industry standards, and to identify the areas of IT control that need to be enhanced or updated. IT control status reporting can also help to demonstrate the compliance or conformance of IT controls with the industry standards, and to provide assurance to the external parties or regulators. However, IT control status reporting is not the same as industry standards, and it is not the only way to benchmark IT controls. References =
Service Reporting in ITIL: Process, Objectives and Examples - KnowledgeHut
Anatomy of an effective status report - Project Management Institute
How to Create a Project Status Report [Template & Examples]
Communicating Document Control Progress on a Project
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
WhichT5f the following is the MOST effective way to promote organization-wide awareness of data security in response to an increase in regulatory penalties for data leakage?
Enforce sanctions for noncompliance with security procedures.
Conduct organization-w>de phishing simulations.
Require training on the data handling policy.
Require regular testing of the data breach response plan.
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most effective way to promote organization-wide awareness of data security in response to an increase in regulatory penalties for data leakage is to require training on the data handling policy, as it educates the employees on the importance, requirements, and procedures of data protection, and enhances their knowledge and skills to prevent, detect, and respond to data leakage incidents. Enforcingsanctions for noncompliance with security procedures, conducting organization-wide phishing simulations, and requiring regular testing of the data breach response plan are not the most effective ways, as they are more related to the enforcement, evaluation, or improvement of the data security, respectively, rather than the promotion of the data security awareness. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 155.
Which of the following tasks should be completed prior to creating a disaster recovery plan (DRP)?
Conducting a business impact analysis (BIA)
Identifying the recovery response team
Procuring a recovery site
Assigning sensitivity levels to data
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual, conducting a business impact analysis (BIA) is the task that should be completed prior to creating a disaster recovery plan (DRP), because it helps to identify the critical business processes and resources, and their dependencies, that need to be recovered in the event of a disaster. The BIA also helps to determine the recovery timeobjectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) for each business process and resource, which are the key inputs for the DRP. The other options are not the tasks that should be completed prior to creating a DRP, as they are part of the DRP itself. Identifying the recovery response team is the task of defining the roles and responsibilities of the personnel involved in the recovery process. Procuring a recovery site is the task of selecting and acquiring an alternative location where the business operations can be resumed. Assigning sensitivity levels to data is the task of classifying the data based on its importance and protection requirements. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.2.1, page 237.
Which of the following should be accountable for ensuring that media containing financial information are adequately destroyed per an organization's data disposal policy?
Compliance manager
Data architect
Data owner
Chief information officer (CIO)
Answer:
Explanation:
The data owner should be accountable for ensuring that media containing financial information are adequately destroyed per an organization’s data disposal policy, as they have the authority and responsibility to define the classification, retention, and disposal requirements for the data they own. The compliance manager, the data architect, and the chief information officer (CIO) are not the best choices, as they have different roles and responsibilities related to data governance, design, and strategy, respectively, but they do not own the data. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 154.
Which of the following s MOST likely to deter an employee from engaging in inappropriate use of company owned IT systems?
A centralized computer security response team
Regular performance reviews and management check-ins
Code of ethics training for all employees
Communication of employee activity monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
Employee activity monitoring is the process of tracking and recording the actions and behaviors of employees on company owned IT systems, such as email, internet, applications, etc. Thepurpose of employee activity monitoring is to ensure compliance with the company’s policies and regulations, prevent data leakage and misuse, detect and deter inappropriate or malicious activities, and improve productivity and performance. The most likely way to deter an employee from engaging in inappropriate use of company owned IT systems is to communicate the employee activity monitoring policy and practice to the employees, and make them aware of the consequences of violating the policy. By doing so, the company can create a deterrent effect and discourage the employees from misusing the IT systems, as they know that their actions are being monitored and recorded, and that they will be held accountable for any misconduct. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 181.
Who should be responsible for approving the cost of controls to be implemented for mitigating risk?
Risk practitioner
Risk owner
Control owner
Control implementer
Answer:
An IT organization is replacing the customer relationship management (CRM) system. Who should own the risk associated with customer data leakage caused by insufficient IT security controls for the new system?
Chief information security officer
Business process owner
Chief risk officer
IT controls manager
Answer:
Explanation:
The business process owner is the stakeholder who is responsible for the business process that is supported by the IT system, such as the CRM system. The business process owner has the authority and accountability to manage the risk and its response associated with the business process and the IT system. The business process owner should own the risk of customer data leakage caused by insufficient IT security controls for the new system, as it directly affects the performance, functionality, and compliance of the business process. The other options are not the correct answer, as they involve different roles or responsibilities in the risk management process:
The chief information security officer is the senior executive who oversees the enterprise-wide information security program, and provides guidance and direction to the information security managers and practitioners. The chief information security officer may advise or support the business process owner in managing the risk of customer data leakage, but does not own the risk.
The chief risk officer is the senior executive who oversees the enterprise-wide risk management program, and provides guidance and direction to the risk managers and practitioners. The chief risk officer may advise or support the business process owner in managing the risk of customer data leakage, but does not own the risk.
The IT controls manager is the person who designs, implements, and monitors the IT controls that mitigate the IT risks, such as the IT security controls for the new system. The IT controls manager may advise or support the business process owner in managing the risk of customer data leakage, but does not own the risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.1.1.1, pp. 95-96.
From a governance perspective, which of the following is MOST important to ensure when risk management policies are being updated to facilitate the pursuit of new opportunities?
Updates align with strategic business objectives.
Updates will be approved by the risk owners.
Updates align with industry standards and benchmarks.
Updates will be reviewed periodically to ensure compliance.
Answer:
An organization's IT infrastructure is running end-of-life software that is not allowed without exception approval. Which of the following would provide the MOST helpful information to justify investing in updated software?
The balanced scorecard
A cost-benefit analysis
The risk management frameworkD, A roadmap of IT strategic planning
Answer:
Explanation:
 A cost-benefit analysis is a tool that compares the costs and benefits of different alternatives, such as updating software or continuing to use end-of-life software. A cost-benefit analysis can provide the mosthelpful information to justify investing in updated software, as it can show the potential savings, benefits, and risks of each option, and help the decision-makers choose the best course of action. A cost-benefit analysis can also include qualitative factors, such as security, compliance, performance, and customer satisfaction, that may be affected by the software update. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, Question 231. CRISC by Isaca Actual Free Exam Q&As, Question 8. CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, Question 231. CRISC Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control – Question231.
A service provider is managing a client’s servers. During an audit of the service, a noncompliant control is discovered that will not be resolved before the next audit because the client cannot afford the downtime required to correct the issue. The service provider’s MOST appropriate action would be to:
develop a risk remediation plan overriding the client's decision
make a note for this item in the next audit explaining the situation
insist that the remediation occur for the benefit of other customers
ask the client to document the formal risk acceptance for the provider
Answer:
Explanation:
A noncompliant control is a control that does not meet the requirements or standards of an audit, regulation, or policy. A noncompliant control can expose the organization to risks such as errors, fraud, or breaches. When a noncompliant control is identified, the service provider and the client should work together to resolve the issue as soon as possible. However, sometimes the resolution may not be feasible or cost-effective, and the client may decide to accept the risk associated with the noncompliant control.
In this case, the service provider’s most appropriate action would be to ask the client to document the formal risk acceptance for the provider. This means that the client should acknowledge the existence and consequences of the noncompliant control, and provide a written justification for accepting the risk. The risk acceptance document should also specify the roles and responsibilities of the service provider and the client, and the duration and conditions of the risk acceptance. The risk acceptance document should be signed by the client’s senior management and the service provider’s management, and kept as part of the audit evidence.
The other options are not appropriate actions for the service provider. Developing a risk remediation plan overriding the client’s decision would be disrespectful and unprofessional, as it would ignore the client’s authority and preference. Making a note for this item in the next audit explaining the situation would be insufficient and misleading, as it would imply that the issue is still unresolved and that the service provider is responsible for it. Insisting that the remediation occur for the benefit of other customers would be unreasonable and impractical, as it woulddisregard the client’s business needs and constraints, and potentially harm the relationship between the service provider and the client. References =
Risk Acceptance - Institute of Internal Auditors
New Guidance on the Evaluation of Non-compliance with the Risk Assessment Standard and its Peer Review Impact - REVISED
The Impact of Non-compliance: Understanding The Risks And Consequences
Which of the following is the MOST important update for keeping the risk register current?
Modifying organizational structures when lines of business merge
Adding new risk assessment results annually
Retiring risk scenarios that have been avoided
Changing risk owners due to employee turnover
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Understanding the Question:
The question asks what the most important update for keeping the risk register current is.
ï‚· Analyzing the Options:
A. Modifying organizational structures when lines of business merge:Reflects significant changes in the organization that impact risk profiles.
B. Adding new risk assessment results annually:Important but periodic.
C. Retiring risk scenarios that have been avoided:Necessary but not as impactful as major organizational changes.
D. Changing risk owners due to employee turnover:Important but secondary to major structural changes.
ï‚·
Organizational Changes:When lines of business merge, it can significantly alter the risk landscape, introducing new risks and changing the impact and likelihood of existing ones. Updating the risk register to reflect these changes is crucial for accurate risk management.
Impact on Risk Profiles:Mergers and acquisitions can affect every aspect of an organization, from operational processes to regulatory compliance, making it essential to update the risk register accordingly.
Which of the following is a PRIMARY reason for considering existing controls during initial risk assessment?
To determine the inherent risk level
To determine the acceptable risk level
To determine the current risk level
To determine the desired risk level
Answer:
Explanation:
During an initial risk assessment, it is crucial to consider existing controls primarily to determine the current risk level. Here's a
Understanding Existing Controls:
Existing controls are measures already in place to mitigate risks. These controls can include technical, administrative, and physical safeguards designed to protect organizational assets.
Knowing what controls are currently in place helps to understand the organization’s current defense mechanisms against potential threats.
Assessing the Current Risk Level:
The current risk level is the risk that remains after considering the effectiveness of existing controls, often referred to as residual risk.
By evaluating these controls, one can determine how much risk is actually mitigated and what level of risk remains.
For instance, if an organization has implemented firewalls and intrusion detection systems, these controls would reduce the risk of cyber attacks. The effectiveness of these controls will determine the residual risk level.
Differentiating Between Risk Types:
Inherent Risk:This is the level of risk that exists before any controls are applied. It’s the raw risk associated with a particular asset or process.
Residual Risk:This is the risk that remains after existing controls have been applied. It's the actual risk that an organization faces after mitigation efforts.
Current Risk:This term is often used interchangeably with residual risk but focuses on the risk level at the present moment, considering the existing controls.
Primary Objective in Initial Risk Assessment:
The primary objective of considering existing controls during the initial risk assessment is to gain an accurate picture of the current risk landscape. This allows risk practitioners to understandwhat additional controls or modifications might be needed to further reduce risk to acceptable levels.
Without considering existing controls, the assessment would only reflect the inherent risk, which doesn’t provide a realistic view of the organization's risk exposure.
Which of the following will provide the BEST measure of compliance with IT policies?
Evaluate past policy review reports.
Conduct regular independent reviews.
Perform penetration testing.
Test staff on their compliance responsibilities.
Answer:
Explanation:
Conducting regular independent reviews will provide the best measure of compliance with IT policies, as this ensures that the policies are implemented and followed consistently and effectively across the organization. Independent reviews can also identify any gaps, weaknesses, or violations in the compliance process, and recommend corrective actions or improvements.Independent reviews can be performed by internal or external auditors, regulators, or consultants, depending on the scope and purpose of the review. Evaluating past policy review reports, performing penetration testing, and testing staff on their complianceresponsibilities are not the best measures of compliance with IT policies, although they may be useful or complementary methods. Evaluating past policy review reports can provide some historical and comparative data, but it may not reflect the current or accurate situation of the compliance status. Performing penetration testing can assess the security and vulnerability of the IT systems and networks, but it does not measure the compliance with all the IT policies, such as those related to governance, operations, or quality. Testing staff on their compliance responsibilities can evaluate the awareness and knowledge of the staff, but it does not measure the actual behaviour or performance of the staff in complying with the IT policies. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, page 187.
Risk mitigation procedures should include:
buying an insurance policy.
acceptance of exposures
deployment of counter measures.
enterprise architecture implementation.
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk mitigation procedures are the actions and plans that an organization implements to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks. Risk mitigation procedures should include the deployment of counter measures, which are the specific controls or solutions that address the root causes or sources of the risks, and prevent or minimize the potential losses or damages. For example, a counter measure for therisk of data breach could be encrypting the data or implementing a firewall. The deployment of counter measures should be based on a cost-benefit analysis, a risk assessment, and a risk response strategy. The other options are not necessarily part of risk mitigation procedures. Buying an insurance policy is an example of risk transfer,which is a risk response strategy that shifts the responsibility or burden of the risk to another party, such as an insurer or a vendor. However, risk transfer does not eliminate or reduce the risk itself, and it may involve additional costs or conditions. Acceptance of exposures is an example of risk acceptance, which is a risk response strategy that acknowledges the existence and consequences of the risk, and decides not to take any action to change the risk situation. However, risk acceptance does not mitigate the risk, and it may require contingency plans or reserves to deal with the potential outcomes. Enterprise architecture implementation is an example of a business process or project that may involve or create risks, but it is not a risk mitigation procedure itself. Enterprise architecture is the design and structure of an organization’s IT systems, networks, and resources, and how they align with the organization’s goals and strategies. Enterprise architecture implementation may require risk management activities, such as risk identification, assessment, and response, but it is not a risk mitigation procedure itself. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 151
A recent audit identified high-risk issues in a business unit though a previous control self-assessment (CSA) had good results. Which of the following is the MOST likely reason for the difference?
The audit had a broader scope than the CSA.
The CSA was not sample-based.
The CSA did not test control effectiveness.
The CSA was compliance-based, while the audit was risk-based.
Answer:
Explanation:
A compliance-based CSA focuses on ensuring that the business unit follows the policies and procedures established by the enterprise, regardless of the actual risk level or impact of the controls.
A risk-based CSA focuses on identifying and evaluating the risks that may affect the business unit’s objectives, and designing and implementing controls that are appropriate to mitigate those risks.
A compliance-based CSA may not capture all the high-risk issues that exist in a business unit, especially if they are not aligned with the enterprise’s standards or expectations.
A risk-based CSA may identify more high-risk issues than a compliance-based CSA, because it considers both internal and external factors that may affect the business unit’s performance or security.
Therefore, a difference in results between a previous control self-assessment (CSA) and an audit indicates that either one of them was not risk-based, but rather compliance-based.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 9
Information Technology & Security, page 3
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 1
A risk practitioner has been asked to assess the risk associated with a new critical application used by a financial process team that the risk practitioner was a member of two years ago. Which of the following is the GREATEST concern with this request?
The risk assessment team may be overly confident of its ability to identify issues.
The risk practitioner may be unfamiliar with recent application and process changes.
The risk practitioner may still have access rights to the financial system.
Participation in the risk assessment may constitute a conflict of interest.
Answer:
Explanation:
Participation in the risk assessment may constitute a conflict of interest, because it may create a situation where the risk practitioner’s personal or professional interests or relationships interfere with their objectivity, independence, or impartiality in conducting the risk assessment. A conflict of interest is a type of risk that may compromise the integrity, quality, or validity of the risk assessment process and outcomes, and may damage the reputation or trust of the risk practitioner or the organization. A conflict of interest may arise when the risk practitioner has a direct or indirect connection or involvement with the subject or stakeholder of the risk assessment, such as a previous or current role, responsibility, or relationship, that may influence or bias theirjudgment or decision. Participation in the risk assessment may constitute a conflict of interest, as the risk practitioner may have a prior or residual interest or loyalty to the financialprocess team or the new critical application, and may not be able to assess the risk in a fair and unbiased manner.
The risk assessment team being overly confident of its ability to identify issues, the risk practitioner being unfamiliar with recent application and process changes, and the risk practitioner still having access rights to the financial system are all possible concerns with the request, but they are not the greatest concern, as they do not necessarily imply a conflict of interest, and they may be mitigated or resolved by other means, such as training, documentation, or review.
A risk practitioner has learned that an effort to implement a risk mitigation action plan has stalled due to lack of funding. The risk practitioner should report that the associated risk has been:
mitigated
accepted
avoided
deferred
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner should report that the associated risk has been deferred, as this means that the risk response has been postponed or delayed due to lack of resources or other constraints. Deferring a risk response implies that the risk owner acknowledges the risk and intends to implement the risk mitigation action plan at a later stage, when the resources or conditions are available. The other options are not correct, as they do not reflect the actual status of the risk response. Mitigating a risk means that the risk response has been implemented and the risk level has been reduced. Accepting a risk means that the risk response has been rejected or waived, and the risk level has been accepted as it is. Avoiding a risk means that the risk response has beenimplemented and the risk level has been eliminated or transferred. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk Response, page 146.
A failure in an organization s IT system build process has resulted in several computers on the network missing the corporate endpoint detection and response (EDR) software. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner’s IMMEDIATE concern?
Multiple corporate build images exist.
The process documentation was not updated.
The IT build process was not followed.
Threats are not being detected.
Answer:
Which of the following is the GREATEST risk associated with the use of data analytics?
Distributed data sources
Manual data extraction
Incorrect data selection
Excessive data volume
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual1, data selection is the process of choosing the appropriate data sources and variables for data analysis. Data selection is the most critical step in data analytics, as it determines the quality and validity of the results and insights derived from the analysis. Incorrect data selection is the greatest risk associated with the use of data analytics, as it can lead to inaccurate, incomplete, irrelevant, or biased outcomes that can adversely affectthe decision making and performance of the organization. Incorrect data selection can also cause legal, regulatory, ethical, or reputational issues for the organization, if the data used for analysis is not authorized, reliable, or compliant. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 255.
An organization retains footage from its data center security camera for 30 days when the policy requires 90-day retention The business owner challenges whether the situation is worth remediating Which of the following is the risk manager s BEST response'
Identify the regulatory bodies that may highlight this gap
Highlight news articles about data breaches
Evaluate the risk as a measure of probable loss
Verify if competitors comply with a similar policy
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk is the possibility of an event that may have a negative impact on the achievement of an organization’s objectives. A risk can be measured by the probability and impact of the event, which indicate the likelihood and consequence of the event. A risk manager is a person who is responsible for performing risk management activities, such as identifying, analyzing, evaluating, treating, monitoring, and communicating risks. When an organization retains footage from its data center security camera for 30 days when the policy requires 90-day retention, the risk manager’s best response to the business owner who challenges whether the situation is worth remediating is to evaluate the risk as a measure of probable loss, which means to estimate thepotential harm or damage that may result from the non-compliance with the policy. By evaluating the risk as a measure of probable loss, the risk manager can provide the business owner with the rationale and justification for the risk remediation, and help the business owner to understand the cost-benefit analysis of the risk response. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 63.
Which of the following is the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of a disaster recovery test of critical business processes?
Percentage of job failures identified and resolved during the recovery process
Percentage of processes recovered within the recovery time and point objectives
Number of current test plans and procedures
Number of issues and action items resolved during the recovery test
Answer:
Explanation:
 The best key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of a disaster recovery test of critical business processes is the percentage of processes recovered within the recovery time and point objectives. Recovery time objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable time period within which a business process or an IT service must be restored after a disruption. Recovery point objective (RPO) is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time before the disruption. The percentage of processes recovered within the RTO and RPO indicates how well the disaster recovery test meets the business continuity and recoveryrequirements and expectations, and how effectively the disaster recovery plan and procedures are executed. The percentage of processes recovered within the RTO and RPO canalso help to identify the gaps, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement in the disaster recovery capabilities. Percentage of job failures identified and resolved during the recovery process, number of current test plans and procedures, and number of issues and action items resolved during the recovery test are not as good as the percentage of processes recovered within the RTO and RPO, as they do not directly measure the achievement of the recovery objectives, and may not reflect the actual impact and performance of the disaster recovery test. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 130.
Which of the following BEST mitigates ethical risk?
Ethics committees
Contingency scenarios
Awareness of consequences for violations
Routine changes in senior management
Answer:
Explanation:
Ethics committees are typically responsible for developing, implementing, and overseeing an organization’s ethical guidelines and policies. They play a crucial role in mitigating ethical risk by ensuring that the organization’s operations align with its ethical standards123.
References
1What Is Ethically Informed Risk Management? - Journal of Ethics
2Five Ways to Reduce Ethics and Compliance Risk - Free Ethics Toolkit
35 Ways to Manage Ethical Risks - ClearRisk
Which of the following groups represents the first line of defense?
Internal audit
Compliance committee
External audit
Operational managers
Answer:
Explanation:
Thefirst line of defenseincludesbusiness and operational managerswho own and manage risks directly. They implement controls as part of their day-to-day duties, making them the first to respond to risk.
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when selecting risk indicators (KRIs)? The ability to:
Monitor the performance of a process
Assess the risk associated with risk scenarios
Measure changes in the threat landscape
Refine the organization’s risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
The main purpose of a Key Risk Indicator (KRI) is to provide early warning of increased risk exposure tied to specific risk scenarios.
CRISC defines KRIs as:
“Metrics that provide a signal of increasing risk exposure in relation to defined risk scenarios.â€
Performance (A) is tracked via KPIs; threat measurement (C) is only one input.
Hence, B. Assess the risk associated with risk scenarios is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 4 – Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Topic: Designing and Using KRIs.
The PRIMARY benefit of classifying information assets is that it helps to:
communicate risk to senior management
assign risk ownership
facilitate internal audit
determine the appropriate level of control
Answer:
Explanation:
Classifying information assets is a process of identifying and categorizing the data and information resources that are owned, controlled, or used by an organization, based on their value, sensitivity, and criticality.
Classifying information assets helps to determine the appropriate level of control that is needed to protect them from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. Control level refers to the degree of protection or assurance that a control provides against a risk.
Classifying information assets also helps to communicate risk to senior management, assign risk ownership, and facilitate internal audit. These are other benefits of risk management that are not directly related to determining the appropriate level of control.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 11
Information Technology & Security, page 5
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 3
Which of the following BEST indicates the effective implementation of a risk treatment plan?
Inherent risk is managed within an acceptable level.
Residual risk is managed within appetite and tolerance.
Risk treatments are aligned with industry peers.
Key controls are identified and documented.
Answer:
Explanation:
The effective implementation of a risk treatment plan is best indicated by managing residual risk within the organization’s appetite and tolerance levels. Residual risk is the remaining risk aftercontrols have been applied, and ensuring it is within acceptable levels demonstrates that the risk treatment plan is effective.
Managing Residual Risk within Appetite and Tolerance (Answer B):
Definition: Residual risk is the risk remaining after risk treatment measures have been implemented.
Significance: Managing residual risk within the set appetite and tolerance levels shows that the implemented controls are effective and aligned with the organization’s risk management objectives.
Outcome: It ensures that the organization's risk exposure is kept within acceptable boundaries, thereby protecting its assets and operations.
Comparison with Other Options:
A. Inherent risk is managed within an acceptable level:
Definition: Inherent risk is the risk before any controls are applied.
Limitation: The focus should be on residual risk post-treatment.
C. Risk treatments are aligned with industry peers:
Purpose: While benchmarking is useful, it does not directly indicate the effectiveness of risk treatment.
D. Key controls are identified and documented:
Purpose: Identifying and documenting controls is necessary, but effectiveness is shown by managing residual risk.
Of the following, who should be responsible for determining the inherent risk rating of an application?
Application owner
Senior management
Risk practitioner
Business process owner
Answer:
Explanation:
Inherent risk rating is a measure of the natural level of risk that is part of an application, before any controls are applied1. Inherent risk rating helps to identify and prioritize the applications that pose the highest risk to the organization and require the most attention and resources for risk management2. The responsibility for determining the inherent risk rating of an application should belong to the risk practitioner, as they have the expertise and knowledge to perform a comprehensive and consistent risk assessment of the application, using a standard methodologyand criteria3. The risk practitioner should also communicate and report the inherent risk rating of the application to the relevant stakeholders, such as the application owner, senior management, and business process owner, and provide recommendations for risk mitigation4. The application owner, senior management, and business process owner are not the best choices for determining the inherent risk rating of an application, as they may not have the same level of skill and objectivity as the risk practitioner. The application owner is the person who has the authority and accountability for the application and its performance5. The application owner may be involved in providing input and feedback to the risk practitioner during the risk assessment process, but they may not be able to assess the inherent risk rating of the application independently and impartially, as they may have a vested interest in the application’s success and reputation6. Senior management is the group of executives who set the strategic direction and objectives of the organization and oversee its performance7. Senior management may be involved in approving and endorsing the risk assessment process and its results, but they may not be able to assess the inherent risk rating of the application in detail and depth, as they may have a broader and higher-level perspective of the organization’s risk profile and priorities8. The business process owner is the person who has the authority and accountability for a business process that is supported or enabled by the application. The business process owner may be involved in providing input and feedback to the risk practitioner during the risk assessment process, but they may not be able to assess the inherent risk rating of the application accuratelyand comprehensively, as they may have a limited and specific view of the application’s functionality and value. References = 2: Introduction toapplication risk rating & assessment | Infosec3: Application Security Risk: Assessment and Modeling - ISACA4: Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: Risk Monitoring, pp. 189-191.1: Inherent Risk Rating - Shared Assessments - Third Party Risk Management5: [Application Owner - Gartner IT Glossary] 6: Perform Inherent Risk Analysis - Oracle7: [Senior Management - Definition, Roles and Responsibilities] 8: Rating Inherent and Residual Risk - Barn Owl : [Business Process Owner - Gartner IT Glossary] : [Business Process Owner - Roles and Responsibilities]
The BEST indicator of the risk appetite of an organization is the
regulatory environment of the organization
risk management capability of the organization
board of directors' response to identified risk factors
importance assigned to IT in meeting strategic goals
Answer:
Explanation:
The board of directors’ response to identified risk factors is the best indicator of the risk appetite of an organization. The board of directors is the highest governing body of the organization, and it is responsible for setting the strategic direction, objectives, and risk appetite of the organization. The board of directors should also oversee the risk management process, and ensure that the risks are aligned with the organization’s goals and values. The board of directors’ response to identified risk factors reflects how much and what type of risk the organization is willing to pursue, retain, or take in order to achieve its objectives. The regulatory environment, the risk management capability, and the importance assigned to IT are not direct indicators of the risk appetite, although they may influence or constrain it. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.2.1, page 1-8.
Which of the following is MOST important for successful incident response?
The quantity of data logged by the attack control tools
Blocking the attack route immediately
The ability to trace the source of the attack
The timeliness of attack recognition
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important factor for successful incident response is the timeliness of attack recognition. Incident response is the process of detecting, analyzing, containing, eradicating, recovering, and reporting on security incidents that could affect the organization’s IT systems or data. The timeliness of attack recognition is the speed and accuracy with which the organization can identify and confirm that an attack has occurred or is in progress. The timeliness of attack recognition is crucial for successful incident response, as it affects the ability and effectiveness of the organization to respond to and mitigate the attack, and to minimize the damage and impact of the attack. The other options are not as important as the timeliness of attack recognition, although they may also contribute to or influence the incident response. The quantity of data logged by the attack control tools, the ability to trace the source of the attack, and the blocking of the attack route immediately are all factors that could help or hinder the incident response, but they are not the most important factor for successful incident response. References = CISA Review Manual, 27th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.4.1, page 5-32.
A data processing center operates in a jurisdiction where new regulations have significantly increased penalties for data breaches. Which of the following elements of the risk register is MOST important to update to reflect this change?
Risk impact
Risk trend
Risk appetite
Risk likelihood
Answer:
Explanation:
 Risk impact is the potential loss or damage that a risk event can cause to an organization. Risk impact can be expressed in qualitative or quantitative terms, such as financial, reputational, operational, or legal. A risk register is a tool that records and tracks the key information about the identified risks, such as their description, likelihood, impact, response, and status. A risk register helps an organization to monitor and manage its risks effectively and efficiently. When there is a change in the external or internal environment that affects the organization’s risks, such as new regulations, the risk register should be updated to reflect this change. The most important element of the risk register to update in this case is the risk impact, because the new regulations have significantly increased the penalties for data breaches, which means that the potential loss or damage that a data breach can cause to the organization has also increased. By updating the risk impact, the organization can reassess the severity and priority of the data breach risk, and adjust its risk response accordingly. The other elements of the risk register are less important toupdate in this case. The risk trend shows the direction and rate of change of the risk over time, which may or may not be affected by the new regulations. The risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives, which is unlikely to change due to the new regulations. The risk likelihood is the probability of a risk event occurring, which is also independent of the new regulations. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 131
Which of the following is MOST important when identifying an organization's risk exposure associated with Internet of Things (loT) devices?
Defined remediation plans
Management sign-off on the scope
Manual testing of device vulnerabilities
Visibility into all networked devices
Answer:
Which of the following MUST be updated to maintain an IT risk register?
Expected frequency and potential impact
Risk tolerance
Enterprise-wide IT risk assessment
Risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
An IT risk register is a document that records and tracks the significant IT risks that an organization faces across its various functions, processes, and activities. An IT risk register can help to provide a comprehensive and consistent view of the organization’s IT risk profile, and to support the decision making and reporting of the IT risk management function1.
One of the data that must be updated to maintain an IT risk register is the expected frequency and potential impact of each IT risk. The expected frequency is the probability or likelihood of the IT risk occurring, based on historical data, statistical analysis, expert judgment, or other methods. The potential impact is the magnitude or severity of the consequences or outcomes of the IT risk, measured in terms of cost, time, quality, reputation, or other criteria2.
Updating the expected frequency and potential impact of each IT risk is essential for maintaining an IT risk register, because it can help to:
Evaluate and prioritize the IT risks based on their risk level, which is calculated by multiplying the frequency and impact
Monitor and track the changes or trends in the IT risk exposure and performance over time
Identify and implement the appropriate risk response strategies and controls, based on the risk level and the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization
Report and communicate the IT risk status and progress to the stakeholders, using risk indicators, dashboards, or matrices3
The other options are not the data that must be updated to maintain an IT risk register, but rather the data that are used as inputs or outputs of the IT risk management process. Risk tolerance is the acceptable variation in the outcomes related to specific objectives or risks. Risk tolerance is used to measure the IT risk analysis and to guide the IT risk response. Enterprise-wide IT risk assessment is a process that identifies, analyzes, and evaluates the IT risks across theorganization. Enterprise-wide IT risk assessment is used topopulate the IT risk register and to inform the IT risk response. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in order to achieve its objectives. Risk appetite is used to guide the IT risk analysis and to align the IT risk response. References =
Risk Register - ISACA
Risk Analysis - ISACA
Risk Register 2021-2022 - UNECE
[How To Conduct Business Impact Analysis in 8 Easy Steps - G2]
[Risk Appetite and Risk Tolerance - ISACA]
[Enterprise Risk Assessment - ISACA]
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of these documents is MOST important to request from a cloud service
provider during a vendor risk assessment?
Nondisclosure agreement (NDA)
Independent audit report
Business impact analysis (BIA)
Service level agreement (SLA)
Answer:
Explanation:
A vendor risk assessment is a process of evaluating and managing the risks associated with outsourcing IT services or functions to a third-party provider, such as a cloud service provider.
One of the most important documents to request from a cloud service provider during a vendor risk assessment is an independent audit report. This is a report that provides an objective and reliable assurance on the quality, security, and performance of the cloud service provider’s operations, processes, and controls, based on the standards and criteria established by an independent auditor or a recognized authority, such as ISACA, ISO, NIST, etc.
An independent audit report helps to verify the compliance and effectiveness of the cloud service provider’s risk management practices, identify any gaps or issues that may affect the service delivery or security, and recommend improvements or corrective actions.
The other options are not the most important documents to request from a cloud service provider during a vendor risk assessment. They are either secondary or not essential for vendor risk management.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 22
Information Technology & Security, page 16
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 14
Which of the following is the MOST important information to cover a business continuity awareness Ira nine, program for all employees of the organization?
Recovery time objectives (RTOs)
Segregation of duties
Communication plan
Critical asset inventory
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important information to cover in a business continuity awareness training program for all employees of the organization is the communication plan. A communication plan is a document that defines the roles, responsibilities, procedures, and resources for communicating with the internal and external stakeholders before, during, and after a business continuity event. A communication plan helps to ensure that the relevant and accurate information is delivered to the appropriate parties in a timely and consistent manner, and that the feedback and responses are received and addressed accordingly. A communication plan also helps to maintain the trust, confidence, and reputation of the organization, and to comply with the legal or regulatory requirements. A communication plan is the most important information to cover in a business continuity awareness training program, because it helps to prepare and educate the employees on how to communicate effectively and efficiently in a business continuity event, and how to avoid or minimize the communication errors, gaps, or conflicts that could affect the business continuity performance and recovery. The other options are not as important as the communication plan, although they may also be covered in a business continuity awareness training program. Recovery time objectives (RTOs), segregation of duties, and critical asset inventory are all factors that could affect the business continuity planning and implementation, but they are notthe most important information to cover in a business continuity awareness training program. References = 6
IT disaster recovery point objectives (RPOs) should be based on the:
maximum tolerable downtime.
maximum tolerable loss of data.
need of each business unit.
type of business.
Answer:
Explanation:
IT disaster recovery point objectives (RPOs) should be based on the:
B. maximum tolerable loss of data.
RPOs are determined by how much data loss an organization can withstand in the event of a disaster. It’s a measure of the maximum age of files that an organization must recover from backup storage for normal operations to resume after a disaster. Therefore, RPOs are directly related to the maximum tolerable loss of data.
Which of the following BEST enables risk mitigation associated with software licensing noncompliance?
Document IT inventory management procedures.
Conduct annual reviews of license expiration dates.
Perform automated vulnerability scans.
Implement automated IT asset management controls.
Answer:
Explanation:
Automated IT asset management ensures real-time visibility and tracking of software usage, licensing, and compliance. It minimizes human error, improves audit readiness, and proactively addresses noncompliance risks.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to ensure software engineers test patches before release to the production environment?
To detect incompatibilities that might disrupt the operation
To provide assurance that deployed patches have been properly authorized
To understand how long it will take to deploy the patch
To support availability by authorizing the release of the patch at the appropriate time
Answer:
Explanation:
Pre-production compatibility testing ensures patches won’t break applications or services, protecting availability—a key control objective outlined in ISACA’s guidance on Change and Configuration Management.
Which of the following presents the GREATEST privacy risk related to personal data processing for a global organization?
Privacy risk awareness training has not been conducted across the organization.
The organization has not incorporated privacy into its risk management framework.
The organization allows staff with access to personal data to work remotely.
Personal data processing occurs in an offshore location with a data sharing agreement.
Answer:
Explanation:
Greatest Privacy Risk:
Jurisdictional Challenges: Processing personal data in an offshore location often involves dealing with different legal and regulatory requirements, which can complicate compliance with data privacy laws such as GDPR or CPRA.
Data Transfer Risks: Even with a data sharing agreement, the protection and enforcement of privacy rights can be less stringent in the offshore location compared to the home jurisdiction. This can lead to increased risks of data breaches and misuse.
Enforcement Difficulties: If privacy violations occur, enforcing legal actions across borders can be challenging, potentially leading to inadequate redress for affected individuals.
Comparison with Other Options:
Privacy Risk Awareness Training Not Conducted: This is a significant risk but can be mitigated relatively quickly with proper training programs.
Privacy Not Incorporated into Risk Management Framework: While critical, the risk can be managed by integrating privacy into the framework without immediate severe consequences.
Remote Work by Staff with Access to Personal Data: This introduces risks related to secure access and data protection but can be managed with proper security controls.
Best Practices:
Data Sovereignty Considerations: Ensure data is processed in jurisdictions with strong privacy laws that align with the organization's regulatory requirements.
Regular Audits and Assessments: Conduct regular audits of data processing practices in offshore locations to ensure compliance with data privacy agreements.
Legal Safeguards: Establish robust legal safeguards and contracts to enforce data protection standards across jurisdictions.
Which of the following BEST indicates that additional or improved controls ate needed m the environment?
Management, has decreased organisational risk appetite
The risk register and portfolio do not include all risk scenarios
merging risk scenarios have been identified
Risk events and losses exceed risk tolerance
Answer:
Explanation:
The best indicator that additional or improved controls are needed in the environment is when risk events and losses exceed risk tolerance. Risk tolerance is the acceptable level of variation in performance or outcomes relative to the achievement of objectives. Risk events and losses are the negative consequences of risk that have occurred or are expected to occur. When risk events and losses exceed risk tolerance, it means that the existing controls are not sufficient or effective to prevent or mitigate the risk, and that the organization is exposed to unacceptable levels of risk that could impair its ability to achieve its objectives. Therefore, additional or improved controls are needed to reduce the risk to an acceptable level. Management decreasing organizational risk appetite, the risk register and portfolio not including all risk scenarios, and emerging risk scenarios being identified are not as clear and direct indicators that additional or improved controls are needed in the environment, as they do not necessarily reflect the actual performance or outcomes of the risk management process. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 41.
An IT risk practitioner is evaluating an organization's change management controls over the last six months. The GREATEST concern would be an increase in:
rolled back changes below management's thresholds.
change-related exceptions per month.
the average implementation time for changes.
number of user stories approved for implementation.
Answer:
Explanation:
= Change management is the process of planning, implementing, and monitoring changes to IT systems, services, or infrastructure in a controlled and coordinated manner1. Change management controls are the policies, procedures, and tools that ensure changes are authorized, documented, tested, and reviewed before they are deployed to the production environment2.
Change-related exceptions are the deviations or violations from the established change management controls, such as unauthorized, untested, or failed changes3. Change-related exceptions pose a high risk to theorganization, as they can cause system instability, performance degradation, security breaches, data loss, or compliance issues3.
An increase in change-related exceptions per month would be the greatest concern for an IT risk practitioner, as it indicates a lack of effectiveness, efficiency, or compliance of the change management process and controls. An increase in change-related exceptions per month could result from:
Poor change planning, prioritization, or scheduling
Insufficient change approval, review, or communication
Inadequate change testing, validation, or verification
Lack of change monitoring, reporting, or auditing
Low change awareness, training, or support
An IT risk practitioner should investigate the root causes of the increase in change-related exceptions per month, and recommend corrective and preventive actions to improve the change management process and controls, such as:
Aligning the change management process with the organization’s goals, strategies, and risk appetite
Implementing a standardized and consistent change management methodology, such as ITIL or COBIT
Defining clear roles and responsibilities for change management stakeholders, such as change owners, change managers, change advisory boards, change implementers, and change users
Establishing clear and measurable criteria and thresholds for change authorization, classification, and evaluation
Leveraging tools and technologies to automate and streamline the change management process and controls, such as change management software, configuration management databases, or change management dashboards
Enhancing the change management culture and capabilities, such as change management awareness, training, support, or feedback
The other options are not as concerning as an increase in change-related exceptions per month, because they do not directly imply a risk to the organization’s IT systems, services, or infrastructure. Rolled backchanges below management’s thresholds, which are the changes that are reversed or undone due to errors, defects, or issues, may indicate a need for improvement in the change testing, validation, or verification processes, but they do not necessarily cause harm or damage to the production environment, as long as they are within the acceptable limits set bythe management. The average implementation time for changes, which is the duration of the change deployment process, may affect the organization’s agility, efficiency, or productivity, but it does not necessarily compromise the quality, security, or reliability of the changes, as long as they are implemented according to the change management controls. The number of user stories approved for implementation, which are the requirements or features that are expressed from the perspective of the end users, may reflect the organization’s demand, innovation, or customer satisfaction, but it does not necessarily increase the risk of the changes, as long as they are managed and controlled by the change management process.
References = What is Change Management? | ITIL | AXELOS, Change Management Controls: Definition, Types, and Best Practices, Change Management Exceptions: Definition, Causes, and Impacts, ITIL Change Management: Best Practices & Processes - BMC Software, COBIT 2019: Change Enablement
A risk practitioner has become aware of production data being used in a test environment. Which of the following should be the practitioner's PRIMARY concern?
Sensitivity of the data
Readability of test data
Security of the test environment
Availability of data to authorized staff
Answer:
Explanation:
Production data is the data that is used in the actual operation of a system or application, such as customer information, financial records, transactions, etc.
Test data is the data that is used in the testing or development of a system or application, such as dummy data, sample data, simulated data, etc.
A risk practitioner has become aware of production data being used in a test environment. This indicates that there is a risk of unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction of the production data, which may affect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data.
The primary concern of the risk practitioner in this situation is the sensitivity of the data. This means that the risk practitioner should assess how valuable, critical, or confidential the data is, and what would be the impact or consequence if the data is compromised or lost.
The sensitivity of the data helps to determine the level of protection and control that is needed to safeguard the data, and the priority and urgency of the risk response actions.
The other options are not the primary concerns of the risk practitioner in this situation. They are either secondary or not essential for data protection.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 32
Information Technology & Security, page 26
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 24
Which of the following would be MOST helpful when estimating the likelihood of negative events?
Business impact analysis
Threat analysis
Risk response analysis
Cost-benefit analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), threat analysis would be the most helpful when estimating the likelihood of negative events, as it involves identifying and evaluating the sources and causes of potential harm or loss to the IT assets and processes. Threat analysis helps to:
Determine the frequency and probability of occurrence of different types of threats, such as natural disasters, human errors, malicious attacks, system failures, etc.
Assess the impact and severity of the threats on the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the IT assets and processes
Prioritize the threats based on their likelihood and impact
Develop appropriate risk response strategies to prevent, mitigate, transfer or accept the threats
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.5: IT Risk Identification Methods and Techniques, pp. 35-361
A risk practitioner has been asked to evaluate the adoption of a third-party blockchain integration platform based on the value added by the platform and the organization's risk appetite. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Conduct a risk assessment with stakeholders.
Conduct third-party resilience tests.
Update the risk register with the process changes.
Review risk related to standards and regulations.
Answer:
Explanation:
Conducting a risk assessment with stakeholders is the best course of action for the risk practitioner to evaluate the adoption of a third-party blockchain integration platform, because it helps to identify, analyze, and evaluate the risks and opportunities associated with the platform, and to compare them with the organization’s risk appetite and value proposition. A risk assessment is a process of systematically identifying and assessing the sources and types of risk that an organization faces, and estimating their likelihood and impact. A risk assessment also involves identifying and evaluating the existing or proposed controls or mitigating factors that can reduce or eliminate the risk. A stakeholder is a person or group that has an interest or influence in the organization or its activities, such as customers, employees, shareholders,suppliers, regulators, or partners. A blockchain integration platform is a software solution that enables the organization to connect and interact with blockchain networks or applications, such as cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, or distributed ledgers. A blockchain integration platform can offer benefits such as transparency, security, efficiency, and innovation, but it can also pose risks such as technical complexity, interoperability issues, regulatory uncertainty, or cyberattacks. Therefore, conducting a risk assessment with stakeholders is the best way to evaluate the adoption of a third-party blockchain integration platform, as it helps to understand the benefits and risks of the platform, and to align them with the organization’s objectives and risk appetite. Conducting third-party resilience tests, updating the risk register with the process changes, and reviewing risk related to standards and regulations are all important tasks to perform after conducting a risk assessment, but they are not the best course of action, as they depend on the results of the risk assessment. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.2, page 87
The PRIMARY benefit associated with key risk indicators (KRls) is that they:
help an organization identify emerging threats.
benchmark the organization's risk profile.
identify trends in the organization's vulnerabilities.
enable ongoing monitoring of emerging risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that provide information on the level of exposure to a given risk. They enable ongoing monitoring of emerging risk by alerting the organization when the risk level exceeds thepredefined threshold or tolerance. By using KRIs, the organization can track the changes in the risk environment and take timely and appropriate actions to mitigate or avoid the risk.
Helping an organization identify emerging threats, benchmarking the organization’s risk profile, and identifying trends in the organization’s vulnerabilities are all possible uses of KRIs, but they are not the primary benefit. The primary benefit is to enable ongoing monitoring of emerging risk, which encompasses all these aspects and more. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, page 27-281
Which of the following provides the MOST important information to facilitate a risk response decision?
Audit findings
Risk appetite
Key risk indicators
Industry best practices
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Risk appetite provides the most important information to facilitate a risk response decision, because it reflects the organization’s risk tolerance, preferences, and expectations, which guide the selection and implementation of the risk response strategies. Risk appetite helps the organization to balance the potential benefits and costs of taking risks, and to align the risk management process with the organizational strategy and culture. The other options are not as important as risk appetite, because they do not indicate the organization’s desired level of risk exposure, but rather provide supplementary or partial information for the risk response decision, as explained below:
A. Audit findings are the results and recommendations of the internal or external audit activities that evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s governance, risk management, and control processes. Audit findings provide useful information to facilitate a risk response decision, because they can identify the gaps or weaknesses in the current risk response strategies, and suggest corrective actions or improvements. However, audit findings do not indicate the organization’s risk appetite, which is the basis for determining the optimal risk response strategies.
C. Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that measure the impact and likelihood of the risks, and provide early warning signs of changes in the risk exposure. KRIs provide useful information to facilitate a risk response decision, because they can monitor and report the performance and effectiveness of the current risk response strategies, and trigger corrective actions or adjustments.However, KRIs do not indicate the organization’s risk appetite, which is the basis for determining the acceptable level of risk exposure and performance.
D. Industry best practices are the standards, norms, and expectations for risk management that are established and followed by the peers or competitors in the same industry or sector. Industry best practices provide useful information to facilitate a risk response decision, because they can benchmark and compare the organization’s risk response strategies with those of the leading or successful organizations, and identify areas for improvement or innovation. However, industry best practices do not indicate the organization’s risk appetite, which is the basis for determining the unique and customized risk response strategies that suit the organization’s needs and goals. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.2, page 40. Risk Appetite: What It Is and How to Use It, Risk Appetite: How Hungry Are You?, Risk Appetite: The Strategic Balancing Act
An organization's risk management team wants to develop IT risk scenarios to show the impact of collecting and storing credit card information. Which of the following is the MOST comprehensive approach to capture this scenario?
Top-down analysis
Event tree analysis
Control gap analysis
Bottom-up analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the ISACA Risk and Information Systems Control study guide and handbook, the most comprehensive approach to capture the risk scenario of collecting and storing credit card information is event tree analysis (ETA). ETA is a forward, top-down, logical modeling technique that explores the responses and outcomes of a single initiating event, such as a data breach or a cyberattack. ETA can help to identify all possible consequences of the scenario, such as financial losses, reputational damages, legal liabilities, regulatory penalties, and customer dissatisfaction. ETA can also help to assess the probabilities of the outcomes and the effectiveness of the controls and mitigation strategies12
1: ISACA Risk and Information Systems Control Study Guide, 4th Edition, page 33 2: ISACA Risk and Information Systems Control Handbook, 1st Edition, page 25
Which of the following will BEST help mitigate the risk associated with malicious functionality in outsourced application development?
Perform an in-depth code review with an expert
Validate functionality by running in a test environment
Implement a service level agreement.
Utilize the change management process.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk associated with malicious functionality in outsourced application development is that the vendor may introduce unauthorized or harmful code into the enterprise’s system, which could compromise its security, integrity, or performance.
To mitigate this risk, the enterprise should perform an in-depth code review with an expert who can verify that the code meets the specifications, standards, and quality requirements, and that it does not contain any malicious or unwanted functionality.
A code review is a systematic examination of the source code of a software program, which can identify errors, vulnerabilities, inefficiencies, or deviations from best practices. A code review can also ensure that the code is consistent, readable, maintainable, and well-documented.
An expert is someone who has the knowledge, skills, and experience to perform the code review effectively and efficiently. An expert may be an internal or external resource, depending on the availability, cost, and independence of the reviewer.
A code review should be performed before the code is deployed to the production environment, and preferably at multiple stages of the development life cycle, such as design, testing, and integration.
A code review can also be complemented by other techniques, such as automated code analysis, testing, and scanning tools, which can detect common or known issues in the code. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, p. 143
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 143
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern associated with the lack of proper control monitoring?
There is potential for an increase in audit findings
Key performance indicators (KPIs) may not be reliable
The potential for risk realization is increased
Control inefficiencies may go undetected
Answer:
Explanation:
Without monitoring, ineffective or failing controls may go unnoticed, leading to ahigher likelihood of risk eventsmaterializing, potentially with severe impact. This outweighs audit or KPI concerns.
Vulnerabilities have been detected on an organization's systems. Applications installed on these systems will not operate if the underlying servers are updated. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Recommend the business change the application.
Recommend a risk treatment plan.
Include the risk in the next quarterly update to management.
Implement compensating controls.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk treatment plan typically includes the following elements2:
Risk description: A brief summary of the risk, its causes, and its consequences.
Risk owner: The person or entity who is responsible for managing the risk and implementing the risk treatment plan.
Risk response: The strategy or method chosen to deal with the risk, such as avoid, reduce, transfer, or accept.
Risk actions: The specific tasks or steps that need to be performed to execute the risk response.
Risk resources: The human, financial, technical, or other resources that are required or available to support the risk actions.
Risk timeline: The schedule or deadline for completing the risk actions and achieving the desired risk level.
By recommending a risk treatment plan, the risk practitioner can help the organization to:
Analyze and prioritize the vulnerabilities detected on the systems, and determine their impact and likelihood.
Evaluate and compare the possible risk responses, and select the most suitable and feasible one for each vulnerability.
Define and assign the roles and responsibilities for the risk treatment process, and ensure the accountability and collaboration of the stakeholders.
Monitor and measure the progress and effectiveness of the risk treatment process, and report the results and outcomes to the management.
The other options are not the best course of action, because:
Recommending the business change the application is not a realistic or practical option, as it may be costly, time-consuming, or technically challenging to modify the application to make it compatible with the updated servers. It may also create other issues or risks, such as compatibility problems with other systems, performance degradation, or user dissatisfaction.
Including the risk in the next quarterly update to management is not a proactive or timely option, as it may delay or defer the risk treatment process and increase the exposure or vulnerability of the systems. It may also indicate a lack of urgency or importance of the risk, and undermine the credibility or trust of the management.
Implementing compensating controls is not a sufficient or comprehensive option, as it may not address the root cause or the source of the risk. Compensating controls are alternative or additionalcontrols that are implemented when the primary or preferred controls are not feasible or effective3. They may reduce the impact or likelihood of the risk, but they may not eliminate or resolve the risk.
References =
Risk Treatment Plan - CIO Wiki
Risk Treatment Plan Template - ISACA
Compensating Control - CIO Wiki
An organization is developing a risk universe to create a holistic view of its overall risk profile. Which of the following is the GREATEST barrier to achieving the initiative's objectives?
Lack of cross-functional risk assessment workshops within the organization
Lack of common understanding of the organization's risk culture
Lack of quantitative methods to aggregate the total risk exposure
Lack of an integrated risk management system to aggregate risk scenarios
Answer:
Explanation:
Lack of common understanding of the organization’s risk culture is the greatest barrier to achieving the initiative’s objectives, because it hinders the alignment and integration of risk management across the organization. Risk culture is the set of shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that influence how risk is perceived and managed in an organization. A risk universe is a comprehensive and structured representation of all the sources and types of risk that an organization faces. Developing a risk universe requires a common understanding of the organization’s risk culture, as it affects the risk appetite, tolerance, and strategy of the organization. Lack of cross-functional risk assessment workshops, lack of quantitative methods to aggregate the total risk exposure, and lack of an integrated risk management system are all challenges that may affect thedevelopment of a risk universe, but they are not the greatest barrier, as they can be overcome with appropriate tools and techniques. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, page 44
What should a risk practitioner do FIRST when a shadow IT application is identified in a business owner's business impact analysis (BIA)?
Include the application in the business continuity plan (BCP).
Determine the business purpose of the application.
Segregate the application from the network.
Report the finding to management.
Answer:
Explanation:
Determining the business purpose of the application is the first thing that a risk practitioner should do when a shadow IT application is identified in a business owner’s business impactanalysis (BIA), because it helps to understand the rationale and value of the application, and the potential risks and issues that it may introduce or affect. A shadow IT application is an IT system or application that is used by the business units or employees without the knowledge or approval of the IT department or management. A shadow IT application may offer benefits such as convenience, efficiency, or innovation, but it may also pose risks such as security breaches, data loss, compatibility issues, or regulatory non-compliance. A BIA is a process of analyzing the potential impact of disruption to the critical business functions or processes, and identifying the recovery priorities and requirements. A BIA may reveal the existence of ashadow IT application, as it may be used to support or enable a critical business function or process. Determining the business purpose of the application is the first thing to do, as it helps to evaluate the necessity and suitability of the application, and to plan the appropriate actions to address the shadow IT application. Including the application in the business continuity plan (BCP), segregating the application from the network, and reporting the finding to management are all possible things to do after determining the business purpose of the application, but they are not the first thing to do, as they depend on the results of the evaluation of the application. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1, page 143
Which of the following BEST supports the communication of risk assessment results to stakeholders?
Monitoring of high-risk areas
Classification of risk profiles
Periodic review of the risk register
Assignment of risk ownership
Answer:
Explanation:
 A risk profile is a summary of the key risks that affect an organization, a business unit, a process, or a project. A risk profile can help stakeholders understand the current and potential exposure to various sources of uncertainty, and prioritize the risk response accordingly. Classification of risk profiles is the process of grouping and categorizing risks based on common characteristics, such as source, impact, likelihood, or response strategy. Classification of risk profiles can help communicate risk assessment results to stakeholders by providing a clear and consistent way of presenting and comparing risks across different domains, levels, or perspectives. Classification of risk profiles can also help identify patterns, trends, and interrelationships among risks, and facilitate the allocation of resources and responsibilities for risk management. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.1: Risk Profile, p. 193-195.
An organization has outsourced its backup and recovery procedures to a cloud service provider. The provider's controls are inadequate for the organization's level of risk tolerance. As a result, the organization has internally implemented additional backup and recovery controls. Which risk response has been adopted?
Mitigation
Acceptance
Transfer
Avoidance
Answer:
Explanation:
Implementing internal controls to address inadequate third-party controls is a risk mitigation strategy. It reduces risk by enhancing control effectiveness.
During an IT department reorganization, the manager of a risk mitigation action plan was replaced. The new manager has begun implementing a new control after identifying a more effective option. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Communicate the decision to the risk owner for approval
Seek approval from the previous action plan manager.
Identify an owner for the new control.
Modify the action plan in the risk register.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk mitigation action plan is a document that specifies the actions to be taken to address the identified risks, the resources required, the timelines, the owners, and the expected outcomes. The risk owner is the person who has the authority and accountability to manage the risk and its response. The risk practitioner is the person who supports the risk owner in the risk management process. The best course of action for the risk practitioner when the manager of a risk mitigation action plan is replaced and a new control is implemented is to communicate the decision to the risk owner for approval. This will ensure that the risk owner is aware of the change, agrees with the new control, and approves the modification of the action plan. The other options are not the best course of action, as they may not involve the risk owner, who is ultimately responsible for the risk and its response. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.1.1.1, pp. 95-96.
When formulating a social media policy lo address information leakage, which of the following is the MOST important concern to address?
Sharing company information on social media
Sharing personal information on social media
Using social media to maintain contact with business associates
Using social media for personal purposes during working hours
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important concern to address when formulating a social media policy to address information leakage is sharing company information on social media. Information leakage is the unauthorized or unintentional disclosure of confidential or sensitive information to unauthorized parties. Social media is a platform that enables the users to create and share content, such as text, images, videos, or links, with other users or the public. Sharing company information on social media is the most important concern, as it could expose the company’s trade secrets, intellectual property, customer data, financial data, or strategic plans to competitors, hackers, or regulators. Sharing company information on social media could also damage the company’s reputation, trust, or credibility, and result in legal or regulatory penalties, fines, or lawsuits. Therefore, a social media policy should clearly define what constitutes company information, and what are the rules and guidelines for sharing or not sharing company information on social media. A social media policy should also specify the roles and responsibilities of the employees, managers, and the social media team, and the consequences and sanctions for violating the policy. Sharing personal information on social media, using social media to maintain contact with business associates, and using social media for personal purposes during working hours are not as important as sharing company information on social media, as they do not directly involve the leakage of company information, and they may not have significant impact or risk on the company. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 217
When updating a risk register with the results of an IT risk assessment, the risk practitioner should log:
high impact scenarios.
high likelihood scenarios.
treated risk scenarios.
known risk scenarios.
Answer:
Explanation:
When updating a risk register with the results of an IT risk assessment, the risk practitioner should log the known risk scenarios, because they are the risk scenarios that have been identified and assessed in the IT risk assessment process. The risk register should document and track the known risk scenarios, their characteristics, their status, and their responses. The other options are not the ones that should be logged, because:
Option A: High impact scenarios are the risk scenarios that have a high potential impact on the business objectives and processes, but they are not the only ones that should be logged. The risk register should include all the known risk scenarios, regardless of their impact level.
Option B: High likelihood scenarios are the risk scenarios that have a high probability of occurrence, but they are not the only ones that should be logged. The risk register should include all the known risk scenarios, regardless of their likelihood level.
Option C: Treated risk scenarios are the risk scenarios that have been addressed by the risk response actions, but they are not the only ones that should be logged. The risk register shouldinclude all the known risk scenarios, regardless of their treatment status. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, p. 108.
Which of the following should be done FIRST upon learning that the organization will be affected by a new regulation in its industry?
Transfer the risk.
Perform a gap analysis.
Determine risk appetite for the new regulation.
Implement specific monitoring controls.
Answer:
Explanation:
A gap analysis is the process of comparing the current state of the organization’s compliance with the new regulation and the desired state of compliance. It helps to identify the gaps or deficiencies that need to be addressed and prioritize the actions to close them. Performing a gap analysis is the first step to understand the impact of the new regulation and plan the appropriate risk response.
References
•ISACA CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Domain 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.2.3: Gap Analysis
•Regulatory Change: Future of Risk in the Digital Era | Deloitte US
•Gap Analysis: What It Is and How to Perform One | The Blueprint
When reporting to senior management on changes in trends related to IT risk, which of the following is MOST important?
Materiality
Confidentiality
Maturity
Transparency
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important factor when reporting to senior management on changes in trends related to IT risk is materiality. Materiality is the extent to which the information reported is significant, relevant, and useful for decision-making purposes. Materiality helps to prioritize the most important risks and communicate them effectively to senior management12
1: Integrating KRIs and KPIs for Effective Technology Risk Management - ISACA 2: CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 271
Which of the following would MOST effectively reduce risk associated with an increase of online transactions on a retailer website?
Scalable infrastructure
A hot backup site
Transaction limits
Website activity monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
The most effective way to reduce risk associated with an increase of online transactions on a retailer website is to implement website activity monitoring. Website activity monitoring can help to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats that may compromise the security and integrity of the website and its data. Scalable infrastructure, a hot backup site, and transaction limits are other possible ways to reduce risk, but they are not as effective as website activity monitoring. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 7; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 202.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when selecting key risk indicators (KRIs) to monitor risk trends over time?
Ongoing availability of data
Ability to aggregate data
Ability to predict trends
Availability of automated reporting systems
Answer:
Explanation:
Ongoing availability of data is the most important consideration when selecting key risk indicators (KRIs) to monitor risk trends over time, as it ensures that the KRIs can provide timely and reliable information on the current and future risk status and performance. KRIs are metrics that measure the level of risk exposureand the effectiveness of risk response strategies, and they should be aligned with the enterprise’s risk appetite and objectives. Ongoing availability ofdatameans that the data sources and collection methods for the KRIs are consistent, accessible, and sustainable, and that the data quality and integrity are maintained and verified. Ability to aggregate data, ability to predict trends, and availability of automated reporting systems are not the most important considerations, as they do not affect the validity and usefulness of the KRIs, but rather the presentation and analysis of the KRI data. References = CRISC Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control – Question213; ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 213.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of continuous monitoring?
Optimizing utilization of personnel
Detecting control errors in a timely manner
Aligning operations with policies and procedures
Minimizing the magnitude of loss from an event
Answer:
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for monitoring activities performed in a production database environment?
Ensuring that database changes are correctly applied
Enforcing that changes are authorized
Deterring illicit actions of database administrators
Preventing system developers from accessing production data
Answer:
Explanation:
Ensuring that database changes are correctly applied is the primary reason for monitoring activities performed in a production database environment, as it helps to maintain the integrity, availability, and performance of the database and the applications that depend on it. Database changes are any modifications made to the database structure, configuration, data, or code, such as adding or deleting tables, columns, indexes, or triggers, updating or inserting data, or altering stored procedures or functions. Database changes can have significant impacts on the database functionality and behavior, and may introduce errors, inconsistencies, or vulnerabilities if not applied correctly. Therefore, monitoring database changes is essential to verify that the changes are implemented as intended, comply with the design specifications and standards, and do not cause any adverse effects or conflicts with the existing database or application components.
The other options are not the primary reasons for monitoring activities performed in a production database environment. Enforcing that changes are authorized is an important aspect of database change management, but it is not the main purpose of database monitoring. Database change management is the process of planning, reviewing, approving, and implementing database changes in a controlled and consistent manner. Database change management helps to ensure that the changes are authorized by the appropriate stakeholders, aligned with the business requirements and objectives, and documented and communicated to the relevant parties. Database monitoring can support database change management by providing information and feedback on the change implementation and performance, but it does not enforce the change authorization. Deterring illicit actions of database administrators is a possible benefit of database monitoring, but it is not the primary reason for it. Database administrators are the users who have the highest level of access and privilege to the database, and they are responsible for managingand maintaining the database operations and security. Database monitoring can help to deter illicit actions of database administrators by tracking and auditing their activities and actions on the database, and alerting or escalating any suspicious or malicious behavior. However, database monitoring is not the only or the most effective way to prevent or detect illicit actions of database administrators. Other measures, such as implementing the principle of least privilege, segregating duties, enforcing password policies, and encrypting data, are also necessary to protect the database from unauthorized or improper access or manipulation by database administrators or other users. Preventing system developers from accessing production data is apossible benefit of database monitoring, but it is not the primary reason for it. System developers are the users who design, develop, and test the applications that interact with the database. System developers should not have access to the production data, as it may contain sensitive or confidential information that could be compromised or misused by the developers. System developers should only use test or dummy data for their development and testing purposes. Database monitoring can help to prevent system developers from accessing production data by controlling and restricting their access and privilege to the database, and logging and reporting any unauthorized or inappropriate access attempts. However, database monitoring is not the only or the most effective way to prevent system developers from accessing production data. Other measures, such as implementing access control policies, masking or anonymizing data, and isolating development and production environments, are also necessary to safeguard the production data from system developers or other users. References = Database Monitoring: Basics & Introduction | Splunk, IT Risk Resources | ISACA, Best Practices for Database Performance Monitoring
An organization has an approved bring your own device (BYOD) policy. Which of the following would BEST mitigate the security risk associated with the inappropriate use of enterprise applications on the devices?
Periodically review application on BYOD devices
Include BYOD in organizational awareness programs
Implement BYOD mobile device management (MDM) controls.
Enable a remote wee capability for BYOD devices
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to mitigate the security risk associated with the inappropriate use of enterprise applications on the BYOD devices is to implement BYOD mobile device management (MDM) controls. MDM controls are software tools or services that allow the organization to remotely manage, monitor, and secure the BYOD devices and the enterprise applications and data on them. MDM controls can help to enforce security policies, restrict unauthorized access, encrypt sensitive data, wipe data in case of loss or theft, and update or patch applications. The other options are not as effective as implementing MDM controls, as they are related to the review, awareness, or recovery of the BYOD devices and applications, not the prevention or protection of the security risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: IT Risk Response Implementation, page 145.
Which of the following is the MOST essential characteristic of a good IT risk scenario?
The scenario is aligned to business control processes.
The scenario is aligned to the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance.
The scenario is aligned to a business objective.
The scenario is aligned to known vulnerabilities in information technology.
Answer:
Explanation:
A good IT risk scenario must be aligned with a business objective. This alignment ensures that the risk scenario is relevant to the organization’s goals and can be effectively integrated into its risk management processes.
Alignment to Business Objective (Answer C):
Importance: Aligning risk scenarios with business objectives ensures that they are relevant and support the organization’s overall strategy.
Impact: This alignment helps in prioritizing risk management efforts and resources toward areas that directly affect the organization’s success.
Outcome: It leads to more effective risk management by focusing on risks that could impact key business outcomes.
Comparison with Other Options:
A. The scenario is aligned to business control processes:
Purpose: Control processes are important but secondary to business objectives.
B. The scenario is aligned to the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance:
Purpose: Important for overall risk management but not the primary characteristic of a good risk scenario.
D. The scenario is aligned to known vulnerabilities in information technology:
Purpose: While addressing vulnerabilities is important, the primary focus should be on how these vulnerabilities affect business objectives.
Which of the following is MOST important requirement to include in a Software as a Service (SaaS) vendor contract to ensure data is protected?
The vendor must provide periodic independent assurance reports.
The vendor must host data in a specific geographic location.
The vendor must be held liable for regulatory fines for failure to protect data.
The vendor must participate in an annual vendor performance review.
Answer:
Explanation:
The vendor must host data in a specific geographic location to ensure that the data is protected by the applicable data protection laws of the EU or the country where the data originates. This is especially important for SaaS customers who transfer personal data from the EU to third countries, as they need to comply with the GDPR and the new Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) that regulate such transfers. The vendor must also provide adequate security measures and guarantees to protect the data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or loss. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: IT Risk Mitigation, Section 5.3: IT Risk Mitigation Strategies and Approaches, Page 253; Data Protection – New EU Standard Contractual Clauses - Bodle Law.
Which of the following is the BEST metric to demonstrate the effectiveness of an organization's patch management process?
Average time to implement patches after vendor release
Number of patches tested prior to deployment
Increase in the frequency of patches deployed into production
Percent of patches implemented within established timeframe
Answer:
Explanation:
The percent of patches implemented within established timeframe is the best metric to demonstrate the effectiveness of an organization’s patch management process, as it measures how well the organization meets its patching objectives and reduces its exposure to vulnerabilities. This metric reflects the timeliness, completeness, and quality of the patching process, and can be compared against the organization’s patch management policy and standards. A high percent of patches implemented within established timeframe indicates that the organization has a mature and efficient patch management process that minimizes the risk of security breaches or operational disruptions due to unpatched systems.
A key risk indicator (KRI) is reported to senior management on a periodic basis as exceeding thresholds, but each time senior management has decided to take no action to reduce the risk. Which of the following is the MOST likely reason for senior management's response?
The underlying data source for the KRI is using inaccurate data and needs to be corrected.
The KRI is not providing useful information and should be removed from the KRI inventory.
The KRI threshold needs to be revised to better align with the organization s risk appetite
Senior management does not understand the KRI and should undergo risk training.
Answer:
Explanation:
A key risk indicator (KRI) is a metric that measures the level and trend of a risk that may affect the organization’s objectives, operations, or performance1. A KRI threshold is a predefined value or range that indicates the acceptable or tolerable level of risk for the organization2. Theorganization’s risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that it is willing to take in order to meet its strategic goals3. Therefore, the most likely reason for senior management’s response is that the KRI threshold needs to be revised to better align with the organization’s risk appetite. This means that the current threshold is either too low or too high, resulting in false alarms or missed signals. By adjusting the threshold to reflect the organization’s risk appetite, senior management can ensure that the KRI provides relevant and actionable information for risk management and decision making. The other options are not the most likely reasons for senior management’s response, as they imply that the KRI is faulty, irrelevant, or misunderstood. The underlying data source for the KRI is using inaccurate data and needs to be corrected. This option assumes that the KRI is based on erroneous or unreliable data, which would affect its validity and reliability. However, this is not the most likely reason, as senior management would be expected to verify the data quality and accuracy before using the KRI for risk monitoring and reporting. The KRI is not providing useful information and shouldbe removed from the KRI inventory. This option assumes that the KRI is not aligned with the organization’s objectives, strategies, or risk profile, which would affect its usefulness and value. However, this is not the most likely reason, as senior management would be expected to review and update the KRI inventory periodically to ensure that the KRIs are relevant and meaningful for risk management. Senior management does not understand the KRI and should undergo risk training. This option assumes that senior management lacks the knowledge or skills to interpret and use the KRI for risk management, which would affect their competence and confidence. However, this is not the most likely reason, as senior management would be expected to have sufficient risk awareness and education to understand and apply the KRI for risk management. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.1.4, Page 53.
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of incorporating IT risk scenarios into the corporate risk register?
Corporate incident escalation protocols are established.
Exposure is integrated into the organization's risk profile.
Risk appetite cascades to business unit management
The organization-wide control budget is expanded.
Answer:
Explanation:
IT risk scenarios are hypothetical situations that describe the sources, causes, and consequences of IT-related risks, and the potential impacts on the organization’s objectives, performance, and value creation12.
A corporate risk register is a document that records and tracks the significant risks that the organization faces, and the responses and actions that are taken to address them34.
The greatest benefit of incorporating IT risk scenarios into the corporate risk register is that exposure is integrated into the organization’s risk profile, which is a comprehensive and integrated representation of the risks that may affect the organization’s objectives, performance, and value creation56.
Exposure is integrated into the organization’s risk profile means that the organization has a complete and consistent view of the IT risk landscape, and the potential impacts andinterdependencies of IT risks on other types of risks, such as financial, operational, strategic, or reputational risks56.
Exposure is integrated into the organization’s risk profile also means that the organization can make informed and balanced decisions on the risk responses and actions, and allocate the appropriate resources and priorities to the IT risk management and control processes56.
The other options are not the greatest benefit, but rather possible outcomes or consequences of incorporating IT risk scenarios into the corporate risk register. For example:
Corporate incident escalation protocols are established is an outcome of incorporating IT risk scenarios into the corporate risk register that indicates the organization has defined and implemented the procedures and mechanisms for reporting and resolving IT-related incidents,and for escalating them to the appropriate authorities or levels when necessary78. However, this outcome does not measure or reflect the exposure or the risk profile of the organization, which may depend on other factors such as the frequency, severity, or complexity of the incidents78.
Risk appetite cascades to business unit management is a consequence of incorporating IT risk scenarios into the corporate risk register that indicates the organization has communicated and aligned the risk appetite, which is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept or pursue, to the business unit management, who are responsible for executing the risk strategy and objectives at the operational level . However, this consequence does not indicate or imply the exposure or the risk profile of the organization, which may vary depending on the context, environment, or stakeholder expectations .
The organization-wide control budget is expanded is an outcome of incorporating IT risk scenarios into the corporate risk register that indicates the organization has increased the amount of resources and funds that are allocated to the control processes, which are the procedures and activities that aim to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s operations, the reliability of its information, and the compliance with its policies and regulations . However, this outcome does not affect or determine the exposure or the risk profile of the organization, which is independent of the control budget . References =
1: IT Risk Scenarios - Morland-Austin3
2: Risk Scenarios Toolkit, ISACA, 2019
3: Risk Register Template and Examples | Prioritize and Manage Risk1
4: Risk Register Examples for Cybersecurity Leaders4
5: Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2009
6: IT Risk Management Framework, University of Toronto, 2017
7: Security Incident Reporting and Response, University of Toronto, 2017
8: Security Incident Reporting and Response, ISACA, 2019
Risk Appetite: Linking Strategy, Risk and Performance, ISACA, 2012
Risk Appetite and Tolerance, ISACA Journal, Volume 4, 2013
The Control Process | Principles of Management2
Control Management: What it is + Why It’s Essential | Adobe Workfront5
Which of the following is MOST effective against external threats to an organizations confidential information?
Single sign-on
Data integrity checking
Strong authentication
Intrusion detection system
Answer:
Explanation:
 Strong authentication is the most effective measure against external threats to an organization’s confidential information. Confidential information is any data or information that is sensitive, proprietary, or valuable to the organization, and that should not be disclosed to unauthorized parties1. External threats are malicious actors outside the organization who attempt to gain unauthorized access to the organization’s networks, systems, and data, using various methods such as malware, hacking, or social engineering2. Strong authentication is a method of verifying the identity and legitimacy of a user or device before granting access to the organization’s resources or data3. Strong authentication typically involves the use of multiple factors or methods of authentication, such as passwords, tokens, biometrics, orcertificates4. Strong authentication can prevent or reduce the risk of external threats to the organization’s confidential information, by making it more difficult and costly for the attackers to compromise the credentials or devices of the authorized users, and by limiting the access to the data or resourcesthat are relevant and necessary for the users’ roles and responsibilities5. The other options are not the most effective measures against external threats to the organization’s confidential information, as they are either less secure or less relevant than strong authentication. Single sign-on is a method of allowing a user to access multiple systems or applications with a single set of credentials, without having to log in separately for each system or application6. Single sign-on can improve the user experience and convenience, as well as reduce the administrative burden and cost of managing multiple accounts and passwords. However, single sign-on is not the most effective measure against external threats to the organization’s confidential information, as it can also increase the risk of credential compromise or misuse, and create a single point of failure or attack for the attackers to access multiple systems or data. Data integrity checking is a method of ensuring that the data or information is accurate, complete, and consistent, and that it has not been altered or corrupted by unauthorized parties or processes. Data integrity checking can involve the use of techniques such as checksums, hashes, digital signatures, or encryption. Data integrity checking can enhance the quality and reliability of the data or information, as well as detect and prevent any unauthorized or malicious changes or tampering. However, data integrity checking is not the most effective measure against external threats to the organization’s confidential information, as it does not prevent or reduce the risk of data theft or leakage, and it does not verify the identity or legitimacy of the users or devices accessing the data. Intrusion detection system is a system that monitors the network or system activities and events, and detects and alerts any suspicious ormalicious behaviors or anomalies that may indicate an attempted or successful breach or attack. Intrusion detection system can help to identify and respond to external threats to the organization’s networks, systems, and data, by providing visibility and awareness of the network or system status and activities, and by enabling timely and appropriate actions or countermeasures. However, intrusion detection system is not the most effective measure againstexternal threats to the organization’s confidential information, as it is a reactive or passive system that does not prevent or block the attacks, and it may generate false positives or negatives that can affect its accuracy and efficiency. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1, Page 189.
Which of the following is the MAIN reason for documenting the performance of controls?
Obtaining management sign-off
Demonstrating effective risk mitigation
Justifying return on investment
Providing accurate risk reporting
Answer:
Explanation:
The main reason for documenting the performance of controls is to provide accurate risk reporting. Risk reporting is a process that communicates and discloses the relevant and reliable information about the risks and their management to the stakeholders and decision makers. Risk reporting is an essential component of the risk management process, as it helps to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk identification, assessment, response, and monitoring activities, as well as to support and inform the risk governance and oversight functions. Documenting the performance of controls is a technique that records and tracks the results and outcomes of the controls that are implemented to address the risks, such as the control objectives,
As part of its risk strategy, an organization decided to transition its financial system from a cloud-based provider to an internally managed system. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
Reassess whether the risk responses properly address known risks and vulnerabilities
Analyze the risk register to identify potential updates and changes
Evaluate existing control test plans of the system for potential changes
Update the processes within impacted financial control assessments
Answer:
Explanation:
Whenever there is a change in sourcing strategy, such as moving from cloud to internal hosting, the first step is to reassess the effectiveness and completeness of existing risk responses and confirm that they still mitigate the risks appropriately.
CRISC emphasizes:
“When transitioning services or changing control environments, practitioners should reassess risk responses and validate that previously identified risks and vulnerabilities remain properly addressed.â€
Only after reassessment should the practitioner proceed to update registers, controls, and audit plans.
Hence, A is the correct answer.
CRISC Reference: Domain 3 – Risk Response and Mitigation, Topic: Managing Control Changes.
The BEST way to mitigate the high cost of retrieving electronic evidence associated with potential litigation is to implement policies and procedures for:
data classification and labeling.
data logging and monitoring.
data retention and destruction.
data mining and analytics.
Answer:
Which of the following is a responsibility of the second line in the three lines model?
Alerting operational management to emerging issues
Implementing corrective actions to address deficiencies
Owning risk scenarios and bearing the consequences of loss
Performing duties independently to provide assurance
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to ISACA CRISC guidance)
In the three lines model (formerly three lines of defense), the second line provides risk management, compliance oversight, and specialized support to the first line (operational management). One of its key responsibilities is monitoring the risk environment and alerting operational management to emerging issues—such as new regulatory requirements, changes in risk levels, and control weaknesses—while advising on appropriate responses. Implementing corrective actions is primarily the responsibility of the first line, which owns the processes. Owning risk scenarios and bearing loss consequences are first-line management responsibilities. Performing duties independently to provide assurance is the role of the third line (internal audit), which maintains organizational independence. Thus, the function of monitoring and advising, including escalation of emerging issues, aligns directly with the mandate of the second line.
Calculation of the recovery time objective (RTO) is necessary to determine the:
time required to restore files.
point of synchronization
priority of restoration.
annual loss expectancy (ALE).
Answer:
Explanation:
The recovery time objective (RTO) is a metric that defines the maximum acceptable time frame for restoring a system or service after a disruption. The RTO is determined by the business impact and requirements of the system or service, as well as the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization. The calculation of the RTO is necessary to determine the priority of restoration,which means the order and urgency of recovering the systems or services based on their criticality and dependency. The priority of restoration helps to optimize the use of resources and minimize the downtime and losses during a disaster recovery. The other options are not the correct answers, as they are not the main purpose of calculating the RTO. The time required to restore files is a factor that affects the RTO, but it is not the outcome of the RTO calculation. The point of synchronization is the point in time to which the data must be restored to ensure consistency and accuracy. The point of synchronization is related to the recovery point objective (RPO), not the RTO. The annual loss expectancy (ALE) is a measure of the expected loss peryear due to a specific risk or threat. The ALE is calculated by multiplying the single loss expectancy (SLE) by the annualized rate of occurrence (ARO). The ALE is not directly related to the RTO, although it may influence the RTO determination. References = Recovery Time Objective (RTO) - What Is It, Examples, Calculation; CRISC Review Manual, pages 197-1981; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 842
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY consideration when prioritizing limited resources needed to implement overdue corrective actions arising from a recent internal audit?
Level of risk impact
Cost-benefit analysis
Key control indicator (KCI) measures
Availability of other technical controls
Answer:
Explanation:
When allocating scarce resources for overdue audit corrective actions, risk impact is the main prioritization criterion.
CRISC guidance dictates that corrective actions should first address risks posing the greatest potential harm to the enterprise’s objectives—whether financial, reputational, operational, or compliance-related.
Supporting extract (CRISC study materials):
“Prioritization of treatment options for numerous risk scenarios will be most effective when based on the likelihood of compromise and subsequent impact.†(Slide 311).
Thus, the level of risk impact determines:
Which issues could cause the most damage if unaddressed.
Which corrective actions are most urgent.
The most effective allocation of resources for mitigation.
While cost-benefit and control indicators are valuable supplementary factors, impact severity always takes precedence in a risk-based prioritization model.
Hence, the correct answer is A. Level of risk impact.
The PRIMARY reason for tracking the status of risk mitigation plans is to ensure:
the proposed controls are implemented as scheduled.
security controls are tested prior to implementation.
compliance with corporate policies.
the risk response strategy has been decided.
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary reason for tracking the status of risk mitigation plans is to ensure that the proposed controls are implemented as scheduled, as this can help to reduce the risk exposure of the organization and to achieve the desired risk objectives. Tracking the status of risk mitigation plans can also help to monitor and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the risk controls, and to identify and address any issues or gaps that may arise during the implementation.Tracking the status of risk mitigation plans can also provide feedback and information to the risk owners and stakeholders, and enable them to adjust the risk strategy and response actions accordingly. References = CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, Question 251. CRISC Sample Questions 2024, Question 251. ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, Question 251. CRISC by Isaca Actual Free Exam Q&As, Question 9.
Which of the following BEST provides an early warning that network access of terminated employees is not being revoked in accordance with the service level agreement (SLA)?
Updating multi-factor authentication
Monitoring key access control performance indicators
Analyzing access control logs for suspicious activity
Revising the service level agreement (SLA)
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), monitoring key access control performance indicators is the best way to provide an early warning that network access of terminated employees is not being revoked in accordance with the service level agreement (SLA), as it measures the effectiveness and efficiency of the access control process and its alignment with the SLA objectives and requirements. The SLA is a contract that defines the expectations and responsibilities of the service provider and the service recipient in terms of the quality, availability, and scope of the service. Monitoring key access control performance indicators helps to:
Evaluate the extent to which the access control process has met the SLA targets and standards
Identify and report any deviations, errors, or breaches in the access control process and its compliance with the SLA
Recommend and implement corrective actions or improvement measures to address the issues or findings in the access control process
Communicate and coordinate the monitoring results and recommendations with the relevant stakeholders, such as the service provider, the service recipient, and the senior management
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 4: IT Risk Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.1: IT Risk Monitoring, pp. 217-2181
When determining which control deficiencies are most significant, which of the following would provide the MOST useful information?
Risk analysis results
Exception handling policy
Vulnerability assessment results
Benchmarking assessments
Answer:
Explanation:
A control deficiency is a weakness or flaw in the design or implementation of a control that reduces its effectiveness or efficiency in achieving its intended objective or mitigating the risk that it is designed to address. A control deficiency may be caused by various factors, such as human error, system failure, process inefficiency, resource limitation, etc.
When determining which control deficiencies are most significant, the most useful information would be the risk analysis results, which are the outcomes or outputs of the risk analysis process that measures and compares the likelihood and impact of various risk scenarios, and prioritizes them based on their significance and urgency. The risk analysis results can help to determine which control deficiencies are most significant by providing the following information:
The level and priority of the risks that are associated with the control deficiencies, and the potential consequences or impacts that they may cause for the organization if they materialize.
The gap or difference between the current and desired level of risk, and the extent or degree to which the control deficiencies contribute to or affect the gap or difference.
The cost-benefit or feasibility analysis of the possible actions or plans to address or correct the control deficiencies, and the expected or desired outcomes or benefits that they may provide for the organization.
The other options are not the most useful information when determining which control deficiencies are most significant, because they do not provide the same level of detail and insight that the risk analysis results provide, and they may not be relevant or actionable for the organization.
An exception handling policy is a policy that defines and describes the procedures and guidelines for dealing with the situations or circumstances that deviate from the normal or expected operation or functionality of a control, and that may require special or alternative actions or measures to address or resolve them. An exception handling policy can provide useful information on how to handle or manage the control deficiencies, but it is not the most usefulinformation when determining which control deficiencies are most significant, because it does not indicate the level and priority of the risks that are associated with the control deficiencies, and the potential consequences or impacts that they may cause for the organization.
A vulnerability assessment is an assessment that identifies and evaluates the weaknesses or flaws in the organization’s assets, processes, or systems that can be exploited or compromised by the threats or sources of harm that may affect the organization’s objectives or operations. A vulnerability assessment can provide useful information on the existence and severity of the control deficiencies, but it is not the most useful information when determining which control deficiencies are most significant, because it does not indicate the likelihood and impact of the risk scenarios that are associated with the control deficiencies, and the potential consequences or impacts that they may cause for the organization.
A benchmarking assessment is an assessment that compares and contrasts the organization’s performance, practices, or processes with those of other organizations or industry standards, and identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, or threats that may affect the organization’s objectives or operations. A benchmarking assessment can provide useful information on the best practices or improvement areas for the organization, but it is not the most useful information when determining which control deficiencies are most significant, because it does not indicate the level and priority of the risks that are associatedwith the control deficiencies, and the potential consequences or impacts that they may cause for the organization. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 176
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Which of the following is the BEST indicator of the effectiveness of IT risk management processes?
Percentage of business users completing risk training
Percentage of high-risk scenarios for which risk action plans have been developed
Number of key risk indicators (KRIs) defined
Time between when IT risk scenarios are identified and the enterprise's response
Answer:
Explanation:
 IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risks related to the use of information technology (IT) in the organization. IT risk management aims to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT resources and information, and to support the IT governance and strategy of the organization1.
The best indicator of the effectiveness of IT risk management processes is the time between when IT risk scenarios are identified and the enterprise’s response. This indicator can help to measure how quickly and efficiently the organization can detect and respond to the IT risks, and how well the organization can prevent or minimize the negative impacts of the IT risks. The time between when IT risk scenarios are identified and the enterprise’s response can include:
The time taken to identify and report the IT risk scenarios, using various methods and sources, such as risk assessments, audits, monitoring, alerts, or incidents
The time taken to analyze and evaluate the IT risk scenarios, using various tools and techniques, such as risk matrices, risk registers, risk indicators, or risk models
The time taken to select and implement the IT risk responses, using various strategies and controls, such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance
The time taken to review and improve the IT risk management processes, using various feedback and learning mechanisms, such as lessons learned, best practices, or benchmarks23
The other options are not the best indicators of the effectiveness of IT risk management processes, but rather some of the inputs or outputs of IT risk management processes. Percentage of business users completing risk training is an indicator of the awareness and competence of the IT users and providers, which can affect the IT risk management performance, but it does not measure the IT risk management processes directly. Percentage of high-risk scenarios for which risk action plans have been developed is an indicator of the completeness and coverage of the IT risk management activities, which can affect the IT risk management outcomes, but it does not measure the IT risk management processes directly. Number of key risk indicators (KRIs) defined is an indicator of the scope and complexity of the IT risk management objectives, whichcan affect the IT risk management resources and capabilities, but it does not measure the IT risk management processes directly. References =
IT Risk Management - ISACA
Risk Management Process - ISACA
Risk Response - ISACA
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of the following controls would BEST reduce the risk of account compromise?
Enforce password changes.
Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Enforce role-based authentication.
Enforce password encryption.
Answer:
Explanation:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)significantly reduces the risk of account compromise by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code, enhancing security beyond single-factor authentication methods.
One of an organization's key IT systems cannot be patched because the patches interfere with critical business application functionalities. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner's BEST recommendation?
Additional mitigating controls should be identified.
The system should not be used until the application is changed
The organization's IT risk appetite should be adjusted.
The associated IT risk should be accepted by management.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s best recommendation when one of an organization’s key IT systems cannot be patched because the patches interfere with critical business application functionalities is to identify additional mitigating controls, as they may reduce the likelihood or impact of the vulnerabilities being exploited, and align the residual risk with the risk tolerance and appetite of the organization. The other options are not the best recommendations, as they may not address the risk adequately, or may introduce unacceptable consequences, such as disrupting the businessoperations, changing the risk strategy, or accepting excessive risk. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 111.
Which of the following risk management practices BEST facilitates the incorporation of IT risk scenarios into the enterprise-wide risk register?
Key risk indicators (KRls) are developed for key IT risk scenarios
IT risk scenarios are assessed by the enterprise risk management team
Risk appetites for IT risk scenarios are approved by key business stakeholders.
IT risk scenarios are developed in the context of organizational objectives.
Answer:
Explanation:
 IT risk scenarios are hypothetical situations that describe how IT-related events or incidents could adversely affect an organization’s objectives, assets, or operations. IT risk scenarios can help to identify, analyze, and prioritize IT risks, and to develop appropriate responses and controls1.
An enterprise-wide risk register is a document that records and tracks the significant risks that an organization faces across its various functions, processes, and activities. An enterprise-wide risk register can help to provide a comprehensive and consistent view of the organization’s risk profile, and to support the decision making and reporting of the risk management function2.
The best practice that facilitates the incorporation of IT risk scenarios into the enterprise-wide risk register is to develop IT risk scenarios in the context of organizational objectives. This means that IT risk scenarios should be aligned with and derived from the organization’s strategic goals, mission, vision, and values. IT risk scenarios should also consider the interdependenciesand interactions between IT and other business domains, and the potential impact of IT risks on the organization’s performance and reputation3.
By developing IT risk scenarios in the context of organizational objectives, the organization can ensure that the IT risk scenarios are relevant, realistic, and meaningful for the enterprise-wide risk management. The organization can also ensure that the IT risk scenarios are consistent and comparable with other types of risk scenarios, such as financial, operational, or reputational risk scenarios. This can facilitate the integration and consolidation of IT risk scenarios into the enterprise-wide risk register, and enable a holistic and balanced assessment and reporting of the organization’s risks4.
The other options are not as effective as developing IT risk scenarios in the context of organizational objectives for incorporating IT risk scenarios into the enterprise-wide risk register. Developing key risk indicators (KRIs) for key IT risk scenarios can help to monitor and measure the IT risk exposure and performance, but it does not ensure that the IT risk scenarios are aligned with the organizational objectives or integrated with other risk scenarios. Assessing IT risk scenarios by the enterprise risk management team can help to validate and prioritize the IT risk scenarios, but it does not ensure that the IT risk scenarios are derived from the organizational objectives or consistent with other risk scenarios. Approving risk appetites for IT risk scenarios by key business stakeholders can help to establish the acceptable level of IT risk taking andtolerance, but it does not ensure that the IT risk scenarios are based on the organizational objectives or comparable with other risk scenarios. References =
IT Risk Scenario Development - ISACA
Risk Register - ISACA
Identifying Risks and Scenarios Threatening the Organization as an Enterprise - A New Enterprise Risk Identification Framework
Risk Register 2021-2022 - UNECE
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of the following will BEST ensure that controls adequately support business goals and objectives?
Using the risk management process
Enforcing strict disciplinary procedures in case of noncompliance
Reviewing results of the annual company external audit
Adopting internationally accepted controls
Answer:
Explanation:
Using the risk management process will best ensure that controls adequately support business goals and objectives, as it involves identifying, assessing, responding, and monitoring the risks that may affect the achievement of the business goals and objectives, and designing and implementing controls to mitigate those risks. Enforcing strict disciplinary procedures in case of noncompliance, reviewing results of the annual company external audit, and adopting internationally accepted controls are also good practices, but they are not the best, as they do not necessarily align the controls with the business goals and objectives. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 146.
Which of the following is the MOST important requirement when implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) system?
Identifying users who have access
Selecting an encryption solution
Defining the data retention period
Determining the value of data
Answer:
Explanation:
Determining the value of data is essential when implementing a DLP system. Understanding data value helps prioritize protection efforts, allocate resources effectively, and ensure that critical information assets are adequately safeguarded against loss or unauthorized access.
Risk acceptance of an exception to a security control would MOST likely be justified when:
automation cannot be applied to the control
business benefits exceed the loss exposure.
the end-user license agreement has expired.
the control is difficult to enforce in practice.
Answer:
Explanation:
The most likely justification for risk acceptance of an exception to a security control is when the business benefits exceed the loss exposure. Risk acceptance is a risk response strategy that involves acknowledging and tolerating the risk, without taking any action to reduce or transfer the risk. An exception to a security control is a deviation or non-compliance from the established security policy or standard, due to a valid business reason or circumstance. Risk acceptance of an exception to a security control may be justified when the business benefits exceed the loss exposure, which means that the value or advantage of the exception outweighs the potential cost or harm of the risk. For example, an exception to a security control may enable faster or easier access to the system or data, which may improve the productivity, efficiency, or satisfaction of the users or customers, and generate more revenue or profit for the business. The business benefits of the exception may exceed the loss exposure of the risk, which may be low or negligible, or may be mitigated by other controls or factors. Therefore, risk acceptance of an exception to a security control may be a reasonable and rational decision, based on the cost-benefit analysis of the exception and the risk. Automation cannot be applied to the control, the end-user license agreement has expired, and the control is difficult to enforce in practice are not the most likely justifications for risk acceptance of an exception to a security control, as they are either irrelevant or insufficient reasons, and they do not consider the business benefits or the loss exposure of the exception and the risk. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 50.
Which of the following is the MOST important objective of establishing an enterprise risk management (ERM) function within an organization?
To have a unified approach to risk management across the organization
To have a standard risk management process for complying with regulations
To optimize risk management resources across the organization
To ensure risk profiles are presented in a consistent format within the organization
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important objective of establishing an enterprise risk management (ERM) function within an organization is to have a unified approach to risk management across the organization. An ERM function is a centralized and coordinated function that oversees and supports the risk management activities of the organization, such as risk identification, assessment, response, monitoring, and reporting. An ERM function helps to ensure that the risk management process is consistent, comprehensive, and integrated with the organization’s strategy, objectives, and culture. An ERM function also helps to align the risk management activities with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance, and to provide a holistic view of the organization’s risk profile and exposure. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, Section 1.1.1, page 131
Which of the following is MOST helpful to facilitate the decision of recovery priorities in a disaster situation?
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs)
Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
Risk Scenario Analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
A BIA identifies critical processes and interdependencies, enabling prioritization of recovery efforts based on business impact.
When reviewing the business continuity plan (BCP) of an online sales order system, a risk practitioner notices that the recovery time objective (RTO) has a shorter lime than what is defined in the disaster recovery plan (DRP). Which of the following is the BEST way for the risk practitioner to address this concern?
Adopt the RTO defined in the BCR
Update the risk register to reflect the discrepancy.
Adopt the RTO defined in the DRP.
Communicate the discrepancy to the DR manager for follow-up.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A recovery time objective (RTO) is the maximum acceptable time that a business process or function can be disrupted or unavailable before it causes significant damage or loss to the organization. A business continuity plan (BCP) is a document that describes how the organization will resume its critical business operations in the event of a disaster or disruption. A disaster recovery plan (DRP) is a document that describes how the organization will restore its IT systems and infrastructure in the event of a disaster or disruption. The RTO defined in the BCP and the DRP should be consistent and aligned, as they both support the continuity and recovery of the business. If the RTO defined in the BCP is shorter than the RTO defined in the DRP, it means that the BCP expects the business process or function to be restored faster than the DRP can provide. This can create a gap or a conflict between the BCP and the DRP, and can compromise the effectiveness and efficiency of the continuity and recovery efforts. Therefore, the best way for the risk practitioner to address this concern is to communicate the discrepancy to the DR manager for follow-up, meaning that the risk practitioner should report the issue and its implications to the DR manager, who is responsible for developing and maintaining the DRP. The DR manager should review the discrepancy and determine whether it is justified or not, and whether it requires any adjustment or alignment of the RTOs in the BCP and the DRP. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.4.2, p. 206-207
When developing risk treatment alternatives for a Business case, it is MOST helpful to show risk reduction based on:
cost-benefit analysis.
risk appetite.
regulatory guidelines
control efficiency
Answer:
Explanation:
 Cost-benefit analysis is the most helpful tool to show risk reduction based on when developing risk treatment alternatives for a business case, because it compares the expected costs and benefits of each alternative and helps to select the most optimal and feasible one. Cost-benefit analysis also helps to justify the investment and resources required for the risk treatment plan and to demonstrate the value and return of the risk reduction. The other options are not the most helpful tools, although they may also be considered when developing risk treatment alternatives. Risk appetite, regulatory guidelines, and control efficiency are examples of factors or criteria that influence the selection of risk treatment alternatives, but they do not show the risk reduction based on the alternatives. References = CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions
An effective control environment is BEST indicated by controls that:
minimize senior management's risk tolerance.
manage risk within the organization's risk appetite.
reduce the thresholds of key risk indicators (KRIs).
are cost-effective to implement
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), an effective control environment is best indicated by controls that manage risk within the organization’s risk appetite, as this reflects the alignment of thecontrol objectives and activities with the organization’s strategic goals and risk preferences. The risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Managing risk within the organization’s risk appetite helps to:
Balance the potential benefits and costs of risk-taking and risk response
Optimize the use of the organization’s resources and capabilities
Enhance the value and performance of the organization
Foster a risk-aware culture that supports the organization’s vision and mission
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.3: IT Risk Assessment Process, pp. 93-941
Which of the following is MOST helpful in determining the effectiveness of an organization's IT risk mitigation efforts?
Assigning identification dates for risk scenarios in the risk register
Updating impact assessments for risk scenario
Verifying whether risk action plans have been completed
Reviewing key risk indicators (KRIS)
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that provide information about the level of exposure to a specific risk or a group of risks.
Reviewing KRIs is the most helpful way to determine the effectiveness of an organization’s IT risk mitigation efforts. This means that the organization monitors and evaluates the actual results and outcomes of the risk responses, compares them with the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization, identifies any deviations or breaches that may require attention or action, and reports them to the appropriate parties for decision making or improvement actions.
The other options are not the most helpful ways to determine the effectiveness of an organization’s IT risk mitigation efforts. They are either secondary or not essential for risk management.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 15
Information Technology & Security, page 9
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 7
The BEST way to improve a risk register is to ensure the register:
is updated based upon significant events.
documents possible countermeasures.
contains the risk assessment completion date.
is regularly audited.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk register is a tool that records and tracks the identified risks, their causes, impacts, probabilities, responses, and owners. It is a living document that should be updated regularly to reflect the changes in therisk environment and the status of the risk responses12. The best way to improve a risk register is to ensure that it is updated based upon significant events, such as:
New risks are identified or existing risks are eliminated
Risk probabilities or impacts change due to internal or external factors
Risk responses are implemented or modified
Risk owners or stakeholders change
Risk incidents or issues occur
Risk thresholds or appetite change
Risk reporting or communication requirements change
Updating the risk register based upon significant events can help to:
Maintain the accuracy and relevance of the risk information
Enhance the risk awareness and accountability of the risk owners and stakeholders
Support the risk monitoring and reporting activities
Facilitate the risk evaluation and decision-making processes
Improve the risk management performance and maturity
References =
Risk Register - Project Management Knowledge
How to Create a Risk Register: A Step-by-Step Guide - ProjectManager.com
An organization's business gap analysis reveals the need for a robust IT risk strategy. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner's PRIMARY consideration when participating in development of the new strategy?
Scale of technology
Risk indicators
Risk culture
Proposed risk budget
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s primary consideration when participating in development of a new IT risk strategy should be the risk culture of the organization. Risk culture is the set of values, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors that shape how the organization perceives, manages, and responds to risks. Risk culture influences the organization’s risk appetite, risk objectives, risk policies, risk processes, and risk performance. The risk practitioner should consider the risk culture whendeveloping a new IT risk strategy, because it helps to align the IT risk strategy with the organization’s mission, vision, values, and strategy, and to ensure that the IT risk strategy is supported and accepted by the organization’s stakeholders, such as the board, management, employees, customers, regulators, etc. The risk practitioner should also consider the risk culture when developing a new IT risk strategy, because it helps to identify and addressany gaps, issues, or challenges that may affect the implementation and effectiveness of the IT risk strategy, such as lack of awareness, communication, coordination, or accountability. The other options are not the primary consideration for the risk practitioner, although they may be related to the IT risk strategy. Scale of technology, risk indicators, and proposed risk budget are all factors that could affect the feasibility and sustainability of the IT risk strategy, but they do not necessarily reflector influence the organization’s risk culture. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.2.1, page 1-9.
During testing, a risk practitioner finds the IT department's recovery time objective (RTO) for a key system does not align with the enterprise's business continuity plan (BCP). Which of the following should be done NEXT?
Report the gap to senior management
Consult with the IT department to update the RTO
Complete a risk exception form.
Consult with the business owner to update the BCP
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the next course of action when a risk practitioner finds the IT department’s recovery time objective (RTO) for a key system does not align with the enterprise’s business continuity plan (BCP) is to consult with the IT department to update the RTO. The RTO is the maximum acceptable time that an application, computer, network, or system can be down after an unexpected disaster, failure, or comparable event takes place. The RTO should be aligned with the BCP, which is a set of policies, procedures, and resources that enable the organization to continue or resume its critical business functions in the event of a disruption. Consulting with the IT department to update the RTO helps to:
Ensure that the RTO reflects the current business requirements and expectations for the availability and recovery of the key system
Evaluate the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of achieving the RTO with the existing IT resources and capabilities
Identify and implement the necessary changes or improvements in the IT infrastructure, processes, and controls to meet the RTO
Test and validate the RTO and the IT recovery procedures and verify their compatibility and consistency with the BCP
Communicate and coordinate the RTO and the IT recovery plan with the relevant stakeholders, such as the business owner, the risk owner, and the senior management
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: Risk Response Options, pp. 174-1751
The MOST important reason to monitor key risk indicators (KRIs) is to help management:
identity early risk transfer strategies.
lessen the impact of realized risk.
analyze the chain of risk events.
identify the root cause of risk events.
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics used by organizations to monitor and assess potential risks that may impact their objectives and performance. KRIs also provide early warning signals that help organizations identify, analyze, and address risks before they escalate into significant issues1. The most importantreason to monitor KRIs is to help management lessen the impact of realized risk, which is the actual or expected negative consequence of a risk event2. By monitoring KRIs, management can gain insight into the current and emerging risk exposures and trends, and evaluate their alignment with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance3. This enables management to make informed and timely decisions and actions to mitigate or eliminate the risks, and to allocate resources and prioritize efforts where they are most needed. By lessening the impact of realized risk, management can also protect and enhance the organization’s reputation, performance, and value. Identifying early risk transfer strategies, analyzing the chain of risk events, and identifying the root cause of risk events are not the most important reasons to monitor KRIs, as they do not provide the same level of benefit and value as lessening the impact of realized risk. Identifying early risk transfer strategies is a process that involves finding and implementing ways to shift or share the risk or its impact to another party, such as through insurance, outsourcing, or hedging4. Identifying early risk transfer strategies can help to reduce the organization’s risk exposure and liability, but it does not necessarily lessen the impact of realized risk, as the risk or its impact may still occur or affect the organization indirectly. Analyzing the chain of risk events is a process that involves tracing and understanding the sequence and interconnection of the risk events that lead to a specific outcome or consequence5. Analyzing the chain of risk events can help to identify and address the root causes and contributing factors of the risk events, but it does not necessarily lessen the impact of realized risk, as the outcome or consequence may have already occurred or be unavoidable. Identifying the root cause of risk events is a process that involves finding and determining the underlying or fundamental source or reason of the risk events. Identifying the root cause of risk events can help to prevent or correct the recurrence or escalation of the risk events, but it does not necessarily lessen the impact of realized risk, as the impact may have already happened or be irreversible. References = 1: Key Risk Indicators: A Practical Guide | SafetyCulture2: Risk Impact - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics3: KRI Framework for Operational Risk Management | Workiva4: Risk Transfer - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics5: EventChainMethodology - Wikipedia : [Root Cause Analysis - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.1: Key Risk Indicators, pp. 181-185.]
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY consideration when assessing the risk of using Internet of Things (loT) devices to collect and process personally identifiable information (PII)?
Business strategies and needs
Security features and support
Costs and benefits
Local laws and regulations
Answer:
Explanation:
Local laws and regulations should be the primary consideration when assessing the risk of using IoT devices to collect and process PII, because they define the legal obligations and liabilities of the organization and the individuals involved. Non-compliance with local laws and regulations can result in fines, lawsuits, reputational damage, and loss of trust. Therefore, it is essential to understand and adhere to the applicable laws and regulations in the jurisdictions where the IoT devices operate and where the PII is stored, processed, and transferred.
References
•Considerations for Managing Internet of Things (IoT) Cybersecurity and Privacy Risks
•The Internet of Things (IoT) and Digitally Stored PII: Avoidable or Inevitable?
•Security Issues in IoT: Challenges and Countermeasures
Which of the following data would be used when performing a business impact analysis (BIA)?
Cost-benefit analysis of running the current business
Cost of regulatory compliance
Projected impact of current business on future business
Expected costs for recovering the business
Answer:
Explanation:
A business impact analysis (BIA) is a process that identifies and assesses the effects that accidents, emergencies, disasters, and other unplanned, negative events could have on a business. The BIA (sometimes also called business impact assessment) predicts how a business will be affected by everything from a hurricane to a labor strike1.
One of the data that would be used when performing a BIA is the expected costs for recovering the business. This data can help to estimate the amount of resources and funds that would be needed to restore the normal operations and functions of the business after a disruption. The expected costs for recovering the business can include:
The costs of repairing or replacing damaged or lost assets, such as equipment, inventory, or facilities
The costs of hiring or training additional staff, or outsourcing some tasks or services
The costs of implementing alternative or backup systems or processes, such as cloud computing or manual procedures
The costs of communicating and coordinating with customers, suppliers, partners, regulators, and other stakeholders
The costs of complying with legal or contractual obligations, or paying fines or penalties
The costs of mitigating or preventing further losses or damages, such as insurance premiums or security measures23
The expected costs for recovering the business can help to determine the priority and urgency of the recovery activities, and to allocate the available resources and funds accordingly. The expected costs for recovering the business can also help to evaluate the cost-effectiveness and feasibility of the recovery strategies and options, and to justify the investment in the business continuity planning and management4.
The other options are not the data that would be used when performing a BIA, but rather the data that would be used for other purposes or processes. A cost-benefit analysis of running the current business is a data that would be used to compare the advantages and disadvantages of different business decisions or alternatives, such as launching a new product or service, or expanding to a new market. A cost-benefit analysis can help to assess the profitability and viability of the current business, but it does not measure the impact of a disruption on the business5. A cost of regulatory compliance is a data that would be used toestimate the amount of resources and funds that would be required to meet the rules and standards set by the authorities or agencies that govern the business, such as laws, regulations, or policies. A cost of regulatory compliance can help to ensure the legality and accountability of the business, but it does not measure the impactof a disruption on the business. A projected impact of current business on future business is a data that would be used to forecast the potential outcomes and consequences of the current business activities or strategies on the future business performance and growth, such as sales, revenue, market share, or customer satisfaction. A projected impact of current business on future business can help to plan and optimize the future business, but it does not measure the impact of a disruption on the current business. References =
Business Impact Analysis | Ready.gov
Business Impact Analysis Toolkit | Smartsheet
Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Prepare for Anything [2023] • Asana
How To Conduct Business Impact Analysis in 8 Easy Steps - G2
Cost Benefit Analysis - ISACA
[Regulatory Compliance - ISACA]
[Impact Analysis - ISACA]
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of the following BEST enables a risk practitioner to understand management's approach to organizational risk?
Organizational structure and job descriptions
Risk appetite and risk tolerance
Industry best practices for risk management
Prior year's risk assessment results
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to enable a risk practitioner to understand management’s approach to organizational risk is to know the risk appetite and risk tolerance of the organization. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to pursue, retain, or take in order to achieve its objectives. Risk tolerance is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in relation to specific performance measures, such as availability, reliability, or security. Risk appetite and risk tolerance reflect the management’s attitude, preferences, and expectations towards risk, and guide the risk management process, such as risk identification, assessment, response, and monitoring. The other options are not as effective as knowing the risk appetite and risk tolerance, although they may provide some input or context for understanding the management’s approach to organizational risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.2.1, page 1-8.
An organization is conducting a review of emerging risk. Which of the following is the BEST input for this exercise?
Audit reports
Industry benchmarks
Financial forecasts
Annual threat reports
Answer:
Explanation:
The best input for conducting a review of emerging risk is the annual threat reports. Emerging risk is the risk that arises from new or evolving sources, or from existing sources that have not been previously considered or recognized. Emerging risk may have significant impact on the organization’s objectives, strategies, operations, or reputation, and may require new or different risk responses. Annual threat reports are the reports that provide information and analysis on the current and future trends, developments, and challenges in the threat landscape, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, geopolitical conflicts, or pandemics. Annual threat reports can help to identify and assess the emerging risk, as they can provide insights into the sources, drivers, indicators, and scenarios of the emerging risk, as well as the potential impact and likelihood of the emerging risk. Annual threat reports can also help to benchmark and compare the organization’s risk exposure and preparedness with the industry and the peers, and to prioritize and respond to the emerging risk. Audit reports, industry benchmarks, and financial forecasts are not as useful as annual threat reports, as they do not focus on the emerging risk, and may not capture the latest or future changes in the threat landscape. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 50.
Which of the following will BEST mitigate the risk associated with IT and business misalignment?
Establishing business key performance indicators (KPIs)
Introducing an established framework for IT architecture
Establishing key risk indicators (KRIs)
Involving the business process owner in IT strategy
Answer:
Explanation:
IT and business misalignment is the risk that the IT objectives, plans, and activities are not aligned with the business goals, needs, and expectations. This can result in wasted resources, missed opportunities, poor performance, and customer dissatisfaction. One of the best ways to mitigate this risk is to involve the business process owner in IT strategy. The business process owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for a specific business process and its outcomes. By involving the business process owner in IT strategy, the organization can ensure that the IT initiatives and solutions are relevant, effective, and beneficial for the business process and its stakeholders. The business process owner can also provide valuable input, feedback, and support for the IT strategy and its implementation. The other options are not the best ways to mitigate the risk associated with IT and business misalignment, although they may be helpful and complementary. Establishing business key performance indicators (KPIs) is a technique to measure and monitor the achievement of business objectives and outcomes. However, KPIs do not necessarily ensure that the IT strategy is aligned with the business strategy or that the IT activities support the business activities. Introducing an established framework for IT architecture is a method to design and implement the IT infrastructure, systems, and services in a consistent and coherent manner. However, an IT architecture framework does not guarantee that the IT architecture is aligned with the business architecture or that the IT capabilities meet the business requirements. Establishing key risk indicators (KRIs) is a tool to monitor and communicate the level of exposure to a given risk or the potential impact of a risk. However, KRIs do not directly address the risk of IT and business misalignment or the actions needed to align them. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 22-231; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 76
Which of the following is the MOST important information to cover in a business continuity awareness training program for all employees of the organization?
Recovery time objectives (RTOs)
Communication plan
Critical asset inventory
Separation of duties
Answer:
A risk practitioner notices a trend of noncompliance with an IT-related control. Which of the following would BEST assist in making a recommendation to management?
Assessing the degree to which the control hinders business objectives
Reviewing the IT policy with the risk owner
Reviewing the roles and responsibilities of control process owners
Assessing noncompliance with control best practices
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk practitioner notices a trend of noncompliance with an IT-related control. This indicates that there is a risk of ineffective or inefficient implementation or operation of the control, which may expose the organization to potential threats or losses.
The best way to assist in making a recommendation to management is to assess the degree to which the control hinders business objectives. This means that the risk practitioner should analyze the impact of the control on the performance, productivity, quality, or customer satisfaction of the business processes or functions that are affected by the control.
Assessing the degree to which the control hinders business objectives helps to identify the root causes of noncompliance, the costs and benefits of compliance, and the potential alternatives or improvements for the control. It also helps to communicate the value and importance of the control to the management and the stakeholders, and to obtain their support and commitment for the control compliance.
The other options are not the best ways to assist in making a recommendation to management. They are either secondary or not essential for control compliance.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 19
Information Technology & Security, page 13
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 11
Which of the following is the MOST effective control to ensure user access is maintained on a least-privilege basis?
User authorization
User recertification
Change log review
Access log monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
User recertification is the most effective control to ensure user access is maintained on a least-privilege basis, as it involves a periodic review and validation of user access rights and privileges by the appropriate authority. User recertification helps to identify and remove any unnecessary, excessive, or obsolete access rights and privileges that may pose a security risk or violate the principle of least privilege. User recertification also helps to ensure that user access rights and privileges are aligned with the current business needs, roles, and responsibilities of the users.
The other options are not the most effective controls to ensure user access is maintained on a least-privilege basis. User authorization is the process of granting or denying access rights and privileges to users based on their identity, role, and credentials, but it does not verify or update the existing access rights and privileges of the users. Change log review is the process of examining and analyzing the records of changes made to the system, configuration, or data, but it does not directly address the user access rights and privileges. Access log monitoring is the process of tracking and auditing the user activities and actions on the system or network, but it does not validate or modify the user access rights and privileges. References = What Is the Principle of Least Privilege and Why is it Important?, Principle of Least Privilege: Definition, Methods & Examples, IT Risk Resources | ISACA
Which of the following is MOST important to include when reporting the effectiveness of risk management to senior management?
Changes in the organization's risk appetite and risk tolerance levels
Impact due to changes in external and internal risk factors
Changes in residual risk levels against acceptable levels
Gaps in best practices and implemented controls across the industry
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most important information to include when reporting the effectiveness of risk management to senior management is the changes in residual risk levels against acceptable levels, as it indicates how well the risk management process and activities have reduced the risk exposure and impact to the level that is aligned with the risk tolerance and appetite of the organization. The other options are not the most important information, as they are more related to thedrivers,factors, or outcomes of risk management, respectively, rather than the effectiveness or value of risk management. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 109.
Which of the following criteria for assigning owners to IT risk scenarios provides the GREATEST benefit to an organization?
The risk owner understands the effect of loss events on business operations.
The risk owner is a member of senior leadership in the IT organization.
The risk owner has strong technical aptitude across multiple business systems.
The risk owner has extensive risk management experience.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk owner should be someone who has the authority, responsibility, and knowledge to manage the risk effectively and align it with the organizational strategy and objectives. The risk owner should also be able to communicate the impact of the risk on the business operations and the value proposition of the risk response. Understanding the effect of loss events on business operations is a key criterion for assigning risk owners, as it helps to prioritize and mitigate the risks that matter most to the organization.
References
•Why Assigning a Risk Owner is Important and How to Do It Right
•How to Write Strong Risk Scenarios and Statements - ISACA
•What Everybody Ought To Know About Project Risk Owners
The BEST way for an organization to ensure that servers are compliant to security policy is
to review:
change logs.
configuration settings.
server access logs.
anti-malware compliance.
Answer:
Explanation:
Reviewing configuration settings is the best way for an organization to ensure that servers are compliant to security policy, because it helps to check and verify that the servers are configured and maintained according to the established security standards and guidelines, and that any deviations or violations are identified and corrected. A configuration setting is a parameter or option that defines the behavior or functionality of a server, such as a system, an application, or aservice. A security policy is a document that outlines the security objectives, principles, and rules that the organization and its employees must follow, and the consequences of non-compliance. Reviewing configuration settings is the best way, as it helps to ensure that the servers are secure and compliant, and that any security risks or issues are detected and resolved. Reviewing change logs, server access logs, and anti-malware compliance are all possible ways to ensure that servers are compliant to security policy, but they are not the best way, as they do not provide a comprehensive and consistent view of the configuration settings and their compliance status. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5, Section 5.3.2, page 200
Which of the following is the PRIMARY concern for a risk practitioner regarding an organization's adoption of innovative big data analytics capabilities?
It may be expensive to maintain a data lake.
It may be difficult to find experts who can develop analytical queries.
There may be a lack of documented processes for big data analysis.
Analytics methods may identify someone who was previously de-identified.
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary concern for a risk practitioner in adopting innovative big data analytics is the potential re-identification of individuals from previously anonymized data. Advanced analytics techniques can inadvertently combine datasets in ways that reveal personal identities, leading to privacy breaches and regulatory non-compliance. This risk is heightened when data from multiple sources are aggregated, increasing the chance of re-identification.
An organization delegates its data processing to the internal IT team to manage information through its applications. Which of the following is the role of the internal IT team in this situation?
Data controllers
Data processors
Data custodians
Data owners
Answer:
Explanation:
Data processing is the activity of collecting, organizing, transforming, and analyzing data to produce useful information for decision making or other purposes12.
The role of the internal IT team in this situation is data processors, which are the people or entities that process data on behalf of the data controllers, who are the people or entities that determine the purposes and means of the data processing34.
Data processors are the role of the internal IT team because they are responsible for managing information through the applications that are used by the organization, and they act under the instructions and authority of the organization, which is the data controller34.
Data processors are also the role of the internal IT team because they have to comply with the data protection laws and regulations that apply to the data processing, and they have to ensure the security and confidentiality of the data34.
The other options are not the role of the internal IT team, but rather possible roles or terms that are related to data processing. For example:
Data custodians are the people or entities that have physical or logical control over the data, and they are responsible for implementing and maintaining the technical and administrative safeguards to protect the data56. However, this role is not the role of theinternal IT team because it is a subset or function of the data processor role, and it does not reflect the full scope of the data processing activities that the internal IT team performs56.
Data owners are the people or entities that have legal rights or authority over the data, and they are responsible for defining and enforcing the policies and rules for the data access, use, and quality . However, this role is not the role of the internal IT team because it is a different or separate role from the data processor role, and it does not reflect the relationship or agreement between the organization and the internal IT team . References =
1: Data Processing - Wikipedia1
2: Data Processing: Definition, Steps, and Types2
3: Data Controller vs Data Processor: What’s the Difference?3
4: Data controller vs data processor: What are the differences and responsibilities?4
5: Data Custodian - Wikipedia5
6: Data Custodian: Definition, Role & Responsibilities6
Data Owner - Wikipedia
Data Owner: Definition, Role & Responsibilities
Which of the following is the MAIN reason for analyzing risk scenarios?
Identifying additional risk scenarios
Updating the heat map
Assessing loss expectancy
Establishing a risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, the main reason for analyzing risk scenarios is to identify additional risk scenarios that may not have been considered in the initial risk identification process. Risk scenarios are hypothetical situations that describe how, where, and why adverse events can occur. By analyzing risk scenarios, the risk manager can gain a better understanding of the relationships between assets, processes, threats, vulnerabilities, and other factors that may affect the organization’s objectives. Analyzing risk scenarios can also help to evaluate the likelihood and impact of the potential risks, as well as the effectiveness of the existing controls and the need for additional controls. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.2.1, Page 215. How to write good risk scenarios and statements
Effective risk communication BEST benefits an organization by:
helping personnel make better-informed decisions
assisting the development of a risk register.
improving the effectiveness of IT controls.
increasing participation in the risk assessment process.
Answer:
Explanation:
Effective risk communication best benefits an organization by helping personnel make better-informed decisions. Risk communication is the process of exchanging information and opinions among stakeholders about the nature, magnitude, significance, or control of a risk. By communicating risk information clearly and consistently, the organization can enhance the understanding and awareness of the risk, and enable the personnel to make decisions that are aligned with the risk appetite and objectives of the organization. Assisting the development of a risk register, improving the effectiveness of IT controls, and increasing participation in the risk assessment process are other possible benefits, but they are not as important as helping personnel make better-informed decisions. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 12; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 215.
Which of the following activities should be performed FIRST when establishing IT risk management processes?
Collect data of past incidents and lessons learned.
Conduct a high-level risk assessment based on the nature of business.
Identify the risk appetite of the organization.
Assess the goals and culture of the organization.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the Guide to Implementing an IT Risk Management Framework, the first activity that should be performed when establishing IT risk management processes is to assess the goals and culture of the organization. This is because the goals and culture of the organization define the context and scope of the IT risk management process, and influence the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization. By assessing the goals and culture of the organization, the IT risk manager can align the IT risk management process with the organization’s strategy, vision, mission, values, and objectives. The IT risk manager can also identify the key stakeholders, roles, and responsibilities involved in the IT risk management process, and ensure that they have the necessary skills, knowledge, and resources to perform their tasks effectively. Additionally, the IT risk manager can establish the communication and reporting mechanisms for the IT risk management process, and ensure that they are consistent with the organization’s culture and expectations. References = Guide to Implementing an IT Risk Management Framework, An Overview of the Risk Management Process
After migrating a key financial system to a new provider, it was discovered that a developer could gain access to the production environment. Which of the following is the BEST way to mitigate the risk in this situation?
Escalate the issue to the service provider.
Re-certify the application access controls.
Remove the developer's access.
Review the results of pre-migration testing.
Answer:
Explanation:
After migrating a key financial system to a new provider, it was discovered that a developer could gain access to the production environment. This indicates that there is a risk of unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction of sensitive data, such as financial records, transactions, reports, etc.
A control that could mitigate this risk is to remove the developer’s access to the production environment. This means that the developer would not be able to alter the source code or configuration of the financial system without proper authorization or approval.
The other options are not the best ways to mitigate the risk in this situation. They are either irrelevant or less effective than removing the developer’s access.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 14
Information Technology & Security, page 8
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 6
An insurance company handling sensitive and personal information from its customers receives a large volume of telephone requests and electronic communications daily. Which of the following
is MOST important to include in a risk awareness training session for the customer service department?
Archiving sensitive information
Understanding the incident management process
Identifying social engineering attacks
Understanding the importance of using a secure password
Answer:
Explanation:
Social engineering attacks are attempts to manipulate or deceive people into revealing confidential or personal information, such as passwords, account numbers, or security codes. Customer service representatives are often targeted by social engineering attacks, as they have access to sensitive customer data and may be pressured to provide quick and satisfactory service. Therefore, it is most important to include in a risk awareness training session for the customer service department how to identify and prevent social engineering attacks, such as phishing, vishing, baiting, or impersonation.
References
•The role of customer service in cybersecurity - Security Intelligence
•How to Improve Risk Awareness in the Workplace [+ Template] - AlertMedia
•Top 4 Risks For Customer Service Teams | Resolver
An assessment of information security controls has identified ineffective controls. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner's FIRST course of action?
Determine whether the impact is outside the risk appetite.
Request a formal acceptance of risk from senior management.
Report the ineffective control for inclusion in the next audit report.
Deploy a compensating control to address the identified deficiencies.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s first course of action when an assessment of information security controls has identified ineffective controls should be A. Determine whether the impact is outside the risk appetite1
According to the CRISC Review Manual, risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Risk appetite reflects the organization’s risk culture, strategy, and values2
When an assessment of information security controls has identified ineffective controls, it means that the controls are not providing the expected level of protection or assurance for the information assets or processes. This may result in increased exposure or vulnerability to threats, or reduced ability to achieve objectives. Therefore, the risk practitioner should first determine whether the impact of the ineffective controls is outside the risk appetite, as this would indicate the need for urgent action or escalation3
The other options are not the first course of action when an assessment of information security controls has identified ineffective controls, because:
•B. Requesting a formal acceptance of risk from senior management may be appropriate if the impact of the ineffective controls is within the risk appetite, and the organization decides to accept the risk as it is. However, this should not be the first course of action, as it may not address the root cause of the ineffective controls, or the potential consequences or opportunities for improvement4
•C. Reporting the ineffective control for inclusion in the next audit report may be part of the risk communication and reporting process, but it should not be the first course of action, as it may delay the resolution or mitigation of the issue, or the implementation of corrective actions. Moreover, the next audit report may not be timely or relevant for the decision-makers or stakeholders who need to be informed of the ineffective controls5
•D. Deploying a compensating control to address the identified deficiencies may be a possible risk response option, but it should not be the first course of action, as it may require further analysis, evaluation, and approval. Moreover, deploying a compensating control may not be the most effective or efficient solution, as it may introduce additional complexity, cost, or risk.
1: CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, Question ID: 100003 2: CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 28 3: CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 223 4: CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 224 5: CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 225 : CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 226
The PRIMARY reason for prioritizing risk scenarios is to:
provide an enterprise-wide view of risk
support risk response tracking
assign risk ownership
facilitate risk response decisions.
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary reason for prioritizing risk scenarios is to facilitate risk response decisions. Risk scenarios are hypothetical situations that describe the possible causes, events, and consequences of a risk. Prioritizing risk scenarios is the process of ranking the risk scenarios according to their level of importance, urgency, or impact. Prioritizing risk scenarios helps to facilitate risk response decisions, which are the choices made to address the risks, such as avoiding, transferring, mitigating, or accepting the risks. Prioritizing risk scenarios helps to allocate the resources and efforts to the most significant or critical risk scenarios, and to select the most appropriate and effective risk responses. Prioritizing risk scenarios also helps to communicate and justify the risk response decisions to the stakeholders, and to monitor and report the risk status and performance. Providing an enterprise-wide view of risk, supporting risk response tracking, and assigning risk ownership are not the primary reasons for prioritizing risk scenarios, as they are either theinputs or the outputs of the risk prioritization process, and they do not address the primary need of responding to the risks. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 50.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of implementing key control indicators (KCIs)?
Confirming the adequacy of recovery plans.
Improving compliance with control standards.
Providing early detection of control degradation.
Reducing the number of incidents.
Answer:
Explanation:
Key Control Indicators (KCIs) are metrics used to monitor the performance of controls. Their primary benefit is the early detection of control degradation, allowing organizations to take corrective actions before issues escalate into significant problems.
Which of the following should be of GREATEST concern lo a risk practitioner reviewing the implementation of an emerging technology?
Lack of alignment to best practices
Lack of risk assessment
Lack of risk and control procedures
Lack of management approval
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk assessment is a key process that identifies, analyzes, and evaluates the risks associated with the implementation of an emerging technology. It helps to determine the potential impact and likelihood of the risks, as well as the appropriate risk responses and controls. Lack of risk assessment can lead to poor decision making, inadequate risk mitigation, and unexpected consequences. Therefore, it should be of greatest concern to a risk practitioner reviewing the implementation of an emerging technology. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5, Section 5.2.1, p. 226-227
Which of the following is a risk practitioner's MOST important course of action after learning that an organization's industry peers have experienced an increase in ransomware attacks?
Recommend additional preventive controls to reduce residual risk.
Document this scenario as a risk event for further risk analysis.
Propose risk acceptance until the organization is directly affected.
Raise a security incident to proactively prevent similar attacks.
Answer:
Which of the following is the ULTIMATE goal of conducting a privacy impact analysis (PIA)?
To identify gaps in data protection controls
To develop a customer notification plan
To identify personally identifiable information (Pll)
To determine gaps in data identification processes
Answer:
Explanation:
 The ultimate goal of conducting a privacy impact analysis (PIA) is to identify gaps in data protection controls, as it involves assessing the privacy risks and impacts of collecting, using, storing, and disclosing personally identifiable information (PII), and determining the adequacy and effectiveness of the existing or proposed controls to mitigate those risks and impacts. Developing a customer notification plan, identifying PII, and determining gaps in data identification processes are possible steps or outcomes of conducting a PIA, but they are not the ultimate goal, as they do not address the root cause or solution of the privacy issues. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 155.
What is the BEST approach for determining the inherent risk of a scenario when the actual likelihood of the risk is unknown?
Use the severity rating to calculate risk.
Classify the risk scenario as low-probability.
Use the highest likelihood identified by risk management.
Rely on range-based estimates provided by subject-matter experts.
Answer:
Explanation:
When likelihood is unknown, range-based estimates from subject-matter experts provideinformed and realistic insights into potential risk exposure. This approach helps approximate the inherent risk based on experience and expertise, supporting effective decision-making.
To drive effective risk management, it is MOST important that an organization's policy framework is:
Approved by relevant stakeholders.
Aligned to the functional business structure.
Included in employee onboarding materials.
Mapped to an industry-standard framework.
Answer:
Explanation:
Policies must reflect the actual structure and processes of the business to be enforceable and effective. Alignment ensures that policies are understood, applicable, and tailored to how the business operates.
The PRIMARY advantage of implementing an IT risk management framework is the:
establishment of a reliable basis for risk-aware decision making.
compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
improvement of controls within the organization and minimized losses.
alignment of business goals with IT objectives.
Answer:
Explanation:
An IT risk management framework is a set of principles, processes, and practices that guide and support the identification, analysis, evaluation, treatment, monitoring, and communication of IT-related risks within an organization12.
The primary advantage of implementing an IT risk management framework is the establishment of a reliable basis for risk-aware decision making, which enables the organization to balance the potential benefits and adverse effects of using IT, and to allocate resources and prioritize actions accordingly12.
A reliable basis for risk-aware decision making consists of the following elements12:
A common language and understanding of IT risk, its sources, impacts, and responses
A consistent and structured approach to IT risk identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment
A clear and transparent governance structure and accountability for IT risk management
A comprehensive and up-to-date IT risk register and profile that reflects the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance
A regular and effective IT risk monitoring and reporting process that provides relevant and timely information to stakeholders
A continuous and proactive IT risk improvement process that incorporates feedback and lessons learned
The other options are not the primary advantage, but rather possible outcomes or benefits of implementing an IT risk management framework. For example:
Compliance with relevant legal and regulatory requirements is an outcome of implementing an IT risk management framework that ensures the organization meets its obligations and avoids penalties or sanctions12.
Improvement of controls within the organization and minimized losses is a benefit of implementing an IT risk management framework that reduces the likelihood and impact of IT-related incidents and events12.
Alignment of business goals with IT objectives is a benefit of implementing an IT risk management framework that ensures the IT strategy and activities support the organization’s mission and vision12. References =
1: Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2009
2: IT Risk Management Framework, University of Toronto, 2017
A systems interruption has been traced to a personal USB device plugged into the corporate network by an IT employee who bypassed internal control procedures. Of the following, who should be accountable?
Business continuity manager (BCM)
Human resources manager (HRM)
Chief risk officer (CRO)
Chief information officer (CIO)
Answer:
Explanation:
A systems interruption caused by a personal USB device plugged into the corporate network by an IT employee who bypassed internal control procedures is a serious breach of information security and IT risk management. The person who should be accountable for this incident is the chief information officer (CIO), who is responsible for overseeing the IT function and ensuring compliance with IT policies and standards. The CIO should also ensure that appropriate corrective and preventive actions are taken to prevent such incidents from recurring and to mitigate the impact of the systems interruption on the business operations and objectives. The CIO should also report the incident to the senior management and the board of directors, and communicate with the relevant stakeholders about the incident and the actions taken. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 181
A risk practitioner has just learned about new malware that has severely impacted industry peers worldwide data loss?
Customer database manager
Customer data custodian
Data privacy officer
Audit committee
Answer:
Explanation:
The data privacy officer is the best person to notify in case of a new malware that has severely impacted industry peers with data loss. The data privacy officer is responsible for ensuring that the enterprise complies with the applicable privacy laws and regulations, and that the personal data of the customers, employees, and other stakeholders are protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or destruction. The data privacy officer can assess the potential impact of the malware on the enterprise’s data privacy obligations and risks, and coordinate the appropriate response and remediation actions. The customer database manager, the customer data custodian, and the audit committee are not the best persons to notify, as they do not have the same level of authority, responsibility, and expertise as the data privacy officer in dealing with data privacy issues. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 191.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for a risk practitioner to review an organization's IT asset inventory?
To plan for the replacement of assets at the end of their life cycles
To assess requirements for reducing duplicate assets
To understand vulnerabilities associated with the use of the assets
To calculate mean time between failures (MTBF) for the assets
Answer:
Explanation:
 Understanding vulnerabilities associated with the use of the assets is the primary reason for a risk practitioner to review an organization’s IT asset inventory, as it helps to identify and assess the potential threats and risks to the assets. The other options are not the primary reasons for a risk practitioner to review an organization’s IT asset inventory, although they may be related to the process.
The PRIMARY benefit of conducting a risk workshop using a top-down approach instead of a bottom-up approach is the ability to:
identify specific project risk.
obtain a holistic view of IT strategy risk.
understand risk associated with complex processes.
incorporate subject matter expertise.
Answer:
Explanation:
Obtaining a holistic view of IT strategy risk is the primary benefit of conducting a risk workshop using a top-down approach instead of a bottom-up approach, because it helps to identify and assess the risks that may affect the alignment and integration of IT with the organization’s objectives and strategy. A risk workshop is a collaborative and interactive method of conducting a risk assessment, where the risk practitioner facilitates a group discussion with the relevant stakeholders to identify, analyze, and evaluate the risks and their controls. A top-down approach is a method of conducting a risk workshop that starts from the high-level or strategic perspective, and then drills down to the lower-level or operational details. A bottom-up approach is a methodof conducting a risk workshop that starts from the low-level or operational details, and then aggregates them to the higher-level or strategic perspective. A top-down approach can offer a holistic view of IT strategy risk, as it helps to understand the big picture and the interrelationships of the risks and their impacts across the organization. A bottom-up approach can offer a detailed view of specific project or process risk, as it helps to capture the granular and technical aspects of the risks and their controls. Therefore, obtaining a holistic view of IT strategy risk is the primary benefit of using a top-down approach, as it supports the strategic alignment and integration of IT with the organization. Identifying specific project risk, understanding risk associated with complex processes, and incorporating subject matter expertise are all possible benefits of conducting a risk workshop, but they are not the primary benefit of using a top-down approach, as they are more suitable for a bottom-up approach. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.2, page 87
An organization is considering allowing users to access company data from their personal devices. Which of the following is the MOST important factor when assessing the risk?
Classification of the data
Type of device
Remote management capabilities
Volume of data
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important factor when assessing the risk of allowing users to access company data from their personal devices is the classification of the data, as it indicates the level of sensitivity, confidentiality, and criticality of the data. Data classification helps to determine the appropriate level of protection and controls that are needed to prevent unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or loss of the data. Data classification also helps to define the roles and responsibilities of the data owners, custodians, and users, and the acceptable use of the data. The other options are not the most important factors, although they may be relevant or influential in the risk assessment. The type of device may affect the security features and vulnerabilities of the device, but it does not determine the value or impact of the data. The remote management capabilities may affect the ability to monitor, control, or wipe the device in case of theft or loss, but they do not reflect the nature or purpose of the data. The volume of data may affect the storage capacity or performance of the device, but it does not indicate the importance or significance of the data. References = What is BYOD (Bring-Your-Own-Device) - CrowdStrike; Understanding BYOD Policy - Get Certified Get Ahead; Addressing cyber security concerns on employees’ personal devices; Personal Devices at Work – Nonprofit Risk Management Center; 10 Keys to an Effective BYOD and Remote Access Policy
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of using IT risk scenarios?
They support compliance with regulations.
They provide evidence of risk assessment.
They facilitate communication of risk.
They enable the use of key risk indicators (KRls)
Answer:
Explanation:
The greatest benefit of using IT risk scenarios is that they facilitate communication of risk, as they provide a clear and realistic description of the risk sources, events, impacts, and responses, and enable the stakeholders to understand and appreciate the risk exposure and appetite of the organization. Supporting compliance with regulations, providing evidence of risk assessment, and enabling the use of key risk indicators (KRIs) are also benefits of using IT risk scenarios, but they are not the greatest benefit, as they are more related to the outcomes or consequences of risk communication, rather than the process or value of risk communication. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 100.
Which of the following is the MOST useful input when developing risk scenarios?
Common attacks in other industries
Identification of risk events
Impact on critical assets
Probability of disruptive risk events
Answer:
Explanation:
Identifying risk events is essential for developing realistic and relevant risk scenarios. This step enables the creation of scenarios that reflect actual vulnerabilities and potential disruptions, adhering to the CRISC's focus onRisk Identification.
An IT department originally planned to outsource the hosting of its data center at an overseas location to reduce operational expenses. After a risk assessment, the department has decided to keep the data center in-house. How should the risk treatment response be reflected in the risk register?
Risk mitigation
Risk avoidance
Risk acceptance
Risk transfer
Answer:
Explanation:
 The risk treatment response that should be reflected in the risk register when an IT department decides to keep the data center in-house instead of outsourcing it to an overseas location is risk avoidance. Risk avoidance is a risk response strategy that involves eliminating the source of the risk, or changing the plan or scope of the activity, to avoid the risk altogether. Risk avoidance can help to reduce the risk exposure and impact to zero, by removing the possibility of the risk occurrence. In this case, the IT department avoids the risk of outsourcing the data center to an overseas location, which could involve various threats, vulnerabilities, and uncertainties, such as data security, legal compliance, service quality, communication, or cultural issues. By keeping the data center in-house, the IT department maintains the control and ownership of the data center, and eliminates the potential risk associated with the outsourcing. Risk mitigation, risk acceptance, and risk transfer are not the correct risk treatment responses, as they do not reflect the actual decision and action taken by the IT department, and they do not eliminate the risk source or occurrence. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 51.
Which of the following is MOST critical to the design of relevant risk scenarios?
The scenarios are based on past incidents.
The scenarios are linked to probable organizational situations.
The scenarios are mapped to incident management capabilities.
The scenarios are aligned with risk management capabilities.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Risk scenarios are hypothetical situations that describe potential events or actions that could affect the achievement of enterprise objectives. The design of relevant risk scenarios should consider the following factors: the risk appetite and tolerance of the enterprise, the key risk indicators and risk drivers, the potential impact and likelihood of the scenarios, and the alignment with the risk management capabilities of the enterprise. The scenarios should be realistic, plausible, and consistent with the enterprise’s context and objectives. The scenarios should also be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect changes in the internal and external environment. The alignment with the risk management capabilities is the most critical factor, as it ensures that the scenarios are relevant for the decision making and risk response processes of the enterprise. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.3.3.2, pp. 67-69.
Which of the following is the BEST way for a risk practitioner to present an annual risk management update to the board''
A summary of risk response plans with validation results
A report with control environment assessment results
A dashboard summarizing key risk indicators (KRIs)
A summary of IT risk scenarios with business cases
Answer:
Explanation:
A dashboard summarizing key risk indicators (KRIs) is the best way for a risk practitioner to present an annual risk management update to the board because it provides a concise and visual overview of the current risk status, trends, and performance of the organization. KRIs are metrics that measure the likelihood and impact of risks, and help the board monitor and prioritize the most critical risks. A summary of risk response plans, a report with control environment assessment results, and a summary of IT risk scenarios are all useful information, but they are too detailed and technical for the board, who needs a high-level and strategic view of the risk management program. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.4.1, page 4-36.
What is MOST important for the risk practitioner to understand when creating an initial IT risk register?
Enterprise architecture (EA)
Control environment
IT objectives
Organizational objectives
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important factor for the risk practitioner to understand when creating an initial IT risk register is the organizational objectives. The organizational objectives are the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that the organization aims to accomplish. The organizational objectives should be aligned with the organization’s vision, mission, and strategy, as well as the stakeholder expectations and needs. The organizational objectives should also reflect the desired outcomes and benefits of the organization, such as increasing revenue, reducing costs, improving quality, or enhancing customer satisfaction. Understanding the organizational objectives is the most important factor when creating an initial IT risk register, because it provides the context, scope, and criteria for identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing the IT risks that may affect or be affected by the organizational objectives.Understanding the organizational objectives also helps to align the IT risk management process with the organizational risk management process, and to communicate the value and impact of the IT risks and the IT risk responses to the senior management and other stakeholders. The other options are not the most important factor, although they may be relevant or influential to the IT risk register. Enterprise architecture (EA) is a conceptual blueprint that defines the structure and operation of an organization. EA describes the current and future state of the organization in terms of its business processes, information systems, and technology infrastructure, and the relationships and dependencies among them. EA also provides the principles, standards, and guidelines for designing, developing, and implementing the organization’s solutions and services. EA can help to understand the IT risk sources, causes, and effects, as well as the IT risk mitigation options and opportunities, but it does not define the purpose or the scope of the IT risk register. Control environment is the set of policies, procedures, and mechanisms that ensure the reliability, security, and quality of the organization’s activities and information. Control environment includes the tone and culture at the top, the roles and responsibilities for governance and oversight, the internal control framework and methodology, and the monitoring and reporting systems. Control environment can help to assess the IT risk levels and the IT risk responses, as well as to ensure the compliance and accountability of the IT risk management process, but it does not provide the context or the criteria for the IT risk register. IT objectives are the specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that the IT function aims to accomplish. IT objectives should be aligned and consistent with the organizational objectives, as well as the IT strategy and IT governance. IT objectives should also reflect the expected outcomes and benefits of the IT function, such as delivering value, enabling innovation, or supporting transformation. IT objectives can help to identify and prioritize the IT risks that may affect or be affected by the IT objectives, but they are not the same as or more important than the organizational objectives. References = Three Steps to Creating a Simple IT Risk Register - Gartner, Risk Register Template and Examples | Prioritize and Manage Risk, IT Resources | Knowledge & Insights | ISACA
Which of the following is the PRIMARY advantage of having a single integrated business continuity plan (BCP) rather than each business unit developing its own BCP?
It provides assurance of timely business process response and effectiveness.
It supports effective use of resources and provides reasonable confidence of recoverability.
It enables effective BCP maintenance and updates to reflect organizational changes.
It decreases the risk of downtime and operational losses in the event of a disruption.
Answer:
Which process is MOST effective to determine relevance of threats for risk scenarios?
Vulnerability assessment
Business impact analysis (BIA)
Penetration testing
Root cause analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
A vulnerability assessment is a process that identifies and quantifies vulnerabilities in a system. It is the most effective process to determine the relevance of threats for risk scenarios as it helps in identifying potential security threats and vulnerabilities, quantifying the seriousness of each, and prioritizing techniques to mitigate attack and protect IT resources1.
References
2Identifying and Estimating Cybersecurity Risk for Enterprise Risk Management
3Threat Modeling Process | OWASP Foundation
1Threat modeling explained: A process for anticipating cyber attacks
4Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: A Guide - SafetyCulture
5How to Write Strong Risk Scenarios and Statements - ISACA
Following an acquisition, the acquiring company's risk practitioner has been asked to update the organization's IT risk profile What is the MOST important information to review from the acquired company to facilitate this task?
Internal and external audit reports
Risk disclosures in financial statements
Risk assessment and risk register
Business objectives and strategies
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important information to review from the acquired company to facilitate the task of updating the organization’s IT risk profile is the risk assessment and risk register. The risk assessment is a process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the IT risks of the acquiredcompany. The risk register is a document that records the details of the IT risks, such as their sources, causes, consequences, likelihood, impact, and responses. By reviewing the risk assessment and risk register, the risk practitioner can gain a comprehensive and accurate understanding of the IT risk profile of the acquired company, and integrate it with the IT risk profile of the acquiring organization. Internal and external audit reports, risk disclosures in financial statements, and business objectives and strategies are other possible sources of information, but they are not as important as the risk assessment and risk register. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 11; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 144.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for a risk practitioner to examine a post-implementation review report for a control automation tool?
To verify that budget for the project is managed effectively
To confirm compliance with project management methodology
To ensure the risk is managed to an acceptable level
To ensure audit findings are addressed in a timely manner
Answer:
Explanation:
The main purpose of implementing controls is to reduce risk to an acceptable level. Reviewing the effectiveness of the new tool post-implementation ensures the control objective has been achieved.
A risk practitioner has determined that a key control does not meet design expectations. Which of the following should be done NEXT?
Document the finding in the risk register.
Invoke the incident response plan.
Re-evaluate key risk indicators.
Modify the design of the control.
Answer:
Explanation:
 The next step after determining that a key control does not meet design expectations is to document the finding in the risk register, because this helps to record and track the information about the identified risk, such as its description, likelihood, impact, response, and status. A key control is a control that addresses a significant risk or supports a critical business process or objective. A control design expectation is a criterion or requirement that defines how the control should operate or perform to achieve its objective. If a key control does not meet its design expectation, it means that there is a gap, weakness, or deficiency in the control that may compromise its effectiveness or efficiency, and increase the risk exposure or impact. By documenting the finding in the risk register, the risk practitioner can communicate and report the risk issue to the relevant stakeholders, such as the risk owner, the management, or the auditor, and initiate the appropriate risk response actions, such as modifying the design of the control, implementing a compensating control, or accepting the risk. The other options are not the best next steps after determining that a key control does not meet design expectations. Invoking the incident response plan is a reactive measure that is triggered when a risk event occurs or is imminent, and requires immediate action to contain, mitigate, or recover from the incident. However, in this case, the risk event has not occurred yet, and there may be time to prevent or reduce it by improving the control design. Re-evaluating key risk indicators is a monitoring activity that measures and evaluates the level and impact of risks, and provides timely signals that something may be going wrong or needs urgent attention. However, in this case, the risk practitioner has already identified the risk issue, and needs to document and address it, rather than re-evaluate it. Modifying the design of the control is a possible risk response action that may be taken to improve the control and reduce the risk, but it is not the next step after determining that the key control does not meet design expectations. The next step is to document the finding in the risk register, and then decide on the best risk response action, which may or may not be modifying the design of the control, depending on the cost-benefit analysis, the risk assessment, and the risk response strategy. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 13
Which of the following BEST indicates that security requirements have been incorporated into the system development life cycle (SDLC)?
Comprehensive security training of developers
Validated security requirements and design documents
Completed user acceptance testing (UAT)
Compliance with laws and regulatory requirements
Answer:
Explanation:
Validated security requirements and design documents demonstrate that security considerations have been integrated into the SDLC from the outset. This proactive approach ensures that security is embedded into system architecture and design, reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing overall system resilience.
When reviewing a report on the performance of control processes, it is MOST important to verify whether the:
business process objectives have been met.
control adheres to regulatory standards.
residual risk objectives have been achieved.
control process is designed effectively.
Answer:
Explanation:
When reviewing a report on the performance of control processes, it is most important to verify whether the residual risk objectives have been achieved, as this indicates the extent to which the control processes have reduced the risk to an acceptable level. Residual risk is the risk that remains after the implementation of controls, and it should be aligned with the risk appetite and tolerance of the enterprise. Business process objectives, regulatory standards, and control process design are not the most important factors to verify,as they do not directly measure the effectiveness and efficiency of the control processes in managing the risk. References = CRISCPractice Quiz and Exam Prep; CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, question 209.
A recent internal risk review reveals the majority of core IT application recovery time objectives (RTOs) have exceeded the maximum time defined by the business application owners. Which of the following is MOST likely to change as a result?
Risk forecasting
Risk tolerance
Risk likelihood
Risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
Recovery time objectives (RTOs) are the maximum acceptable time frames for restoring the critical functions and processes after a disruption1. RTOs are derived from the business impact analysis (BIA) andreflect the organization’s risk appetite, which is the amount of risk that an organization is willing to accept to achieve its objectives2. Risk tolerance is the level of risk a company is willing to tolerate, and it is affected by a number of factors, including how much uncertainty or financial loss can be tolerated and where those losses will impact operations3. Risk tolerance is used to measure if the risk exposure is within the risk appetite and to implement controls to reduce the residual risk to an acceptable level2. If the majority of core IT application RTOs have exceeded the maximum time defined by the business application owners, it means that the organization is not meeting its risk appetite and is exposed to more risk than it can accept. Therefore, the most likely change as a result is to adjust the risk tolerance to reflect the current reality and to take actions to improve the recovery capabilities and reduce the risk exposure4. Risk forecasting is the process of estimating the potential outcomes and impactsof future events that may affect the organization’s objectives5. Risk forecasting may change as aresult of the RTOs exceeding the maximum time, but it is not the most likely change, as it does not directly address the gap between the risk appetite and the risk exposure. Risk likelihood is the probability of a risk event occurring5. Risk likelihood may change as a result of the RTOs exceeding the maximum time, but it is not the most likely change, as it does not directly measure the impact of the risk event on the organization’s objectives. Risk appetite is the amount of risk that an organization is willing to accept to achieve its objectives2. Risk appetite may change as a result of the RTOs exceeding the maximum time, but it is not the most likely change, as it is a strategic decision that reflects the organization’s vision and mission, and not a tactical response to a specific risk event. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Risk Response and Mitigation, Section 5.3: Business Continuity Planning, pp. 227-238.
To implement the MOST effective monitoring of key risk indicators (KRIs), which of the following needs to be in place?
Threshold definition
Escalation procedures
Automated data feed
Controls monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are the metrics or measures that provide information and insight on the level and trend of the risks that may affect the organization’s objectives and operations. KRIscan help the organization to monitor and communicate the risks, and to support the decision making and planning for the risk management.
To implement the most effective monitoring of KRIs, one of the essential elements that needs to be in place is threshold definition, which is the process of establishing and specifying the acceptable or tolerable ranges or limits for the KRIs, based on the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. Threshold definition can help the organization to monitor KRIs by providing the following benefits:
It can enable the comparison and evaluation of the actual or current values of the KRIs with the expected or desired values of the KRIs, and to identify and quantify the deviations or variations that may indicate the changes or developments in the risk level or performance.
It can trigger the alerts or notifications when the values of the KRIs exceed or fall below the thresholds, and to initiate the appropriate actions or responses to address or correct the risks and their impacts.
It can provide useful references and benchmarks for the alignment and integration of the KRIs with the organization’s risk management function, and for the compliance with the organization’s risk policies and standards.
The other options are not the essential elements that need to be in place to implement the most effective monitoring of KRIs, because they do not address the main purpose and benefit of threshold definition, which is to establish and specify the acceptable or tolerable ranges or limits for the KRIs.
Escalation procedures are the processes and guidelines for communicating and sharing the information and status of the risks and their responses among the relevant stakeholders, and for escalating or transferring the risks and their responses to the appropriate levels orparties when necessary or required. Escalation procedures can help the organization to monitor KRIs by ensuring the awareness and involvement of the stakeholders, but they are not the essential elements that need to be in place, because they do not establish and specify the acceptable or tolerable ranges or limits for the KRIs.
Automated data feed is the process of using a software tool or system to collect and transmit the data or information that are related or relevant to the KRIs, and to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and timeliness of the data or information. Automated data feed can help the organization to monitor KRIs by providing the data or information that are necessary and relevant for the KRIs, but they are not the essential elements that need to be in place, because they do not establish and specify the acceptable or tolerable ranges or limits for the KRIs.
Controls monitoring is the process of verifying and validating the adequacy and effectiveness of the controls that are intended to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, availability, and reliabilityof the information systems and resources that are affected by the risks. Controls monitoring can help the organization to monitor KRIs by providing the assurance and evidence on the performance and compliance of the controls, but they are not the essential elements that need to be in place, because they do not establish and specify the acceptable or tolerable ranges or limits for the KRIs. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 206
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
A highly regulated enterprise is developing a new risk management plan to specifically address legal and regulatory risk scenarios What should be done FIRST by IT governance to support this effort?
Request a regulatory risk reporting methodology
Require critical success factors (CSFs) for IT risks.
Establish IT-specific compliance objectives
Communicate IT key risk indicators (KRIs) and triggers
Answer:
Explanation:
The first thing that should be done by IT governance to support the development of a new risk management plan to specifically address legal and regulatory risk scenarios is to establish IT-specific compliance objectives. Compliance objectives are the goals or targets that the organization sets to ensure that its IT activities and processes comply with the relevant laws, regulations, standards, and contracts. Compliance objectives help to define the scope, criteria, and expectations for the IT compliance program, and to align the IT compliance activities with the organization’s strategy, risk appetite, and performance measures. Compliance objectives also help to communicate and demonstrate the organization’s commitment and accountability for IT compliance to the internal and external stakeholders, such as the board, management, regulators, auditors, and customers. The other options are not the first thing that should be done, although they may be useful or necessary steps or components of the IT compliance program. Requesting a regulatory risk reporting methodology, requiring critical success factors (CSFs) for IT risks, and communicating IT key risk indicators (KRIs) and triggers are all activities that can help to implement and monitor the IT compliance program, but they require the prior definition and agreement of the IT compliance objectives. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.4.1, page 2-37.
Which organizational role should be accountable for ensuring information assets are appropriately classified?
Data protection officer
Chief information officer (CIO)
Information asset custodian
Information asset owner
Answer:
Explanation:
The organizational role that should be accountable for ensuring information assets are appropriately classified is the information asset owner, as they have the authority and responsibility to define the classification, retention, and disposal requirements for the information assets they own, and to manage the risk and controls related to the information assets. The other options are not the correct roles, as they have different roles and responsibilities related to the protection, governance, or maintenance of the information assets, respectively, rather than the classification of the information assets. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 154.
How does an organization benefit by purchasing cyber theft insurance?
It decreases the amount of organizational loss if risk events occur.
It justifies the acceptance of risk associated with cyber theft events.
It transfers risk ownership along with associated liabilities to a third party.
It decreases the likelihood of risk events occurring.
Answer:
A risk practitioner recently discovered that sensitive data from the production environment is required for testing purposes in non-production environments. Which of the following i the BEST recommendation to address this situation?
Enable data encryption in the test environment
Implement equivalent security in the test environment.
Prevent the use of production data for test purposes
Mask data before being transferred to the test environment.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Masking data before being transferred to the test environment is the best recommendation to address the situation where sensitive data from the production environment is required for testing purposes in non-production environments. Data masking is a technique that replaces sensitive data elements with realistic but fictitious data, preserving the format, structure, and meaning of the original data. Data masking ensures that the test data is sufficiently anonymized and de-identified, while still maintaining its functionality and validity for testing purposes. Data masking also reduces the risk of data leakage, exposure, or breach in the test environment, which may have lower security controls than the production environment. The other options are not the best recommendations, as they do not adequately protect the sensitive data or meet the testingrequirements. Enabling data encryption in the test environment may protect the data from unauthorized access, but it does not prevent the data from being decrypted by authorized users who may misuse or mishandle it. Implementing equivalent security in the test environment may be costly, complex, or impractical, and it may not be feasible to replicate the same level of security controls as in the production environment. Preventing the use of production data for test purposes may not be possible or desirable, as production data may be required to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and quality of the testing results. References = P = NP: Cloud dataprotection in vulnerable non-production environments …; Data masking secures sensitive data in non-production environments …; CRISC EXAM TOPIC 2 LONG Flashcards | Quizlet
Which of the following situations reflects residual risk?
Risk that is present before risk acceptance has been finalized
Risk that is removed after a risk acceptance has been finalized
Risk that is present before mitigation controls have been applied
Risk that remains after mitigation controls have been applied
Answer:
Explanation:
Residual riskrefers to the risk that remains after mitigation measures have been applied. It represents the exposure that an organization decides to accept, transfer, or further address, aligning with its risk appetite and tolerance.
Which element of an organization's risk register is MOST important to update following the commissioning of a new financial reporting system?
Key risk indicators (KRIs)
The owner of the financial reporting process
The risk rating of affected financial processes
The list of relevant financial controls
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important element of an organization’s risk register to update following the commissioning of a new financial reporting system is the risk rating of affected financial processes. A risk rating is a measure of the level and nature of the risk exposure, based on the impact and likelihood of the risk events. A risk rating can help to prioritize and respond to the risks, and to monitor and report the risk status. A new financial reporting system may introduce new or different risks, or change the existing risks, that could affect the financial processes of the organization, such as data quality, accuracy, timeliness, compliance, or security. Therefore, the risk rating of affected financial processes should be updated to reflect the current risk situation and to ensure that the risk register is accurate and complete. Key risk indicators (KRIs), the owner of the financial reporting process, and the list of relevant financial controls are not asimportant as the risk rating of affected financial processes, as they are not directly affected by the commissioning of a new financial reporting system, and they do not measure the risk exposure and impact of the financial processes. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 48.
Which of the following BEST confirms the existence and operating effectiveness of information systems controls?
Self-assessment questionnaires completed by management
Review of internal audit and third-party reports
Management review and sign-off on system documentation
First-hand direct observation of the controls in operation
Answer:
Explanation:
First-hand direct observation of the controls in operation is the best way to confirm the existence and operating effectiveness of information systems controls because it provides the auditor with the most reliable and persuasive evidence. Direct observation involves inspecting the physicaland logical aspects of the controls, such as the hardware, software, network, data, procedures, and personnel involved in the information systems. Direct observation also allows the auditor to verify that the controls are functioning as intended, and to identify any deviations or weaknesses that may affect the reliability of the information systems. Direct observation can be performed by using various techniques, such as walkthroughs, inquiries, inspections, reperformance, and analytical procedures1. References = Auditing Standard No. 13, The Auditor’s Responses to the Risks of Material Misstatement, PCAOB, 20101
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit when enterprise risk management (ERM) provides oversight of IT risk management?
Aligning IT with short-term and long-term goals of the organization
Ensuring the IT budget and resources focus on risk management
Ensuring senior management's primary focus is on the impact of identified risk
Prioritizing internal departments that provide service to customers
Answer:
Explanation:
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is a holistic and strategic approach to managing the risks that an organization faces across its various functions, processes, and activities. ERM aims to align the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance with its objectives and vision, and to optimize the value and performance of the organization1.
IT risk management is a subset of ERM that focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risks related to the use of information technology (IT) in the organization. IT risk management aims to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT resources and information, and to support the IT governance and strategy of the organization2.
The greatest benefit when ERM provides oversight of IT risk management is aligning IT with short-term and long-term goals of the organization, because it can help to:
Integrate IT risk management with the overall business strategy and risk management, and ensure that IT risks are considered and addressed at the enterprise level
Align IT risk appetite and tolerance with the business risk appetite and tolerance, and ensure that IT risks are balanced with the expected benefits and opportunities
Enhance IT risk awareness and communication among the stakeholders, and ensure that IT risks are reported and escalated appropriately
Optimize IT risk response and control, and ensure that IT risks are managed efficiently and effectively
Demonstrate IT risk value and impact, and ensure that IT risks are measured and monitored against the business objectives and performance34
The other options are not the greatest benefit when ERM provides oversight of IT risk management, but rather some of the outcomes or consequences of it. Ensuring the IT budget and resources focus on risk management is a benefit that can help to allocate and prioritize the IT resources and funds according to the IT risk level and the business needs. Ensuring senior management’s primary focus is on the impact of identified risk is a benefit that can help to increase the senior management’s involvement and accountability in IT risk management, and to support the IT risk decision making and reporting. Prioritizing internal departments that provide service to customers is a benefit that can help to improve the quality and efficiency of the IT service delivery and customer satisfaction. References =
Enterprise Risk Management - ISACA
IT Risk Management - ISACA
Aligning IT risks with Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
Five Benefits of Enterprise Risk Management : Articles : Resources …
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of the following activities is MOST likely to be assigned to the second line in the three lines model?
Validating whether IT risk control systems are operational
Monitoring IT security policy compliance
Calculating phishing attack key risk indicators (KRIs)
Appropriately configuring the web application firewall (WAF)
Answer:
Explanation:
In the three lines model, the second line provides oversight and monitoring of risk and compliance. CRISC states that functions such as risk management, compliance monitoring, and policy oversight belong to the second line. Monitoring IT security policy compliance fits this role because it evaluates whether operational controls align with requirements. The first line (operations) configures systems like WAFs and calculates operational KRIs. The third line (internal audit) validates whether controls are functioning independently. Thus, the responsibility most aligned with the second line is monitoring compliance.
Which of the following is the MOST critical factor to consider when determining an organization's risk appetite?
Fiscal management practices
Business maturity
Budget for implementing security
Management culture
Answer:
Explanation:
The most critical factor to consider when determining an organization’s risk appetite is the management culture. The management culture reflects the values, beliefs, and attitudes of the senior management and the board of directors toward risk management. The management culture influences how the organization defines, communicates, and implements its risk appetite and tolerance. Fiscal management practices, business maturity, and budget for implementing security are other factors that may affect the risk appetite, but they are not as critical as the management culture. References = ISACA Certified in Risk andInformation Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 8; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 97.
The software version of an enterprise's critical business application has reached end-of-life and is no longer supported by the vendor. IT has decided to develop an in-house replacement application. Which of the following should be the PRIMARY concern?
The system documentation is not available.
Enterprise risk management (ERM) has not approved the decision.
The board of directors has not approved the decision.
The business process owner is not an active participant.
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary concern when IT decides to develop an in-house replacement application for a critical business application is that the business process owner is not an active participant. The business process owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for the business process that is supported by the application, and who understands the business requirements, objectives, and expectations of the application. The business process owner should be involved in all stages of the application development lifecycle, from planning, analysis, design, testing, implementation, to maintenance, to ensure that the application meets the business needs and delivers value. Without the active participation of the business process owner, the application development project may face risks such as scope creep, miscommunication, user dissatisfaction, poor quality, or failure.
Which of the following BEST enables a risk practitioner to identify the consequences of losing critical resources due to a disaster?
Risk management action plans
Business impact analysis (BIA)
What-if technique
Tabletop exercise results
Answer:
Explanation:
Business Impact Analysis (BIA):
Purpose: A BIA is a systematic process to evaluate the potential effects of an interruption to critical business operations as a result of a disaster, accident, or emergency.
Identification of Consequences: It identifies critical resources and the consequences of their loss, allowing an organization to determine the operational and financial impacts of such losses.
Steps Involved in BIA:
Identify Critical Functions: Determine which business functions and processes are essential to the organization's operations.
Assess Impact: Evaluate the impact of losing these functions on the organization’s ability to operate.
Estimate Downtime Tolerance: Determine the maximum allowable downtime for critical functions before significant harm occurs.
Identify Dependencies: Document dependencies between systems, processes, and resources to understand how disruptions to one part affect the whole.
Comparison with Other Options:
Risk Management Action Plans: These are detailed plans developed to address identified risks but do not specifically focus on the impact of losing critical resources.
What-if Technique: This is a brainstorming technique used to explore potential risks and their impacts but is not as structured as a BIA.
Tabletop Exercise Results: These exercises simulate disaster scenarios to test response plans but do not provide the comprehensive impact analysis that a BIA does.
Best Practices:
Regular Updates: Regularly update the BIA to reflect changes in the business environment and operational dependencies.
Integration with DR/BC Plans: Ensure that findings from the BIA are integrated into disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity (BC) plans to enhance overall preparedness.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration for a risk practitioner when making a system implementation go-live recommendation?
Completeness of system documentation
Results of end user acceptance testing
Variances between planned and actual cost
availability of in-house resources
Answer:
Explanation:
End user acceptance testing is a process that verifies that a system or service meets the requirements and expectations of the end users, who are the actual or potential customers or beneficiaries of the system or service. End user acceptance testing is the final stage of testing before the system or service is deployed or released to the production environment. The results of end user acceptance testing are the most important consideration for a risk practitioner when making a system implementation go-live recommendation, as they indicate the quality, functionality, usability, and reliability of the system or service from the end user perspective. The results of end user acceptance testing can help to identify and resolve any defects, errors, or issues that may affect the performance, satisfaction, or acceptance of the system or service by the end users. The results of end user acceptance testing can also help to evaluate the benefits, value, and risks of the system or service for the end users and the organization. The other options are not the most important consideration for a risk practitioner when making a system implementation go-live recommendation, although they may be relevant and useful. The completeness of system documentation is a factor that affects the maintainability, supportability, and auditability of the system or service, but it does not measure the end user experience or satisfaction. The variances between planned and actual cost is a measure of the efficiency and budget management of the system or service development or implementation, but it does not reflect the end user needs or expectations. The availability of in-house resources is a resource that supports the system or service delivery and operation, but it does not ensure the end user acceptance or approval. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 180-1811; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 87
A deficient control has been identified which could result in great harm to an organization should a low frequency threat event occur. When communicating the associated risk to senior management the risk practitioner should explain:
mitigation plans for threat events should be prepared in the current planning period.
this risk scenario is equivalent to more frequent but lower impact risk scenarios.
the current level of risk is within tolerance.
an increase in threat events could cause a loss sooner than anticipated.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner should explain to senior management that mitigation plans for threat events should be prepared in the current planning period, as this would demonstrate a proactive and responsible approach to risk management. Mitigation plans are documents that outline the actions and resources needed to reduce the likelihood and/or impact of a specific risk scenario. Mitigation plans should include the following elements:
Risk scenario description and risk ID
Risk owner and other stakeholders
Risk response strategy and objectives
Risk response actions and tasks
Resources, costs, and benefits
Roles and responsibilities
Timeline and milestones
Performance indicators and monitoring mechanisms
Contingency plans and triggers
Mitigation plans help to address the gap between the current and desired risk levels and align the risk response with the organizational risk appetite and objectives. Mitigation plans also facilitate the communication, coordination, and collaboration among the risk owners and other stakeholders involved in the risk response process. Mitigation plans should be prepared in the current planning period, as this would allow the organization to act timely and effectively in the event of a low frequency threat event. Preparing mitigation plans in advance would also help to avoid or minimize the potential harm to the organization and its reputation.
The other options are not the best ways to communicate the associated risk to senior management. Explaining that this risk scenario is equivalent to more frequent but lower impact risk scenarios may not accurately reflect the true nature and severity of the risk. Explaining that the current level of risk is within tolerance may not convey the urgency and importance of addressing the risk. Explaining that an increase in threat events could cause a loss sooner than anticipated may not provide a clear and actionable solution for the risk. References = Four steps for managing risk at the CEO level, IT Risk Resources | ISACA, How to Communicate Risk to Stakeholders | Anitian
The GREATEST benefit of introducing continuous monitoring to an IT control environment is that it:
Enables timely detection of emerging risk
Enables the collection of benchmarking data
Identifies stakeholders involved in the process
Helps to obtain buy-in for future IT investments
Answer:
Explanation:
Continuous monitoring systems automatically track key control indicators (KCIs) and risk metrics in real-time, enabling early identification of anomalies or emerging risks.
ISACA CRISC states:
“Continuous monitoring allows the enterprise to identify deviations and emerging risk conditions in a timely manner to take proactive corrective actions.â€
Benchmarking and stakeholder mapping are secondary benefits.
Thus, A. Enables timely detection of emerging risk is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 4 – Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Topic: Continuous Monitoring Benefits.
An organization practices the principle of least privilege. To ensure access remains appropriate, application owners should be required to review user access rights on a regular basis by obtaining:
business purpose documentation and software license counts
an access control matrix and approval from the user's manager
documentation indicating the intended users of the application
security logs to determine the cause of invalid login attempts
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to ensure that access remains appropriate for an organization that practices the principle of least privilege is to review user access rights on a regular basis by obtaining an access control matrix and approval from the user’s manager. An access control matrix is a table that shows the access rights and permissions of each user or role for each resource or function. An access control matrix helps to verify that the users have the minimum level of access required to perform their duties, and to identify any unauthorized or excessive access rights. Approval from the user’s manager helps to confirm that the user’s access rights are consistent with their current role and responsibilities, and to authorize any changes or exceptions as needed. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.2, page 1281
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of having a mature enterprise architecture (EA) in place?
Standards-based policies
Audit readiness
Efficient operations
Regulatory compliance
Answer:
Explanation:
The greatest benefit of having a mature enterprise architecture (EA) in place is efficient operations, as EA provides a holistic view of the organization’s business processes, information systems, and technology infrastructure, and enables alignment, integration, and optimization of these components. Standards-based policies, audit readiness, and regulatory compliance are also benefits of EA, but they are not the greatest benefit. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 145.
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY focus of a risk owner once a decision is made to mitigate a risk?
Updating the risk register to include the risk mitigation plan
Determining processes for monitoring the effectiveness of the controls
Ensuring that control design reduces risk to an acceptable level
Confirming to management the controls reduce the likelihood of the risk
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary focus of a risk owner once a decision is made to mitigate a risk is to ensure that the control design reduces the risk to an acceptable level. This means that the risk owner shouldverify that the control objectives, specifications, and implementation are aligned with the risk mitigation plan, and that the control is effective in reducing the risk exposure to within the risk appetite and tolerance of the enterprise. The risk owner should also ensure that the control design is consistent with the enterprise’s policies, standards, and procedures, and that it complies with any relevant laws, regulations, or contractual obligations. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.4, page 185.
An organization's finance team is proposing the adoption of a blockchain technology to provide a secure method for moving funds. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
Recommend permissionless blockchain.
Perform a risk assessment.
Perform a business impact analysis (BIA).
Recommend permissioned blockchain.
Answer:
Explanation:
Before selecting technologies or deployment models, a risk assessment should be conducted to evaluate potential threats, vulnerabilities, and controls. This ensures the technology aligns with the risk appetite and regulatory requirements of the organization.
Which of the following BEST protects organizational data within a production cloud environment?
Data encryption
Continuous log monitoring
Right to audit
Data obfuscation
Answer:
Explanation:
Data encryption is the best method to protect organizational data within a production cloud environment, as it ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. Data encryption is the process oftransforming data into an unreadable format using a secret key or algorithm, so that only authorized parties can access and decrypt the data. Data encryption can protect data at rest (stored in the cloud) and data in transit (transferred over the network) from unauthorized access, modification, or deletion by malicious actors or accidental errors. Data encryption can also help organizations comply with legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements for data protection and privacy, such as GDPR, CCPA, and PCI DSS.
An organization has outsourced its IT security operations to a third party. Who is ULTIMATELY accountable for the risk associated with the outsourced operations?
The third party s management
The organization's management
The control operators at the third party
The organization's vendor management office
Answer:
Explanation:
Outsourcing IT security operations is a common practice that can provide benefits such as cost savings, access to specialized skills, and improved service quality12. However, outsourcing also introduces risks such as loss of control, dependency, contractual issues, and service failures12.
When an organization outsources its IT security operations to a third party, it does not transfer the accountability for the risk associated with the outsourced operations. Accountability is the obligation to answer for the execution of one’s assigned responsibilities34.
The organization’s management is ultimately accountable for the risk associated with the outsourced operations, as they are responsible for defining the organization’s risk appetite, strategy, and objectives, and for ensuring that the organization’s IT security operations are aligned with them34.
The organization’s management is also accountable for selecting, contracting, and overseeing the third party, and for ensuring that the third party meets the agreed service levels, standards, and compliance requirements34.
The organization’s management is also accountable for monitoring and reporting the risk associated with the outsourced operations, and for taking corrective actions when necessary34.
The other options are not ultimately accountable, but rather have different roles and responsibilities in relation to the outsourced operations. For example:
The third party’s management is responsible for delivering the IT security services according to the contract, and for managing the risk within their own organization34. They are accountable to the organization’s management, but not to the organization’s stakeholders.
The control operators at the third party are responsible for implementing and operating the IT security controls according to the service specifications, and for reporting any issues orincidents to the organization’s management34. They are accountable to the third party’s management, but not to the organization’s management or stakeholders.
The organization’s vendor management office is responsible for facilitating the relationship between the organization and the third party, and for supporting the organization’s management in the outsourcing process34. They are accountable to the organization’s management, but not for the risk associated with the outsourced operations. References =
1: Outsourcing IT Security: A Risk Management Perspective, ISACA Journal, Volume 2, 2019
2: The Cyber Security Risks Of Outsourcing, Cybersecurity Intelligence, January 4, 2022
3: Accountability for Information Security Roles and Responsibilities, Part 1, ISACA Journal, Volume 5, 2019
4: Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2009
Which of the following is the BEST approach to resolve a disagreement between stakeholders regarding the impact of a potential risk scenario?
Modify the risk scenario to address stakeholder concerns.
Calculate the historical impact of risk occurring at industry peers.
Identify data that could be used to help quantify the risk.
Use the highest value of potential impact suggested by the stakeholders.
Answer:
Who should be accountable for monitoring the control environment to ensure controls are effective?
Risk owner
Security monitoring operations
Impacted data owner
System owner
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk owner is the person or entity that has the accountability and authority to manage a risk. The risk owner should be accountable for monitoring the control environment to ensure controls are effective, as they are responsible for implementing, maintaining, and improving the risk controls, and for reporting and communicating the risk status and performance. The risk owner should also ensure that the controls are aligned with the risk appetite and tolerance of the enterprise, and that they support the achievement of the enterprise’s objectives and value creation. References = Most Asked CRISC Exam Questions and Answers. CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, Question 244.
Accountability for a particular risk is BEST represented in a:
risk register
risk catalog
risk scenario
RACI matrix
Answer:
Explanation:
A RACI matrix is a tool that assigns the roles and responsibilities for each risk, such as who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed. A RACI matrix helps to clarify the expectations and accountabilities for each risk owner and stakeholder, and to ensure that the risk is managed and monitored effectively and efficiently.
A risk register is a document that records and tracks the identified risks, their likelihood, impact, and mitigation strategies. A risk register does not assign the accountability for each risk, but rather the ownership and response.
A risk catalog is a collection of risks that have been identified and categorized based on common attributes, such as source, type, or impact. A risk catalog does not assign the accountability for each risk, but rather the classification and description.
A risk scenario is a technique that simulates the possible outcomes of different risk events and assesses their impact on the enterprise’s objectives and operations. A risk scenario does not assign the accountability for each risk, but rather the analysis and evaluation.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when communicating the risk associated with technology end-of-life to business owners?
Cost and benefit
Security and availability
Maintainability and reliability
Performance and productivity
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most important consideration when communicating the risk associated with technology end-of-life to business owners is the cost and benefit of the risk response options. Technology end-of-life is the situation when a technology product or service is no longer supported by the vendor or manufacturer, and may pose security, compatibility, or performance issues. The risk practitioner should communicate the cost and benefit of the possible risk responses, such as replacing, upgrading, or maintaining the technology, to the business owners, and help them to make informed and rational decisions. Security and availability, maintainability and reliability, and performance and productivity are other possible considerations, but they are not as important as the cost and benefit. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 8; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 97.
Which of the following is the BEST Key control indicator KCO to monitor the effectiveness of patch management?
Percentage of legacy servers out of support
Percentage of severs receiving automata patches
Number of unpremeditated vulnerabilities
Number of intrusion attempts
Answer:
Explanation:
The percentage of servers receiving automatic patches is the best key control indicator (KCI) to monitor the effectiveness of patch management, because it measures how well the patch management process is ensuring that the servers are updated with the latest security patches and fixes. A high percentage of servers receiving automatic patches indicates that the patch management process is effective and efficient, and that the servers are protected from known vulnerabilities and threats. The other options are not the best KCIs, because they do not directly measure the effectiveness of patch management. The percentage of legacy servers out of support, the number of unpatched vulnerabilities, and the number of intrusion attempts are examples of risk indicators or consequence indicators that measure the exposure or impact of the lack of patch management, but not the performance or outcome of the patch management process. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers
Which of the following would be MOST useful to management when allocating resources to mitigate risk to the organization?
Risk assessments
Control self-assessments (CSAs)
Risk-based audits
Vulnerability analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk assessmentsprovide a prioritized view of potential threats, their likelihood, and impact. This enables management tofocus resourceson high-priority risks, ensuring cost-effective mitigation aligned with organizational goals.
A risk practitioner notes control design changes when comparing risk response to a previously approved action plan. Which of the following is MOST important for the practitioner to confirm?
Appropriate approvals for the control changes
The reason the action plan was modified
The risk owner's approval of the revised action plan
The effectiveness of the resulting control
Answer:
Explanation:
The MOST important aspect for the risk practitioner to confirm is:
A. Appropriate approvals for the control changes
Ensuring that the control design changes have the appropriate approvals is crucial. This confirms that the changes are recognized and sanctioned by the necessary authority within the organization, aligning with governance practices and maintaining the integrity of the risk management process.
Which of the following BEST enables effective risk reporting to the board of directors?
Presenting case studies of breaches from other similar organizations
Mapping risk scenarios to findings identified by internal audit
Communicating in terms that correlate to corporate objectives and business value
Reporting key metrics that indicate the efficiency and effectiveness of risk governance
Answer:
Explanation:
Effective risk reporting to the board of directors requires communication that aligns with the organization's strategic goals and business value. By correlating risk information to corporate objectives, the board can better understand the implications of risks on the organization's performance and make informed decisions. This approach ensures that risk discussions are relevant and meaningful at the executive level.​
The BEST way to determine the likelihood of a system availability risk scenario is by assessing the:
availability of fault tolerant software.
strategic plan for business growth.
vulnerability scan results of critical systems.
redundancy of technical infrastructure.
Answer:
Explanation:
A system availability risk scenario is a situation where a system or a service is not accessible or functional due to a failure or an attack. The likelihood of such a scenario depends on the vulnerabilities or weaknesses that exist in the system or the service, and the threats or attackers that could exploit them. Therefore, by scanning the critical systems or services for vulnerabilitiesand analyzing the results, one can estimate the probability or frequency of a system availability risk scenario1.
A vulnerability scan is a process of identifying and evaluating the potential security risks in a system or a service. A vulnerability scan report provides a list of vulnerabilities that have been detected, categorized by their severity levels, and accompanied by remediation recommendations. By reviewing the report, one can understand the current security posture of the system or the service, and the actions that need to be taken to address the vulnerabilities2.
The other options are not the best ways to determine the likelihood of a system availability risk scenario, but rather some of the factors or outcomes of it. Availability of fault tolerant software is a factor that can reduce the likelihood of a system availability risk scenario, as it means that the software can continue to operate without interruption even if some of its components fail. Fault tolerant software can achieve this by using backup or redundant components, or by implementing error detection and correction mechanisms3. Strategic plan for business growth is an outcome of a system availability risk scenario, as it can affect the organization’s objectives and strategies. A system availability risk scenario can have negative impacts on the organization’s performance, reputation, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage, and thus hamper its growth potential4. Redundancy of technical infrastructure is a factor that can reduce the likelihood of a system availability risk scenario, as it means that the infrastructure has duplicate or alternativedevices or paths that can take over in case of a failure or an attack. Redundancy of technical infrastructure can ensure network availability and prevent data loss5. References =
Describe the risk scenarios | NZ Digital government
How to Read a Vulnerability Scan Report | Evolve Security
Learn about Fault Tolerant Servers | What is Fault Tolerance?-Stratus
The Importance of Redundancies in Your Infrastructure - INAP
What is Redundancy? - Your IT Department
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
An organization's stakeholders are unable to agree on appropriate risk responses. Which of the following would be the BEST course of action?
Escalate to senior management.
Identify a risk transfer option.
Reassess risk scenarios.
Benchmark with similar industries.
Answer:
Explanation:
Escalating to senior management is the best course of action when an organization’s stakeholders are unable to agree on appropriate risk responses. This is because senior management has the authority and responsibility to make strategic decisions and resolve conflicts regarding risk management. Senior management can also provide guidance and direction on the risk appetite, tolerance, and criteria for the organization, as well as allocate resources and assign roles and responsibilities for risk response. According to the CRISC Review Manual 2022, one of the key risk response techniques is to escalate the risk to senior management when the risk exceeds the acceptable level or when there is a disagreement on the risk response1. According to the CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual 2022, escalating to senior management is the correct answer to this question2.
Identifying a risk transfer option, reassessing risk scenarios, and benchmarking with similar industries are not the best courses of action when an organization’s stakeholders are unable to agree on appropriate risk responses. These are possible actions that can be taken as part of the risk response process, but they do not address the underlying issue of stakeholder disagreement. Identifying a risk transfer option can help reduce or share the risk with a third party, such as an insurance company or a vendor, but it may not be suitable or acceptable for all types of risks or stakeholders. Reassessing risk scenarios can help update the risk analysis and evaluation, but it may not change the risk level or the risk response options. Benchmarking with similar industries can help compare the risk performance and practices of the organization with its peers, but it may not reflect the organization’s specific needs or risks.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to compare the business impact analysis (BIA) against the organization's business continuity plan (BCP)?
The results of the BIA quantify the BCP objectives and supporting technology for each operational area.
The BCP provides detailed information on alternative facilities to use in case of business interruptions.
The results of the BIA quantify the cost of the technology environment needed to restart each operational area.
The BCP provides the backup and restoration procedures to follow in case of business interruptions.
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to ISACA CRISC guidance)
The BIA identifies critical processes, maximum tolerable downtime, and the business impact of disruptions. CRISC and business continuity practices emphasize that the BCP must be aligned with BIA results. Comparing the BIA with the BCP ensures that recovery strategies, objectives (RTOs/RPOs), and supporting technologies specified in the BCP actually reflect the priorities and impact levels identified in the BIA for each operational area. Alternative facilities and backup/restoration procedures are important BCP components, but the primary reason for comparison is to validate that the chosen solutions and recovery targets match business requirements. The BIA does not primarily “quantify the cost of the technology environmentâ€; cost analysis may follow but is not the core BIA purpose. Therefore, ensuring that BCP objectives and enabling technology are consistent with BIA findings is the key objective of the comparison.
Which of the following is the MOST important course of action for a risk practitioner when reviewing the results of control performance monitoring?
Evaluate changes to the organization's risk profile.
Validate whether the controls effectively mitigate risk.
Confirm controls achieve regulatory compliance.
Analyze appropriateness of key performance indicators (KPIs).
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important course of action for a risk practitioner when reviewing the results of control performance monitoring is to validate whether the controls effectively mitigate risk, as it involves verifying and testing the adequacy and performance of the controls, and identifying any control gaps or deficiencies that may affect the risk level and response. The other options are not the most important courses of action, as they are more related to the evaluation, confirmation, or analysis of the risk profile, compliance, or indicators, respectively, rather than the validation of the control effectiveness. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 154.
Which of the following BEST assists in justifying an investment in automated controls?
Cost-benefit analysis
Alignment of investment with risk appetite
Elimination of compensating controls
Reduction in personnel costs
Answer:
Explanation:
A cost-benefit analysis is the best method to assist in justifying an investment in automated controls, as it helps to compare and evaluate the costs and benefits of the investment and to determine its feasibility and profitability. A cost-benefit analysis is a process of identifying, measuring, and comparing the expected costs and benefits of a project or a decision, such asinvesting in automated controls. A cost-benefit analysis can help to justify an investment in automated controls by providing the following benefits:
It enables a data-driven and evidence-based approach to decision making, rather than relying on subjective or qualitative judgments.
It facilitates a consistent and standardized way of assessing and communicating the value and impact of the investment across the organization and to the external stakeholders.
It supports the alignment of the investment with the organizational strategy and objectives, and helps to evaluate the achievement of the desired outcomes.
It helps to identify and prioritize the opportunities and challenges of the investment, and to develop and implement appropriate strategies and actions to address them.
It provides feedback and learning opportunities for the investment and its outcomes, and helps to foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
The other options are not the best methods to assist in justifying an investment in automated controls. Alignment of investment with risk appetite is an important aspect of risk management, but it does not directly address the costs and benefits of the investment. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Alignment of investment with risk appetite helps to ensure that the investment is consistent with the organizational risk tolerance and preferences,and does not expose the organization to excessive or unacceptable risk. Elimination of compensating controls is a possible benefit of investing in automated controls, but it is not a method to justify the investment. Compensating controls are alternative or additional controls that are implemented to mitigate the risk when the primary or preferred controls are not feasible or effective. Elimination of compensating controls can help to reduce the complexity and costs of the control environment, and to improve the efficiency and reliability of the controls. Reduction in personnel costs is a possible benefit of investing in automated controls, but it is not a method to justify the investment. Personnel costs are the expenses related to the staff and employees involved in the processes or functions that are automated. Reduction in personnel costs can help to increase the profitability and productivity of the organization, and to allocate the resources more effectively and efficiently. References = Cost Benefit Analysis: An Expert Guide | Smartsheet, IT Risk Resources | ISACA, Automation - Efficiency, Cost-Savings, Robotics | Britannica
Which of the following is the PRIMARY responsibility of a control owner?
To make risk-based decisions and own losses
To ensure implemented controls mitigate risk
To approve deviations from controls
To design controls that will eliminate risk
Answer:
Explanation:
A control owner's primary responsibility is to ensure that the controls under their purview are effectively implemented and functioning as intended to mitigate associated risks. This involves regular monitoring, evaluation, and reporting on the performance of controls to maintain the organization's risk posture within acceptable limits.
Which of the following provides The BEST information when determining whether to accept residual risk of a critical system to be implemented?
Single loss expectancy (SLE)
Cost of the information system
Availability of additional compensating controls
Potential business impacts are within acceptable levels
Answer:
Explanation:
The BEST information when determining whether to accept residual risk of a critical system to be implemented is the potential business impacts are within acceptable levels, because it indicates that the residual risk, which is the risk that remains after the risk response actions, does not exceed the risk tolerance and appetite of the organization, and that it does not pose a significant threat or disruption to the business objectives and processes. The potential business impacts are the consequences or outcomes of the residual risk on the organization’s performance, reputation, and value. The other options are not as informative as the potential business impacts, because:
Option A: Single loss expectancy (SLE) is a measure of the monetary loss that is expected from a single occurrence of a risk event, but it does not provide the best information when determining whether to accept residual risk, because it does not consider the frequency or probability of the risk event, or the qualitative aspects of the risk impact, such as customer satisfaction, employee morale, or regulatory compliance.
Option B: Cost of the information system is a measure of the total expenditure that is required to acquire, develop, operate, and maintain the information system, but it does not provide the best information when determining whether to accept residual risk, because it does not reflect the value or benefit of the information system, or the risk exposure or variation that the information system may introduce or encounter.
Option C: Availability of additional compensating controls is a measure of the alternative or supplementary controls that can be implemented to reduce the residual risk, but it does not provide the best information when determining whether to accept residual risk, because it does not indicate the effectiveness or efficiency of the compensating controls, or the cost-benefitanalysis of implementing them. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, p. 122.
A risk practitioner has identified that the agreed recovery time objective (RTO) with a Software as a Service (SaaS) provider is longer than the business expectation. Which ot the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Collaborate with the risk owner to determine the risk response plan.
Document the gap in the risk register and report to senior management.
Include a right to audit clause in the service provider contract.
Advise the risk owner to accept the risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action for the risk practitioner who has identified that the agreed RTO with a SaaS provider is longer than the business expectation is to collaborate with the risk owner to determine the risk response plan. The risk owner is the person who has the authority and accountability to manage the risk within their scope of responsibility. The risk response plan is the document that describes the actions and resources needed to address the risk. By collaborating with the risk owner, the risk practitioner can help toanalyze the gap between the agreed RTO and the business expectation, evaluate the potential impact and consequences, and select the most appropriate risk response option, such as avoiding, reducing, transferring, or accepting the risk. Documenting the gap in the risk register, including a right to audit clause in the service provider contract, or advising the risk owner to accept the risk are not the best courses of action, because they do not address the root cause of the problem, or provide a solution to reduce the risk to an acceptable level. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.1, page 4-23.
The MAIN reason for prioritizing IT risk responses is to enable an organization to:
determine the risk appetite.
determine the budget.
define key performance indicators (KPIs).
optimize resource utilization.
Answer:
Explanation:
Optimizing resource utilization is the main reason for prioritizing IT risk responses, as it helps to allocate resources to the most critical and urgent risks. The other options are not the main reasons for prioritizing IT risk responses, although they may be related to the process.
Which of the following roles is BEST suited to help a risk practitioner understand the impact of IT-related events on business objectives?
IT management
Internal audit
Process owners
Senior management
Answer:
Explanation:
 Process owners are the best suited to help a risk practitioner understand the impact of IT-related events on business objectives, as they have the responsibility and authority over the design, execution, and performance of business processes. Process owners are also accountable for the risks and controls associated with their processes, and they can provide valuable input and feedback on the likelihood and impact of IT-related events on the process outcomes and objectives.
The other options are not the best suited to help a risk practitioner understand the impact of IT-related events on business objectives. IT management is responsible for the delivery and support of IT services and solutions, but they may not have the full visibility or understanding of the business objectives and processes. Internal audit is responsible for providing independent and objective assurance and consulting services on the effectiveness and efficiency of governance, risk management, and control processes, but they may not have the direct involvement or influence on the business objectives and processes. Senior management is responsible for settingthe strategic direction and objectives of the organization, but they maynot have the detailed knowledge or experience of the business processes and their risks and controls. References = IT Risk Manager: Skills and Roles & Responsibilities, IT Risk Resources | ISACA, Managing information technology risk | Business Queensland
During a risk assessment, what should an assessor do after identifying threats to organizational assets?
Request funding for the security program
Determine threats to be reported to upper management
Implement controls to achieve target risk levels
Evaluate the controls currently in place
Answer:
Explanation:
The CRISC risk assessment process follows a sequence:
Identify assets →
Identify threats →
Identify vulnerabilities →
Evaluate existing controls →
Assess likelihood and impact.
Per ISACA CRISC guidance:
“After identifying threats, the next step is to evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls to determine residual risk.â€
Implementing new controls (Option C) happens after risk evaluation and treatment planning.
Hence, D. Evaluate the controls currently in place is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 2 – IT Risk Assessment, Topic: Risk Identification and Control Evaluation Steps.
Ensure compliance with local legislation because it has a higher priority.
Conduct a risk assessment and develop mitigation options.
Terminate the current cloud contract and migrate to a local cloud provider.
Accept the risk because foreign legislation does not apply to the organization.
Answer:
Explanation:
When regulatory conflicts arise, the best practice is to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to understand the impact and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. Immediate termination may be premature without understanding options, and accepting risk without assessment may expose the organization to legal or compliance issues. Prioritizing compliance requires understanding the full scope of risks and controls necessaryã€5:35, 5:48†CRISC_SentenceinNOTE30.pptx】.
During an internal IT audit, an active network account belonging to a former employee was identified. Which of the following is the BEST way to prevent future occurrences?
Conduct a comprehensive review of access management processes.
Declare a security incident and engage the incident response team.
Conduct a comprehensive awareness session for system administrators.
Evaluate system administrators' technical skills to identify if training is required.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to prevent future occurrences of active network accounts belonging to former employees is to conduct a comprehensive review of access management processes. This review should include verifying that the access rights of all employees are updated regularly, especially when they change roles or leave the organization. The review should also ensure that there are clear policies and procedures for granting, modifying, and revoking access rights, and that these are followed consistently and documented properly. The review should also identify and address any gaps or weaknesses in the access management processes that could lead to unauthorized orinappropriate access. By conducting a comprehensive review of access management processes, the organization can improve its security posture and reduce the risk of data breaches or misuse of resources. References = IT audit: The ultimate guide [with checklist] | Zapier, IT auditing and controls – planning the IT audit [updated 2021]
Which of the following is the STRONGEST indication an organization has ethics management issues?
Employees do not report IT risk issues for fear of consequences.
Internal IT auditors report to the chief information security officer (CISO).
Employees face sanctions for not signing the organization's acceptable use policy.
The organization has only two lines of defense.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual, ethics management is the process of ensuring that the enterprise’s values and principles are embedded in its culture and practices. Ethics management helps to promote trust, integrity, accountability, and transparency among the stakeholders. One of the key elements of ethics management is to encourage the reporting of IT risk issues and incidents, and to protect the whistleblowers from any retaliation or negative consequences. Therefore, if employees do not report IT risk issues for fear of consequences, it is the strongest indication that the organization has ethics management issues, as it implies that there is a lack of trust, openness, and support in the organization. The other options are not the strongest indications of ethics management issues, as they are related to other aspects of IT governance,such as audit independence, policy compliance, and risk management framework. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, Section 1.3.2, page 34.
When determining risk ownership, the MAIN consideration should be:
who owns the business process.
the amount of residual risk.
who is responsible for risk mitigation.
the total cost of risk treatment.
Answer:
The MOST significant benefit of using a consistent risk ranking methodology across an organization is that it enables:
allocation of available resources
clear understanding of risk levels
assignment of risk to the appropriate owners
risk to be expressed in quantifiable terms
Answer:
Explanation:
The most significant benefit of using a consistent risk ranking methodology across an organization is that it enables a clear understanding of risk levels, as this facilitates the comparison and prioritization of risks, the communication and reporting of risks, and the alignment of risk management with the enterprise’s objectives and strategy. A consistent risk ranking methodology is a set of criteria and scales that are used to measure and rate the likelihood and impact of risks, as well as other factors such as urgency, velocity, and persistence. A consistent risk ranking methodology ensures that the risk assessment results are objective, reliable, and comparable across different business units, processes, and projects. The other options are not the most significant benefits of using a consistent risk ranking methodology,although they may be secondary benefits or outcomes of doing so. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: IT Risk Assessment, page 97.
Which of the following outcomes of disaster recovery planning is MOST important to enable the initiation of necessary actions during a disaster?
Definition of disaster recovery plan (DRP) scope and key stakeholders
Recovery time and maximum acceptable data loss thresholds
A checklist including equipment, location of data backups, and backup sites
A list of business areas and critical functions subject to risk analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
Defining recovery time objectives (RTOs) and acceptable data loss thresholds is critical for effective disaster response, ensuring recovery activities are aligned with business priorities. This supportsBusiness Continuity Planning.
Which of the following is a specific concern related to machine learning algorithms?
Low software quality
Lack of access controls
Data breaches
Data bias
Answer:
Explanation:
Data biasin machine learning algorithms can lead to inaccurate predictions or decisions, as biases in training data are amplified in the output. Addressing bias is essential for ethical and reliable algorithm performance.
Which of the following BEST helps to identify significant events that could impact an organization?
Control analysis
Vulnerability analysis
Scenario analysis
Heat map analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
 Scenario analysis is the best method to identify significant events that could impact an organization. Scenario analysis is the process of creating and evaluating hypothetical situations or scenarios that represent plausible outcomes of various events or actions. Scenario analysis helps to anticipate and prepare for potential risks and opportunities, as well as to test the robustness and resilience of the organization’s strategies and plans. Control analysis, vulnerability analysis, and heat map analysis are not as effective as scenario analysis, because they focus on the existing or current state of the organization, rather than the future or alternative states. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1, page 4-13.
An application owner has specified the acceptable downtime in the event of an incident to be much lower than the actual time required for the response team to recover the application. Which of the following should be the NEXT course of action?
Invoke the disaster recovery plan during an incident.
Prepare a cost-benefit analysis of alternatives available
Implement redundant infrastructure for the application.
Reduce the recovery time by strengthening the response team.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the next course of action when there is a gap between the acceptable downtime and the actual recovery time of an application is to prepare a cost-benefit analysis of alternatives available to reduce the gap. The cost-benefit analysis should compare the costs of implementing different risk response options, such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer or acceptance, with the benefits of reducing the impact and likelihood of the risk. The cost-benefit analysis should also consider the alignment of the risk response options with the enterprise’s risk appetite, business objectives and strategy. The cost-benefit analysis should help the application owner and the risk owner to select the most appropriate risk response option that optimizes the value of the application and minimizes the residual risk.
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.2: Risk Response Process, pp. 162-1631
Which of the following scenarios presents the GREATEST risk of noncompliance with data privacy best practices?
Making data available to a larger audience of customers
Data not being disposed according to the retention policy
Personal data not being de-identified properly
Data being used for purposes the data subjects have not opted into
Answer:
Explanation:
Data Privacy Principles:
Consent and Purpose Limitation: According to data privacy regulations like GDPR, data subjects must provide explicit consent for specific purposes. Using data for purposes beyond what was consented to violates these principles, posing significant compliance risks.
Transparency and Accountability: Organizations must be transparent about how they use personal data and ensure accountability in data processing. Using data without consent undermines this transparency and accountability.
Greatest Risk of Noncompliance:
Legal and Regulatory Risks: Using personal data without consent can lead to severe penalties under laws like GDPR and CPRA. These laws impose heavy fines for noncompliance, making this scenario the highest risk.
Reputational Damage: Unauthorized use of personal data can severely damage an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and potential financial losses.
Operational Impact: Ensuring compliance with consent requirements is fundamental to an organization's data processing activities. Failure to do so can disrupt business operations and necessitate significant remediation efforts.
Comparison with Other Options:
Making Data Available to a Larger Audience of Customers: While potentially risky, this does not inherently violate data privacy principles if done within consented uses.
Data Not Being Disposed According to the Retention Policy: This poses risks related to data minimization and retention principles but is less severe than unauthorized data use.
Personal Data Not Being De-identified Properly: This is a significant risk but typically involves fewer direct legal and regulatory implications compared to using data without consent.
Which of the following is MOST important for an organization to continuously manage after implementing a Zero Trust security model?
Privileged user access reviews
Integration with existing security protocols
Policy enforcement inconsistencies
Network segmentation errors
Answer:
Explanation:
In a Zero Trust model, access is never implicitly trusted and must be continuously verified — making privileged access review critical.
ISACA CRISC guidance:
“Under the Zero Trust model, continuous validation and review of privileged user access is essential to prevent privilege escalation and insider threats.â€
Integration and segmentation are design concerns; privileged access management is the ongoing control requirement.
Thus, A is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 4 – Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Topic: Zero Trust and Continuous Authorization.
The results of a risk assessment reveal risk scenarios with high impact and low likelihood of occurrence. Which of the following would be the BEST action to address these scenarios?
Assemble an incident response team.
Create a disaster recovery plan (DRP).
Develop a risk response plan.
Initiate a business impact analysis (BIA).
Answer:
Explanation:
Developing a risk response plan is the best action to address the risk scenarios with high impact and low likelihood of occurrence, because it helps to define and implement the appropriate actions to reduce or eliminate the risk, or to prepare for and recover from the potential consequences. A risk response plan is a document that outlines the strategies and tactics for managing the identified risks, such as avoiding, transferring, mitigating, or accepting the risk. A risk response plan also assigns the roles and responsibilities for the risk owners and stakeholders, and sets the timelines and budgets for the risk response activities. A risk scenario with high impact and low likelihood of occurrence is a rare but severe event that may cause significant disruption or damage to the organization or its objectives, such as a natural disaster, a cyberattack, or a pandemic. Therefore, developing a risk response plan is the best action to address these scenarios, as it helps to minimize the exposure and impact of the risk, and to enhance the resilience and recovery of the organization. Assembling an incident response team, creating a disaster recovery plan (DRP), and initiating a business impact analysis (BIA) are all important actions to perform as part of the risk response plan, but they are not the best action, as they do not cover the whole spectrum of risk response strategies and activities. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.2, page 103
Which of the following would be the GREATEST concern for an IT risk practitioner when an employees.....
The organization's structure has not been updated
Unnecessary access permissions have not been removed.
Company equipment has not been retained by IT
Job knowledge was not transferred to employees m the former department
Answer:
Explanation:
The greatest concern for an IT risk practitioner when an employee transfers to another department is that unnecessary access permissions have not been removed. Unnecessary access permissions are the access rights or privileges that are no longer needed, relevant, or appropriate for the employee’s new role or responsibility. If these access permissions are not removed, they may pose a significant security risk, as the employee may be able to access, modify, or delete sensitive or critical data and systems that are not related to their current function. This may result in data leakage, fraud, sabotage, or compliance violations. The other options are not as concerning as unnecessary access permissions, as they are related to the organizational, operational, or knowledge aspects of the employee transfer, not the security or risk aspects of the employee transfer. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: IT Risk Response Implementation, page 145.
An organization has outsourced a critical process involving highly regulated data to a third party with servers located in a foreign country. Who is accountable for the confidentiality of this data?
Third-party data custodian
Data custodian
Regional office executive
Data owner
Answer:
Explanation:
 The data owner is accountable for the confidentiality of the data that is outsourced to a third party with servers located in a foreign country. The data owner is the person or entity that has the authority and responsibility to classify, label, and protect the data according to the organization’s policies and standards. The data owner is also responsible for defining the data access rights and privileges, and for ensuring that the data is handled in compliance with the applicable laws and regulations. The data owner retains the accountability for the data even when it is outsourced to a third party, and must monitor and evaluate the security performance and compliance of the service provider. The third-party data custodian, the data custodian, and the regional office executive are not accountable for the confidentiality of the data, as they have different roles and responsibilities in the outsourcing process. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.2.1.2, page 2461
1: ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC®) Exam Guide, Answer to Question 654.
It is MOST appropriate for changes to be promoted to production after they are:
communicated to business management
tested by business owners.
approved by the business owner.
initiated by business users.
Answer:
Explanation:
The most appropriate time for changes to be promoted to production is after they are approved by the business owner, who is the individual or group that is accountable and responsible for the business objectives and requirements that are supported or affected by the changes. The approval by the business owner ensures that the changes are aligned and compatible with the business objectives and requirements, and that they provide the expected or desired outcomes or benefits for the business.
The other options are not the most appropriate times for changes to be promoted to production, because they do not ensure that the changes are aligned and compatible with the businessobjectives and requirements, and that they provide the expected or desired outcomes or benefits for the business.
Communicating the changes to business management means informing or reporting the changes to the senior management or executives that oversee or direct the business activities or functions. Communicating the changes to business management is important for ensuring the awareness and support of the business management, but it is not the most appropriate time for changes to be promoted to production, because it does not indicatewhether the changes are approved or authorized by the business owner, who is accountable and responsible for the business objectives and requirements.
Testing the changes by business owners means verifying and validating the functionality and usability of the changes, using the input and feedback from the business owners. Testing the changes by business owners is important for ensuring the quality and performance of the changes, but it is not the most appropriate time for changes to be promoted to production, because it does not indicate whether the changes are approved or authorized by the business owner, who is accountable and responsible for the business objectives and requirements.
Initiating the changes by business users means requesting or proposing the changes by the end users or customers that interact with the information systems and resources that are affected by the changes. Initiating the changes by business users is important for ensuring the relevance and appropriateness of the changes, but it is not the most appropriate time for changes to be promoted to production, because it does not indicate whether the changes are approved or authorized by the business owner, who is accountable and responsible for the business objectives and requirements. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 194
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Several vulnerabilities have been identified in an organization’s core financial systems. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner’s BEST course of action?
Evaluate the associated risk.
Determine the cost of remediation.
Initiate the incident response plan.
Remediate the vulnerabilities.
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to ISACA CRISC guidance)
When vulnerabilities are discovered, the CRISC approach requires first understanding the risk those vulnerabilities represent before deciding on actions. Evaluating the associated risk means analyzing the likelihood that the vulnerabilities will be exploited and the potential impact on financial reporting, confidentiality, integrity, and availability of core systems. Only after this analysis can the risk practitioner prioritize which vulnerabilities to address, decide on appropriate treatment options, and determine whether remediation is cost-effective and aligned to risk appetite. Immediately remediating without assessment may misallocate resources or disrupt critical services. Initiating incident response is appropriate when an actual incident or compromise is detected, not merely the existence of vulnerabilities. Estimating remediation cost is important but comes after understanding the significance of the risk.
Which of the following will BEST help to ensure implementation of corrective action plans?
Contracting to third parties
Establishing employee awareness training
Setting target dates to complete actions
Assigning accountability to risk owners
Answer:
Explanation:
Assigning accountability to risk owners is the best way to ensure implementation of corrective action plans, because it clarifies the roles and responsibilities of those who are in charge of managing and mitigating the risks. Contracting to third parties, establishing employee awareness training, and setting target dates tocomplete actions are all helpful measures, but they do not guarantee the implementation of corrective action plans without accountability. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.3, page 105
Which of the following is the BEST approach for selecting controls to minimize risk?
Industry best practice review
Risk assessment
Cost-benefit analysis
Control-effectiveness evaluation
Answer:
Explanation:
The best approach for selecting controls to minimize risk is to perform a risk assessment. A risk assessment is a process that identifies, analyzes, and evaluates the risks that could affect the organization’s objectives or operations. A risk assessment helps to determine the likelihood and impact of the risks, and to prioritize them based on their severity and relevance. A risk assessment also helps to select the most appropriate and effective controls to minimize the risks, such as avoiding, reducing, transferring, or accepting the risks. A risk assessment is the best approach for selecting controls, because it helps to align the controls with the organization’s risk profile, risk appetite, and risk objectives, and to ensure that the controls are adequate, suitable, and cost-effective. The other options are not the best approach for selecting controls, although they may be part of or derived from the risk assessment. Industry best practice review, cost-benefit analysis, and control-effectiveness evaluation are all activities that can help to support or improve the control selection, but they are not the best approach for selecting controls. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1, page 4-13.
Which of the following BEST mitigates the risk of sensitive personal data leakage from a software development environment?
Tokenized personal data only in test environments
Data loss prevention tools (DLP) installed in passive mode
Anonymized personal data in non-production environments
Multi-factor authentication for access to non-production environments
Answer:
Explanation:
 Anonymizing personal data in non-production environments means replacing the real data with fictitious but realistic data that does not allow identification of the individuals. This is a good way to mitigate the risk of sensitive personal data leakage from a software development environment, as it reduces the exposure of the data to unauthorized access or misuse. Tokenizing personal data only in test environments is not sufficient, as the data may still be exposed in other non-production environments, such as development or staging. Data loss prevention tools (DLP) installed in passive mode may detect and report data leakage incidents, but they do not prevent them from happening. Multi-factor authentication for access to non-production environments may enhance the security of the access, but it does not protect the data from being leaked by authorized users or compromised by other means. References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), page 226; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, question 195.
Which of the following is the BEST course of action when risk is found to be above the acceptable risk appetite?
Review risk tolerance levels
Maintain the current controls.
Analyze the effectiveness of controls.
Execute the risk response plan
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action when risk is found to be above the acceptable risk appetite is to execute the risk response plan, which is the set of actions and measures that are designed to reduce, avoid, transfer, or accept the risk. The risk response plan is based on the risk assessment results, the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization, and the cost-benefit analysis of the risk response options. The risk response plan helps to achieve the optimal balance between the potential benefits and threats of the risk, and to align the risk decisions with the organizationalobjectives and context. The other options are not the best courses of action, as they are either too passive or too reactive in dealing with the risk. Reviewing risk tolerance levels may help to adjust the acceptable variation between the risk thresholds and the business objectives, but itdoes not address the actual risk level or impact. Maintaining the current controls may help to prevent the risk from increasing further, but it does not reduce the existing risk exposure or mitigation. Analyzing the effectiveness of controls may help to identify the gaps or weaknesses in the current risk management, but it does not implement the necessary improvements or changes. References = Risk Response Plan in Project Management: Key Strategies & Tips; A Practitioner’s Guide to Ethical Decision Making; How to Manage Project Risk: A 5-Step Guide
Average time to contain security incidents
Percentage of systems being monitored
Number of false positives reported
Number of personnel dedicated to security monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
The average time to contain security incidents directly reflects how quickly and effectively an organization can respond to cybersecurity threats, which is a critical measure of the program’s effectiveness. Other options like percentage of systems monitored or number of personnel indicate resources or scope but do not measure outcome or effectiveness. False positives may indicate detection issues but are less tied to program effectiveness than incident containment time.
Which of the following is MOST important to consider before determining a response to a vulnerability?
The likelihood and impact of threat events
The cost to implement the risk response
Lack of data to measure threat events
Monetary value of the asset
Answer:
Explanation:
 A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in the IT system or environment that could be exploited by a threat. A threat event is an occurrence or action that exploits a vulnerability and causes harm or damage to the IT system or environment. The lack of data to measure threat events is the most important factor, because it may affect the accuracy and reliability of the risk assessment and evaluation, and consequently, the risk response and strategy. The lack of data to measure threat events may also create challenges or risks for the organization, such as compliance, legal, reputational, or operational risks, or conflicts or inconsistencies with the organization’s risk appetite, risk objectives, or risk policies. The other options are not as important as the lack of data to measure threat events, although they may also influence the risk response and strategy. The likelihood and impact of threat events, the cost to implement the risk response, and the monetary value of the asset are all factors that could affect the feasibility and sustainability of the risk response and strategy, but they do not necessarily affect the validity and quality of the risk assessment and evaluation
Which of the following should be considered when selecting a risk response?
Risk scenarios analysis
Risk response costs
Risk factor awareness
Risk factor identification
Answer:
Explanation:
When selecting a risk response, the following should be considered:
B. Risk response costs
It’s important to evaluate the costs associated with implementing a risk response to ensure that they are justified by the benefits of mitigating the risk. This helps in making cost-effective decisions that align with the organization’s risk management objectives.
A MAJOR advantage of using key risk indicators (KRIs) is that they:
Identify scenarios that exceed defined risk appetite.
Help with internal control assessments concerning risk appetite.
Assess risk scenarios that exceed defined thresholds.
Identify when risk exceeds defined thresholds.
Answer:
Explanation:
KRIs provide measurable indicators that flag when risks exceed predefined thresholds, enabling swift and effective risk response. This supports theMonitoring and Reportingfunction in risk management, ensuring risks are managed proactively.
Zero Trust architecture is designed and deployed with adherence to which of the following basic tenets?
Incoming traffic must be inspected before connection is established.
Security frameworks and libraries should be leveraged.
Digital identities should be implemented.
All communication is secured regardless of network location.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Zero Trust Architecture:
Zero Trust is a security concept centered on the belief that organizations should not automatically trust anything inside or outside their perimeters and must verify everything attempting to connect to their systems.
ï‚· Basic Tenets of Zero Trust:
The primary principle is "never trust, always verify." This means every access request is authenticated, authorized, and encrypted regardless of where it originates.
Zero Trust requires securing all communication, whether it occurs within the internal network or comes from external sources. This approach prevents lateral movement by potential attackers who have breached the network perimeter.
ï‚· Key Components:
Authentication and Authorization:Continuous verification of user identities and access privileges.
Microsegmentation:Dividing the network into small, isolated segments to limit the spread of threats.
Encryption:Ensuring that all data, whether at rest or in transit, is encrypted to protect its confidentiality and integrity.
ï‚· Other Options:
Incoming Traffic Inspection:While important, this is just one aspect of Zero Trust.
Security Frameworks and Libraries:These are tools and guidelines to implement security but do not define the core tenets of Zero Trust.
Digital Identities:Implementing digital identities is part of the broader Zero Trust strategy but not a standalone tenet.
ï‚· References:
The CISSP Study Guide explains the Zero Trust architecture and its emphasis on securing all communications regardless of network location (Sybex CISSP Study Guide, Chapter 8: Principles of Security Models, Design, and Capabilities)​​.
A risk practitioner has been notified that an employee sent an email in error containing customers' personally identifiable information (Pll). Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Report it to the chief risk officer.
Advise the employee to forward the email to the phishing team.
follow incident reporting procedures.
Advise the employee to permanently delete the email.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action for the risk practitioner is to follow the incident reporting procedures established by the organization. This will ensure that the incident is properly documented, escalated, and resolved in a timely and consistent manner. Reporting the incident to the chief risk officer, advising the employee to forward the email to the phishing team, or advising the employee to permanently delete the email are not the best courses of action, as they may not comply with the organization’s policies and standards, and may not address the root cause and impact of the incident. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.2.1, page 193.
When creating a program to manage data privacy risk, which of the following is MOST important to ensure that the program is successful?
Compliance with industry frameworks
Alignment with applicable legal and regulatory requirements
Approval of mitigating and compensating controls
Adoption of mission and vision statements
Answer:
Explanation:
Privacy risk management programs must align withspecific regulatory obligations(e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) to be effective and compliant. Legal alignment defines scope, control requirements, and accountability.
Which of the following should be a risk practitioner's NEXT step after learning of an incident that has affected a competitor?
Activate the incident response plan.
Implement compensating controls.
Update the risk register.
Develop risk scenarios.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s next step after learning of an incident that has affected a competitor is to develop risk scenarios, as it involves identifying and describing the potential sources, events, impacts, and responses of the risk that may affect the organization in a similar way as the competitor, and assessing the likelihood and magnitude of the risk. Activating the incident response plan, implementing compensating controls, and updating the risk register are not the next steps, as they are more related to the reaction, mitigation, or reporting of the risk, respectively, rather than the identification and assessment of the risk. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 100.
Which of the following is the BEST reason to use qualitative measures to express residual risk levels related to emerging threats?
Qualitative measures require less ongoing monitoring.
Qualitative measures are better aligned to regulatory requirements.
Qualitative measures are better able to incorporate expert judgment.
Qualitative measures are easier to update.
Answer:
Explanation:
Qualitative measures are methods of expressing risk levels using descriptive terms, such as high, medium, or low, based on subjective criteria, such as likelihood, impact, or severity. Qualitative measures are often used to identify and prioritize risks, and to communicate risk information to stakeholders1.
Residual risk is the level of risk that remains after the risk response has been implemented. Residual risk reflects the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk response, and the need for further action or monitoring2.
Emerging threats are new or evolving sources or causes of risk that have the potential to adversely affect the organization’s objectives, assets, or operations. Emerging threats are oftencharacterized by uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity, and may require innovative or adaptive risk responses3.
The best reason to use qualitative measures to express residual risk levels related to emerging threats is that qualitative measures are better able to incorporate expert judgment. Expert judgment is the opinion or advice of a person or a group of people who have specialized knowledge, skills, or experience in a particular domain or field. Expert judgment can help to:
Provide insights and perspectives on the nature and characteristics of the emerging threats, and their possible causes and consequences
Assess the likelihood and impact of the emerging threats, and their interactions and dependencies with other risks
Evaluate the suitability and effectiveness of the risk responses, and their alignment with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance
Identify and recommend the best practices and lessons learned for managing the emerging threats, and for improving the risk management process45
Qualitative measures are better able to incorporate expert judgment than quantitative measures, which are methods of expressing risk levels using numerical or measurable values, such as percentages, probabilities, or monetary amounts. Quantitative measures are often used to estimate and analyze risks, and to support risk decision making1. However, quantitative measures may not be suitable or feasible for expressing residual risk levels related to emerging threats, because:
Quantitative measures require reliable and sufficient data and information, which may not be available or accessible for the emerging threats
Quantitative measures rely on mathematical models and techniques, which may not be able to capture or reflect the complexity and uncertainty of the emerging threats
Quantitative measures may create a false sense of precision or accuracy, which may not be justified or warranted for the emerging threats
Quantitative measures may be influenced or manipulated by biases or assumptions, which may not be valid or appropriate for the emerging threats67
Therefore, qualitative measures are better able to incorporate expert judgment, which can enhance the understanding and management of the residual risk levels related to emerging threats.
The other options are not the best reasons to use qualitative measures to express residual risk levels related to emerging threats, but rather some of the advantages or disadvantages of qualitative measures. Qualitative measures require less ongoing monitoring than quantitative measures, because they are simpler and easier to apply and update. However, this does not mean that qualitative measures can eliminate or reduce the need for monitoring, which is an essential part of the risk management process. Qualitative measures are better aligned to regulatory requirements than quantitative measures, because they are more consistent and comparable across different domains and contexts. However, this does not mean that qualitative measures can satisfy or comply with all the regulatory requirements, which may vary depending on theindustry or sector. Qualitative measures are easier to update than quantitative measures, because they do not depend on complex calculations or formulas. However, this does not mean that qualitative measures can always reflect the current or accurate risk levels, which may change over time or due to external factors. References =
Qualitative Risk Analysis vs. Quantitative Risk Analysis - ISACA
Residual Risk - ISACA
Emerging Threats - ISACA
Expert Judgment - ISACA
Expert Judgment in Project Management: Narrowing the Theory-Practice Gap
Quantitative Risk Analysis - ISACA
Quantitative Risk Analysis: A Critical Review
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when determining the risk associated with re-identification of obfuscated personal data?
The type of shared data
The level of residual risk after data loss prevention (DLP) controls are implemented
The monetary value of the unique records that could be re-identified
The impact to affected stakeholders
Answer:
Explanation:
The impact to affected stakeholdersis the most critical factor when considering risks tied to re-identification. ISACA notes that risk is ultimately measured by how it affects stakeholders—including customers, partners, and regulators—particularly when personal data is involved.
===========
A business delegates its application data management to the internal IT team. Which of the following is the role of the internal IT team in this situation?
Data controllers
Data custodians
Data analysts
Data owners
Answer:
Explanation:
In this context, the internal IT team acts as data custodians. Data custodians are responsible for the safe custody, transport, storage, and overall safeguarding of data. They ensure that data is properly maintained and that access controls are in place, but they do not make decisions about data usage—that responsibility lies with data owners.
Who is accountable for risk treatment?
Enterprise risk management team
Risk mitigation manager
Business process owner
Risk owner
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk treatment is the process of selecting and implementing the appropriate risk response strategy and actions to address the identified risks. Risk treatment can involve different strategies, such as avoiding, reducing, transferring, or accepting the risk. Risk owner is the person or group who has the authority and accountability to manage the risk and its response. Risk owner is accountable for risk treatment, as they are responsible for deciding, approving, and executing the risk treatment plan, and for monitoring and reportingthe results and outcomes of the risk treatment. The other options are not accountable for risk treatment, as they have different roles or responsibilities in the risk management process:
Enterprise risk management team is the group of risk managers and practitioners who support the enterprise-wide risk management program, and provide guidance and direction to the risk owners and stakeholders. Enterprise risk management team may advise or assist the risk owner in risk treatment, but they are not accountable for risk treatment.
Risk mitigation manager is the person who designs, implements, and monitors the risk mitigation actions or measures that reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk to an acceptable level, such as controls, policies, or procedures. Risk mitigation manager may advise or assist the risk owner in risk treatment, but they are not accountable for risk treatment.
Business process owner is the stakeholder who is responsible for the business process that is supported by the IT system or application, such as the CRM system. Business process owner may be affected by or contribute to the risk, and may be involved in the risk treatment, but they are not accountable for risk treatment, unless they are also the risk owner. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.1.1.1, pp. 95-96.
An organization has allowed its cyber risk insurance to lapse while seeking a new insurance provider. The risk practitioner should report to management that the risk has been:
transferred
mitigated.
accepted
avoided
Answer:
Explanation:
Cyber risk insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides coverage against losses and damages caused by cyber incidents such as data breaches, hacking, and other cyber attacks. When an organization decides to purchase cyber risk insurance, it transfers the risk of financial loss due to a cyber incident to the insurance company. In the scenario described in the question, the organization allowed its cyber risk insurance to lapse while seeking a new insurance provider. This means that the organization is currently not covered by any cyber risk insurance policy and is therefore exposed to financial losses due to cyber incidents. The risk practitioner should report to management that the risk has been accepted. Accepting risk means that the organization is aware of the potential consequences of the risk and has decided not to take any action to mitigate, transfer, or avoid it. The other options are not correct because they do not reflect the current situation of the organization. The organization has not transferred the risk to another party, as it has no cyber risk insurance policy in place. The organization has not mitigated the risk, as it has not implemented anycontrols or measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. The organization has not avoided the risk, as it has not eliminated the source or cause of the risk or changed its activities to prevent the risk from occurring. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 32-331; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 752
Which of the following is the MOST important responsibility of a risk owner?
Testing control design
Accepting residual risk
Establishing business information criteria
Establishing the risk register
Answer:
Explanation:
 Accepting residual risk is the most important responsibility of a risk owner, as it implies that the risk owner is accountable for the risk and its impact on the enterprise’s objectives and operations. Residual risk is the risk that remains after the implementation of controls, and it should be aligned with the risk appetite and tolerance of the enterprise. The risk owner is responsible for implementing the risk response strategies and monitoring the risk status and outcomes, as well as for reporting and escalating the risk issues and incidents. Testing control design, establishing business information criteria, and establishing the risk register are not the most important responsibilities of a risk owner, but rather the tasks or activities that the risk owner may performor delegate as part of the risk management process. References = CRISC Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control – Question218; ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 218.
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of centralizing IT systems?
Risk reporting
Risk classification
Risk monitoring
Risk identification
Answer:
Explanation:
Centralizing IT systems is a process of consolidating and integrating the IT systems or resources in the organization into a single or unified platform or location. Centralizing IT systems helps to improve risk reporting, because it helps to simplify and standardize the risk management process and activities, and to enhance the visibility and transparency of the IT risks and controls. Centralizing IT systems also helps to improve risk reporting, because it helps to facilitate and automate the risk data collection, analysis, and evaluation, and to provide consistent and comprehensive risk information and insights to the organization’s stakeholders, such as the board, management, business units, and IT functions. The other options are not the greatest benefit of centralizing IT systems, although they may be related to the risk management process. Risk classification, risk monitoring, and risk identification are all activities that can help to support or improve the risk management process, but they do not necessarily benefit from centralizing IT systems
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when developing an organization's risk taxonomy?
Leading industry frameworks
Business context
Regulatory requirements
IT strategy
Answer:
A new risk practitioner finds that decisions for implementing risk response plans are not being made. Which of the following would MOST likely explain this situation?
Risk ownership is not being assigned properly.
The organization has a high level of risk appetite.
Risk management procedures are outdated.
The organization's risk awareness program is ineffective.
Answer:
Which of the following has the GREATEST impact on ensuring the alignment of the risk profile with business objectives?
An effective enterprise-wide risk awareness program
Senior management approval of risk appetite and tolerance
Stage gate reviews throughout the risk management process
Incorporation of industry best practice benchmarks and standards
Answer:
An organization is considering adopting artificial intelligence (AI). Which of the
following is the risk practitioner's MOST important course of action?
Develop key risk indicators (KRIs).
Ensure sufficient pre-implementation testing.
Identify applicable risk scenarios.
Identify the organization's critical data.
Answer:
Explanation:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create machines or systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, decision making, etc.
An organization that is considering adopting AI should be aware of the potential risks and challenges that may arise from using AI, such as ethical, legal, social, technical, operational, or security issues.
The most important course of action for the risk practitioner is to identify applicable risk scenarios. This means that the risk practitioner should analyze the context and objectives of theAI adoption, the stakeholders and their expectations, the data and information sources and quality, the AI models and algorithms and their reliability, the AI outputs and outcomes and their impact, and the AI governance and oversight mechanisms and their effectiveness.
Identifying applicable risk scenarios helps to assess the likelihood and impact of the risks, prioritize the risks, design and implement appropriate risk responses, monitor and evaluate the risk performance, and report and communicate the risk status and issues.
The other options are not the most important courses of action for the risk practitioner. They are either secondary or not essential for AI risk management.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 24
Information Technology & Security, page 18
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 16
Which of the following is the BEST way to ensure adequate resources will be allocated to manage identified risk?
Prioritizing risk within each business unit
Reviewing risk ranking methodology
Promoting an organizational culture of risk awareness
Assigning risk ownership to appropriate roles
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to ensure adequate resources will be allocated to manage identified risk is to assign risk ownership to appropriate roles. Risk ownership is the process of assigning the authority and responsibility to manage a specific risk or a group of related risks to a person or entity. Risk ownership helps to ensure adequate resources for managing risk, because it helps to define and clarify the roles and responsibilities of the risk owners, and to establish and enforce the expectations and standards for the risk owners. Risk ownership also helps to measure and evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk owners, and to identify and address any issues or gaps in the risk management activities. The other options are not as effective as assigning risk ownership to appropriate roles, although they may be related to the risk management process. Prioritizing risk within each business unit, reviewing risk ranking methodology, and promoting an organizational culture of risk awareness are all activities that can help to support or improve the risk management process, but they do not necessarily ensureadequate resources for managing risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, page 2-11.
Which of the following BEST helps to mitigate risk associated with excessive access by authorized users?
Monitoring user activity using security logs
Revoking access for users changing roles
Granting access based on least privilege
Conducting periodic reviews of authorizations granted
Answer:
Explanation:
The principle of least privilege is a key concept in information security that aims to provide users with the minimum level of access—or permissions—necessary to perform their job functions. Byensuring that users only have the access they need, organizations can significantly reduce the risk associated with excessive access by authorized users.
Understanding Least Privilege
The principle of least privilege restricts access rights for users to the bare minimum permissions they need to perform their work. This minimizes the potential damage from accidents or malicious activities.
Least privilege should be applied to all user accounts, including administrative and service accounts.
Implementation
Implementing least privilege involves a detailed analysis of job functions and the necessary access required for each role.
Regularly review and update access permissions to ensure they remain aligned with current job responsibilities and organizational needs.
Mitigating Risk
By limiting access to only what is necessary, organizations can prevent users from having permissions that could be exploited, intentionally or unintentionally, to cause harm.
This also includes revoking unnecessary privileges when users change roles or no longer need access.
Comparison with Other Options
A. Monitoring user activity using security logs: While monitoring can detect inappropriate activity, it does not prevent it.
B. Revoking access for users changing roles: This is a necessary practice but does not address the initial allocation of excessive privileges.
D. Conducting periodic reviews of authorizations granted: Periodic reviews are important but are reactive rather than proactive.
References
Sybex-CISSP-Official-Study-Guide-9-Edition.pdf, p. 641, discussing the principle of least privilege and its implementation​​.
Which of the following is the MOST important document regarding the treatment of sensitive data?
Encryption policy
Organization risk profile
Digital rights management policy
Information classification policy
Answer:
Explanation:
The information classification policy is the most important document regarding the treatment of sensitive data, because it defines the categories and criteria for classifying data according to their sensitivity, confidentiality, and value to the organization, and specifies the appropriate handling and protection measures for each category. Sensitive data are data that contain personal,proprietary, or confidential information that may cause harm or damage to the organization or its stakeholders if disclosed, modified, or destroyed without authorization. An information classification policy helps to ensure that sensitive data are identified and treated in a consistent and secure manner, and that the organization complies with the applicable laws andregulations regarding data protection and privacy. An encryption policy, an organization risk profile, and a digital rights management policy are all useful documents for the treatment of sensitive data, but they are not the most important document, as they do not directly address the classification and handling of sensitive data. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.2, page 158
Which of the following is the BEST method for determining an enterprise's current appetite for risk?
Comparative analysis of peer companies
Reviews of brokerage firm assessments
Interviews with senior management
Trend analysis using prior annual reports
Answer:
Explanation:
Conducting interviews with senior management is the best method for determining an enterprise’s current appetite for risk, because it helps to obtain the direct and qualitative input and feedback from the senior management on their expectations and preferences regarding thelevel and type of risk that the enterprise is willing to accept or pursue, in relation to its objectives and strategy. Risk appetite is the amount and nature of risk that an enterprise is willing to take in order to achieve its objectives and create value. Risk appetite is influenced by factors such as the enterprise’s culture, values, vision, mission, and strategy, as well as the externalenvironment and stakeholders. Risk appetite may vary depending on the context and situation, and may change over time. Conducting interviews with senior management is the best method, as it helps to understand and capture the current and explicit risk appetite of the enterprise, and to align the risk management process and activities with the senior management’s risk vision and direction. Conducting comparative analysis of peer companies, reviewing brokerage firm assessments, and performing trend analysis using prior annual reports are all possible methods for determining an enterprise’s current appetite for risk, but they are not the best method, as they may provide only indirect, quantitative, or historical information, and may not reflect the current and specific risk appetite of the enterprise. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, page 45
An organization is unable to implement a multi-factor authentication requirement until the next fiscal year due to budget constraints. Consequently, a policy exception must be submitted. Which of the following is MOST important to include in the analysis of the exception?
Sections of the policy that may justify not implementing the requirement
Risk associated with the inability to implement the requirement
Budget justification to implement the new requirement during the current year
Industry best practices with respect to implementation of the proposed control
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important factor to include in the analysis of the policy exception is the risk associated with the inability to implement the multi-factor authentication requirement. A policy exception is a temporary orpermanent deviation from the established policies or standards of the organization, due to various reasons, such as budget constraints, technical limitations, or business needs. A policy exception must be submitted and approved by the appropriate authority, and it must include a clear and comprehensive analysis of the rationale, impact, and mitigation of the exception. The risk associated with the inability to implement the multi-factor authentication requirement is the most important factor to include in the analysis, because it evaluates the probability and severity of potential threats or incidents that could exploit the lack of multi-factor authentication, such as unauthorized access, data breach, or identity theft. The risk analysis also helps to justify the need and urgency of the policy exception, and to propose alternative or compensating controls to reduce or transfer the risk, such as password policies, access restrictions, or encryption. The other options are not the most important factor, although they may be relevant or supportive to the policy exception analysis. Sections of the policy that may justify not implementing the requirement are the clauses or provisions in the policy that allow or enable the policy exception, such as exemptions, waivers, or variances. These sections can help to validate the legitimacy and feasibility of the policy exception, but they do not assess the risk or the impact of the exception. Budget justification to implement the new requirement during the current year is the explanation and evidence of the financial resources and constraints that affect the implementation of the multi-factor authentication requirement. This justification can help to demonstrate the cost-benefit and return on investment of the requirement, but it does not measure the risk or the mitigation of the exception. Industry best practices with respect to implementation of the proposed control are the proven methods and standards that are adopted by the leading organizations in a specific field or sector for implementing the multi-factor authentication requirement. These best practices can help to benchmark and improve the quality and effectiveness of the requirement, but they do not quantify the risk or the impact of the exception. References = Policy Exception Management - ISACA, Multi-Factor Authentication Policy - University of Arkansas, Common Conditional Access policy: Require MFA for all users
A bank recently incorporated blockchain technology with the potential to impact known risk within the organization. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
reflect the results of risk assessments.
be available to all stakeholders.
effectively support a business maturity model.
be reviewed by the IT steering committee.
Answer:
Senior management has asked the risk practitioner for the overall residual risk level for a process that contains numerous risk scenarios. Which of the following should be provided?
The sum of residual risk levels for each scenario
The loss expectancy for aggregated risk scenarios
The highest loss expectancy among the risk scenarios
The average of anticipated residual risk levels
Answer:
Explanation:
Residual risk is the remaining risk after the risk response has been implemented. Residual risk can be expressed as a combination of the probability and impact of the risk scenario, or as a single value such as loss expectancy. Residual risk can be compared with the inherent risk, which is the risk level before considering the existing controls or responses, to evaluate the risk reduction and value creation of the risk response. Senior management has asked the risk practitioner for the overall residual risk level for a process that contains numerous risk scenarios. The best way to provide this information is to calculate the average of anticipated residual risklevels for each risk scenario, and to present it as a single value or a range. This can help to provide a comprehensive and consistent view of the residual risk exposure and performance of the process, as well as to align it with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. The sum of residual risk levels for each scenario, the loss expectancy for aggregated risk scenarios, or the highest loss expectancy among the risk scenarios are not the best ways to provide the overall residual risk level, as they may overestimate or underestimate the risk exposure and performance of the process, and may not reflect the actual risk reduction and value creation of the risk response. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.2, p. 108-109
Which of the following is the MOST important reason to restrict access to the risk register on a need-to-know basis?
It contains vulnerabilities and threats.
The risk methodology is intellectual property.
Contents may be used as auditable findings.
Risk scenarios may be misinterpreted.
Answer:
Explanation:
Restricting access to the risk register on a need-to-know basis is important because it contains vulnerabilities and threats that could expose the organization to potential harm or loss if they are disclosed or exploited by unauthorized parties. The risk register is a tool that captures and documents the risk identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment processes1. The risk register contains sensitive information such as the sources and causes of risk, the potential impacts and consequences of risk, the likelihood and frequency of risk occurrence, and the risk response actions and plans1. If this information is accessed by unauthorized parties, such as competitors, hackers, or malicious insiders, they could use it to launch attacks, sabotageoperations, or gain an unfair advantage over the organization. Therefore, access to the risk register should be limited to those who have a legitimate need and authorization to view, modify, or use the information, such as the risk owners, managers, or practitioners
Which of the following would BEST facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements?
Implementing a data toss prevention (DLP) solution
Assigning a data owner
Scheduling periodic audits
Implementing technical controls over the assets
Answer:
Explanation:
 The best way to facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements is to assign a data owner. A data owner is a person who has the authority and responsibility for defining, classifying, and protecting the data. A data owner can help to facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements by providing the criteria, categories, roles, and procedures for classifying the data according to its sensitivity, value, and criticality. A data owner can also ensure that the data is handled and stored appropriately, and that the data classification policy is enforced and monitored. The other options are not as effective as assigning a data owner, as they are related to the prevention, audit, or control of the data, not the classification or protection of the data. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.4: Key Control Indicators, page 211.
Which of the following is the BEST indication of an effective risk management program?
Risk action plans are approved by senior management.
Residual risk is within the organizational risk appetite
Mitigating controls are designed and implemented.
Risk is recorded and tracked in the risk register
Answer:
Explanation:
An effective risk management program is a systematic and consistent process of identifying, analyzing, evaluating, treating, monitoring, and communicating risks that may affect the achievement of the organization’s objectives12.
The best indication of an effective risk management program is that the residual risk, which is the risk remaining after risk treatment, is within the organizational risk appetite, which is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives12.
This indicates that the organization has successfully implemented appropriate risk responses that align with its risk strategy and criteria, and that the organization is able to balance the potential benefits and costs of taking risks12.
The other options are not the best indication, but rather components or outcomes of an effective risk management program. For example:
Risk action plans are approved by senior management is an outcome of an effective risk management program that demonstrates the commitment and accountability of the leadership for risk management12.
Mitigating controls are designed and implemented is a component of an effective risk management program that involves reducing the likelihood or impact of a risk event12.
Risk is recorded and tracked in the risk register is a component of an effective risk management program that involves documenting and updating the risk information and status12. References =
1: Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2009
2: IT Risk Management Framework, University of Toronto, 2017
Which of the following is the BEST control for a large organization to implement to effectively mitigate risk related to fraudulent transactions?
Segregation of duties
Monetary approval limits
Clear roles and responsibilities
Password policies
Answer:
Explanation:
Segregation of duties is a key control for preventing and detecting fraudulent transactions, especially in a large organization where there are many employees and transactions involved. Segregation of duties means that no single person has the authority or ability to initiate, approve, execute, and record a transaction without the involvement or oversight of another person. This reduces the opportunity and incentive for fraud, as well as the risk of errors or omissions. Segregation of duties also facilitates the detection of fraud by creating an audit trail and increasing the likelihood of whistleblowing.
The other options are not as effective as segregation of duties for mitigating risk related to fraudulent transactions. Monetary approval limits (B) are useful for controlling the amount and frequency of transactions, but they do not prevent unauthorized or fraudulent transactions from occurring. Clear roles and responsibilities © are important for defining the expectations and accountabilities of employees, but they do not ensure that employees comply with them or that their actions are monitored and verified. Password policies (D) are essential for securing access to systems and data, but they do not prevent fraudsters from exploiting weak or compromised passwords or from using legitimate passwords for fraudulent purposes.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when establishing a recovery point objective (RPO)?
Latency of the alternate site
Amount of acceptable data loss
Time and resources for offsite backups
Cost of testing the business continuity plan (BCP)
Answer:
Explanation:
RPO defines the maximum tolerable data loss in case of a disruption — i.e., how much data the enterprise can afford to lose between the last backup and an incident.
ISACA’s business continuity and CRISC guidance:
“The recovery point objective (RPO) is based on the amount of acceptable data loss determined by business requirements.â€
A, C, D are logistical concerns; only B defines the RPO itself.
CRISC Reference: Domain 3 – Risk Response and Mitigation, Topic: Business Continuity Objectives (RTO/RPO).
Which of the following approaches BEST identifies information systems control deficiencies?
Countermeasures analysis
Best practice assessment
Gap analysis
Risk assessment
Answer:
Explanation:
A gap analysis is the best approach to identify information systems control deficiencies, as it helps to compare and evaluate the current and desired states of the information systems and their controls, and to identify and prioritize the gaps or weaknesses that need to be addressed. A gap analysis is a process of assessing and measuring the difference between the actual and expected performance or outcomes of a system or a process, such as an information system or a control process. A gap analysis can help to identify information systems control deficiencies by providing the following benefits:
It enables a data-driven and evidence-based approach to information systems control assessment and improvement, rather than relying on subjective or qualitative judgments.
It facilitates a consistent and standardized way of measuring and communicating information systems control performance and quality across the organization and to the external stakeholders.
It supports the alignment of information systems and their controls with the organizational strategy and objectives, and helps to evaluate the achievement of the desired outcomes.
It helps to identify and prioritize the root causes and contributing factors of information systems control deficiencies, and to develop and implement appropriate strategies and actions to address them.
It provides feedback and learning opportunities for the information systems and their controls, and helps to foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
The other options are not the best approaches to identify information systems control deficiencies. Countermeasures analysis is a method of identifying and evaluating the potential countermeasures or solutions to mitigate or eliminate a specific threat or risk, but it does not directly address the information systems control deficiencies. Best practice assessment is a method of comparing and benchmarking the information systems and their controls against the industry standards or best practices, but it does not provide a comprehensive or customized analysis of the information systems control deficiencies. Risk assessment is a method ofidentifying and analyzing the potential risks and their impacts on the information systems and their objectives, but it does not measure or evaluate the information systems control performance or quality. References = Gap Analysis: A Practical Guide | Smartsheet, IT Risk Resources | ISACA, How to Perform a Gap Analysis: Step-By-Step Guide & Template
The maturity of an IT risk management program is MOST influenced by:
the organization's risk culture
benchmarking results against similar organizations
industry-specific regulatory requirements
expertise available within the IT department
Answer:
Explanation:
The maturity of an IT risk management program is most influenced by the organization’s risk culture, as this reflects the shared values, beliefs, and attitudes that shape how the organization perceives and responds to risk. The risk culture determines the level of awareness, commitment, and involvement of the stakeholders in the IT risk management process, as well as the degree of integration and alignment with the enterprise’s objectives and strategy. A mature IT risk management program requires a strong and positive risk culture that fosters trust, collaboration, and accountability among the stakeholders, and supports continuous improvement and learning. The other options are not the most influential factors for the maturity of an IT risk management program, although they may have some impact or relevance. Benchmarking results against similar organizations can provide useful insights and comparisons, but they do not necessarily reflect the organization’s own risk culture or context. Industry-specific regulatory requirements can impose certain standards and expectations, but they do not guarantee the effectiveness or efficiency of the IT risk management program. Expertise available within the IT department can enhance the technical and operational aspects of the IT risk management program, but it does not ensure the strategic and cultural alignment with the enterprise. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, page 23.
A risk practitioner has collaborated with subject matter experts from the IT department to develop a large list of potential key risk indicators (KRIs) for all IT operations within theorganization of the following, who should review the completed list and select the appropriate KRIs for implementation?
IT security managers
IT control owners
IT auditors
IT risk owners
Answer:
Explanation:
 IT risk owners are the most appropriate people to review the completed list of potential key risk indicators (KRIs) and select the ones that should be implemented. IT risk owners are the individuals who have the authority and accountability to manage the IT risks within their scope of responsibility. They are also responsible for defining the risk appetite, tolerance, and thresholds for their IT operations, and for ensuring that the KRIs are aligned with the business objectives and risk management strategy. IT security managers, IT control owners, and IT auditors are also involved in the risk management process, but they do not have the same level of authority and accountability as IT risk owners, and they may have different perspectives and priorities on the selection of KRIs. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.3.1, page 1-13.
Which of the following would be MOST helpful in assessing the risk associated with data loss due to human vulnerabilities?
Reviewing password change history
Performing periodic access recertification
Conducting social engineering exercises
Reviewing the results of security awareness surveys
Answer:
Explanation:
Social engineering exercises are simulations of real-world attacks that exploit human vulnerabilities, such as phishing, baiting, pretexting, or quid pro quo. Conducting social engineering exercises can help assess the risk associated with data loss due to human vulnerabilities by measuring the employees’ susceptibility to such attacks, their awareness of security policies and procedures, and their response to incidents. Reviewing password change history, performing periodic access recertifications, and reviewing the results of security awareness surveys are also useful, but they do not directly test the employees’ behavior and resilience in the face of social engineering attacks.
Which of the following activities should only be performed by the third line of defense?
Operating controls for risk mitigation
Testing the effectiveness and efficiency of internal controls
Providing assurance on risk management processes
Recommending risk treatment options
Answer:
Explanation:
Providing assurance on risk management processes is the activity that should only be performed by the third line of defense, because it is the role and responsibility of the independent andobjective assurance function, such as internal audit or external audit, to evaluate and report on the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk management processes and controls. The third line of defense is the last layer of the three lines of defense model, which is a framework that defines the roles and responsibilities of different functions and levels within the organization for risk management and control. The first line of defense is the operational management and staff, who are responsible for identifying, assessing, and managing the risks and controls within their areas of responsibility. The second line of defense is the oversight and support functions, such as risk management, compliance, or legal, who are responsible for establishing and monitoring the risk policies, standards, and frameworks, and providing guidance and advice to the first line of defense. The third line of defense is the assurance function, who are responsible for providing independent and objective assurance on the adequacy and effectiveness of the risk management processes and controls, and reporting to the senior management and the board of directors. Operating controls for risk mitigation, testing the effectiveness and efficiency of internal controls, and recommending risk treatment options are all activities that can be performed by the first or second line of defense, but not by the third line of defense, as they are not part of the assurance function. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.4.1, page 59
Which of the following would BEST facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements?
Assigning a data owner
Implementing technical control over the assets
Implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) solution
Scheduling periodic audits
Answer:
Explanation:
Assigning a data owner would best facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements. A data owner is responsible for defining the classification of the data, ensuring that the data is properly labeled, and approving access requests. Implementing technical control over the assets, implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) solution, and scheduling periodic audits are important activities, but they are not as effective as assigning a data owner. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 8; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 97.
An organization has agreed to a 99% availability for its online services and will not accept availability that falls below 98.5%. This is an example of:
risk mitigation.
risk evaluation.
risk appetite.
risk tolerance.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Risk tolerance is the best term to describe the situation where an organization has agreed to a 99% availability for its online services and will not accept availability that falls below 98.5%. Risk tolerance is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in order to achieve its objectives. Risk tolerance defines the acceptable variation in outcomes related to specific performance measures, such as availability, reliability, or security. Risk tolerance is usually expressed as a range, such as 99% +/- 0.5%. Risk mitigation, risk evaluation, and risk appetite are not the correct terms to describe this situation, because they refer to different aspects of risk management, such as reducing, assessing, or pursuing risk, respectively. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.2.1, page 1-8.
After entering a large number of low-risk scenarios into the risk register, it is MOST important for the risk practitioner to:
prepare a follow-up risk assessment.
recommend acceptance of the risk scenarios.
reconfirm risk tolerance levels.
analyze changes to aggregate risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
After entering a large number of low-risk scenarios into the risk register, it is most important for the risk practitioner to analyze changes to aggregate risk. Aggregate risk is the total amount and type of risk that the organization faces or accepts, considering all the individual and interrelated risk scenarios. Aggregate risk helps to measure and monitor the organization’s risk profile, riskappetite, and risk performance, and to support the risk decision-making and reporting processes. Analyzing changes to aggregate risk is important after entering a large number of low-risk scenarios, because even though the individual risk scenarios may have low likelihood or impact, they may still have a significant cumulative or combined effect on the organization’s objectives or operations. Analyzing changes to aggregate risk also helps to identify and prioritize the most critical or relevant risk scenarios, and to select the most appropriate and effective risk responses and strategies. The other options are not as important as analyzing changes to aggregate risk, although they may be part of or derived from the risk analysis process. Preparing a follow-up risk assessment, recommending acceptance of the risk scenarios, and reconfirming risk tolerance levels are all activities that can help to implement or update the risk management process, but they are not the most important after entering a large number of low-risk scenarios. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.1, page 4-25.
Which of the following is the BEST way to determine the potential organizational impact of emerging privacy regulations?
Evaluate the security architecture maturity.
Map the new requirements to the existing control framework.
Charter a privacy steering committee.
Conduct a privacy impact assessment (PIA).
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to determine the potential organizational impact of emerging privacy regulations is to conduct a privacy impact assessment (PIA). A PIA is a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the privacy risks and impacts of a new or existing system, process, program, or initiative that involves the collection, use, storage, or disclosure of personal information. A PIA can help to ensure that the enterprise complies with the emerging privacyregulations, and that the privacy rights and expectations of the individuals are respected and protected. A PIA can also help to identify the gaps, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement in the enterprise’s privacy policies, procedures, and controls. Evaluating the security architecture maturity, mapping the new requirements to the existing control framework, and chartering a privacy steering committee are not as comprehensive and effective as conducting a PIA, as they do not address the specific privacy risks and impacts of the enterprise’s activities. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 192.
After a high-profile systems breach at an organization s key vendor, the vendor has implemented additional mitigating controls. The vendor has voluntarily shared the following set of assessments:
Which of the assessments provides the MOST reliable input to evaluate residual risk in the vendor's control environment?

External audit
Internal audit
Vendor performance scorecard
Regulatory examination
Answer:
Explanation:
An external audit is the most reliable input to evaluate residual risk in the vendor’s control environment, as it provides an independent and objective assessment of the vendor’s financial systems and processes. An external audit is conducted by a third party, such as a certified public accountant (CPA) or a professional auditing firm, that follows the generally accepted auditing standards (GAAS) and the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). An external audit can help to verify the accuracy and completeness of the vendor’s financial statements, identify any material misstatements or errors, and evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the vendor’s internal controls. An external audit can also provide assurance and confidence to the organization and other stakeholders that the vendor is complying with the relevant laws, regulations, and contractual obligations.
The other options are not the most reliable inputs to evaluate residual risk in the vendor’s control environment. An internal audit is conducted by the vendor itself, which may introduce bias or conflict of interest. An internal audit may also have a different scope, methodology, or quality than an external audit. A vendor performance scorecard is completed by the organization, which may not have the sufficient access, expertise, or authority to assess the vendor’s control environment. A vendor performance scorecard may also focus more on the service level agreement (SLA) compliance, rather than the financial systems and processes. A regulatory examination is conducted by a regulator, such as a government agency or a standard-settingbody, which may have a different purpose, criteria, or perspective than the organization. A regulatory examination may also have a limited scope, frequency, or transparency. References = Guide to VendorRisk Assessment | Smartsheet, Understanding Inherent Vs. Residual Risk Assessments - Resolver, Assessing Internal Controls over Compliance - HCCA Official Site
Which of the following resources is MOST helpful when creating a manageable set of IT risk scenarios?
Results of current and past risk assessments
Organizational strategy and objectives
Lessons learned from materialized risk scenarios
Internal and external audit findings
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual1, lessons learned from materialized risk scenarios are the insights and knowledge gained from analyzing the causes, impacts, and responses of actual risk events that occurred in the past. Lessons learned from materialized risk scenarios are the most helpful resource when creating a manageable set of IT risk scenarios, as they help to identify and prioritize the most relevant and realistic risks that could affect the organization’s objectives, processes, and resources. Lessons learned from materialized risk scenarios also helpto improve the risk management practices and capabilities, and to avoid repeating the same mistakes or gaps in the future. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 206.
The BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of the security patching process is the percentage of patches installed:
by the security administration team.
successfully within the expected time frame.
successfully during the first attempt.
without causing an unplanned system outage.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of the security patching process is the percentage of patches installed successfully within the expected time frame. This KPI can help to evaluate how well the security patching process meets the predefined objectives and standards, and how timely the patches are applied to reduce the risk exposure. The percentage of patches installed by the security administration team, successfully during the first attempt, or without causing an unplanned system outage are other possible KPIs, but they are not as relevant as the percentage of patches installed successfully within the expected time frame. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 7; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 202.
Which of the following BEST enables senior management to make risk treatment decisions in line with the organization's risk appetite?
Quantitative risk analysis
Industry risk benchmarks
Risk scenarios
Risk remediation plans
Answer:
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of reviewing security trends reported by a log monitoring system?
Identification of process weaknesses
Assessment of system performance
Confirmation that risk is at acceptable levels
Identification of emerging risk scenarios
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to ISACA CRISC guidance)
Log monitoring and security trend analysis provide visibility into changes in the threat landscape and control effectiveness. From a CRISC perspective, the most valuable outcome of trend review is identifying emerging risk scenarios—patterns of events, anomalies, or repeated alerts that signal new attack vectors, control bypasses, or increased threat activity. Recognizing these trends early allows the organization to adjust controls, update risk assessments, and revise scenarios before major incidents occur. While process weaknesses can be discovered through logs and performance can be indirectly assessed, these are secondary benefits. Simply reviewing trends does not in itself confirm that risk is at acceptable levels; that requires a broader comparison to risk appetite and KPI/KRI thresholds. The primary strategic value is early detection and understanding of new or evolving risks.
Which of the following BEST enforces access control for an organization that uses multiple cloud technologies?
Senior management support of cloud adoption strategies
Creation of a cloud access risk management policy
Adoption of a cloud access security broker (CASB) solution
Expansion of security information and event management (SIEM) to cloud services
Answer:
Explanation:
 A cloud access security broker (CASB) solution is the best way to enforce access control for an organization that uses multiple cloud technologies, as it provides a centralized and consistent platform to manage and monitor the access to various cloud services and applications. A CASB solution can help to implement and enforce the enterprise’s access policies and standards, as well as to detect and prevent unauthorized or malicious access attempts. Senior management support of cloud adoption strategies, creation of a cloud access risk management policy, and expansion of security information and event management (SIEM) to cloud services are not the best ways to enforce access control for an organization that uses multiple cloud technologies, as they do not provide the technical capabilities or tools to manage and monitor the access to various cloud services and applications. References = CRISC by Isaca Actual Free Exam Q&As, question 210; CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, question 210.
Which of the following is the MAIN purpose of monitoring risk?
Communication
Risk analysis
Decision support
Benchmarking
Answer:
Explanation:
The main purpose of monitoring risk is to provide decision support for the organization. Risk monitoring is the process of tracking and reviewing the risk management activities, the risk profile, and the risk performance of the organization. By monitoring risk, the organization can obtain timely and relevant information and feedback on the risk situation, and use it to make informed and effective decisions on risk management and business objectives. Communication, risk analysis, and benchmarking are other possible purposes of risk monitoring, but they are not as important as decision support. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 12; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 215.
Risk management strategies are PRIMARILY adopted to:
take necessary precautions for claims and losses.
achieve acceptable residual risk levels.
avoid risk for business and IT assets.
achieve compliance with legal requirements.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), risk management strategies are primarily adopted to achieve acceptable residual risk levels, which are the remaining risk levels after implementing risk response actions. Residual risk levels should be aligned with the organization’s risk appetite and risk tolerance, which are the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives and the acceptable variation in outcomes related to specific performance measures linked to objectives. Risk management strategies are the approaches or methods used to address risks, such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer, sharing, or acceptance. Risk management strategies should be based on a cost-benefit analysis of the alternatives available and the value of the assets at risk.
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: Risk Response Options, pp. 166-1691
Which of the following is a crucial component of a key risk indicator (KRI) to ensure appropriate action is taken to mitigate risk?
Management intervention
Risk appetite
Board commentary
Escalation triggers
Answer:
Explanation:
The best answer is D. Escalation triggers. Escalation triggers are predefined thresholds or conditions that indicate when a key risk indicator (KRI) has reached a critical level that requires immediate attention or action. Escalation triggers can be based on quantitative or qualitative measures, such as percentages, scores, ratings, or colors. Escalation triggers can help to ensure appropriate action is taken to mitigate risk, because they provide clear and timely signals that alert the risk owners, managers, and other stakeholders of the need to review and revise the risk response plan, or to implement additional or alternative controls. Escalation triggers can also help to communicate and report the risk status and the risk response actions to the senior management and the board, and to obtain their support and approval, if needed. The otheroptions are not the best answer, although they may be related or influential to the KRI and the risk mitigation. Management intervention is a part of the risk response process, which involves the actions and decisions taken by the management to address the risk, such as approving, implementing, or monitoring the controls. Management intervention can help to mitigate risk, but it is not a component of the KRI, rather it is a consequence or a result of the escalation triggers. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept or pursue in order to achieve its objectives. Risk appetite can help to define and align the KRI and the escalation triggers with the organizational strategy and culture, but it is not a component of the KRI, rather it is a factor or a driver of the KRI. Board commentary is a part of the risk reporting process, which involves the feedback and guidance provided by the board on the risk management process and performance. Board commentary can help to improve and enhance the KRI and the risk mitigation, but it is not a component of the KRI, rather it is a source or a resource of the KRI. References = Key Risk Indicators: A Practical Guide | SafetyCulture, KRI Framework for Operational Risk Management | Workiva
An organization is developing a plan to address new information security risks emerging from business changes. Which of the following BEST enables stakeholders to make decisions impacting organizational strategy?
The impact of the new risk is clearly presented
Benchmarking information is provided
Technical expertise to address new risk scenarios is available
The cost of implementing the strategy is within budget
Answer:
Explanation:
CRISC emphasizes risk communication in decision-making. Stakeholders can only make effective strategic decisions if the business impact of risk is clearly presented.
“The purpose of risk communication is to enable informed decision-making by clearly presenting the potential impact of risk on business objectives.â€
Benchmarking and cost data support the discussion but are secondary to understanding impact severity.
Hence, A is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 4 – Risk Monitoring and Reporting, Topic: Risk Communication Principles.
An organization is considering the adoption of an aggressive business strategy to achieve desired growth From a risk management perspective what should the risk practitioner do NEXT?
Identify new threats resorting from the new business strategy
Update risk awareness training to reflect current levels of risk appetite and tolerance
Inform the board of potential risk scenarios associated with aggressive business strategies
Increase the scale for measuring impact due to threat materialization
Answer:
Explanation:
The next thing that the risk practitioner should do from a risk management perspective when the organization is considering the adoption of an aggressive business strategy to achieve desired growth is to identify new threats resulting from the new business strategy. A threat is a potentialcause of an unwanted incident that may affect the achievement of the objectives. An aggressive business strategy is a strategy that involves pursuing high-risk, high-reward opportunities or initiatives to gain a competitive advantage or a significant market share. An aggressive business strategy may introduce new threats or increase thelikelihood or impact of existing threats, such as market volatility, regulatory changes, customer dissatisfaction, or competitor retaliation. Therefore, the risk practitioner should identify the new threats resulting from the new business strategy, and assess their potential consequences and implications for the organization. The other options are not as immediate as identifying new threats resulting from the new business strategy, as they are related to the update, information, or measurement of the risk management process, not the identification or analysis of the risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.3: IT Risk Scenarios, page 23.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for conducting peer reviews of risk analysis?
To enhance compliance with standards
To minimize subjectivity of assessments
To increase consensus among peers
To provide assessments for benchmarking
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual1, peer reviews are the process of evaluating the quality and validity of risk analysis by independent experts or colleagues. Peer reviews are conducted to ensure that the risk analysis is consistent, objective, and reliable, and that it follows the established standards and methods. The primary reason for conducting peer reviews of risk analysis is to minimize subjectivity of assessments, as peer reviews can help to reduce personal biases, preferences, and assumptions that may affect the risk analysis outcomes. Peer reviews can also help to identify and correct any errors, gaps, or inconsistencies in the risk analysis, and to improve the risk analysis skills and knowledge of the reviewers and the reviewees. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 209.
Following a review of a third-party vendor, it is MOST important for an organization to ensure:
results of the review are accurately reported to management.
identified findings are reviewed by the organization.
results of the review are validated by internal audit.
identified findings are approved by the vendor.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A review of a third-party vendor is a process that involves examining and evaluating the performance, quality, and compliance of the vendor that provides a product or service to the organization1. A review of a third-party vendor can help to identify and address the risks and issues that may arise from the vendorrelationship, such as data breaches, service disruptions, contract violations, or reputation damage2. Following a review of a third-party vendor, it is most important for an organization to ensure that the results of the review are accurately reported to management, as this will enable the management to make informed and timely decisions and actions based on the findings and recommendations of the review. Accurate reporting of the results of the review will also help to establish and maintain the trust and transparency between the organization and the vendor, and to demonstrate the accountability and responsibility of the organization for its vendor risk management3. Identified findings are reviewed by the organization, results of the review are validated by internal audit, and identified findings are approved by the vendor are not the most important things to ensure following a review of a third-party vendor, as they do not provide the same level of impact and value as accurate reporting of the results of the review. Identified findings are reviewed by the organization is a process that involves analyzing and interpreting the outcomes and implications of the review of a third-party vendor, and determining the appropriate risk responses and actions to address the findings4. Thisis an important step in the vendor risk management process, but it is not the most important thing to ensure following a review of a third-party vendor, as it does not communicate or inform the management or the vendor of the results of the review. Results of the review are validated by internal audit is a process that involves verifying and confirming the accuracy and reliability of the review of a third-party vendor, and providing assurance and advice on the adequacy and effectiveness of the vendor risk management. This is an important step in the vendor risk management process, but it is not the most important thing to ensure following a review of a third-party vendor, as it does not report or share the results of the review with the management or the vendor. Identified findings are approved by the vendor is a process that involves obtaining the consent and agreement of the vendor on the outcomes and recommendations of the review of a third-party vendor, and ensuring their cooperation and compliance with the risk responses and actions. This is an important step in the vendor risk management process, but it is not the most important thing to ensure following a review of a third-party vendor, as it does not report or inform the management of the results of the review. References = 1: The guide to third-party vendor reviews - TerraTrue HQ | TerraTrue2: 4 Tips For Organizations To Evaluate Third-Party Vendors – Forbes Advisor3: Vendor Risk Management: Best Practices for 2023 - Venminder4: [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: Risk Response, Section 3.1: Risk Response Options, pp. 113-115.] : [IT Risk Resources | ISACA] : Who Is Considered a Third Party or Vendor? - Venminder : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.1: Risk Identification, pp. 57-59.] : [Risk and Information SystemsControl Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: Risk Monitoring, pp. 189-191.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.1:Control Design, pp. 233-235.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.2: Control Implementation, pp. 243-245.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.3: Control Monitoring and Maintenance, pp. 251-253.]
An organization is subject to a new regulation that requires nearly real-time recovery of its services following a disruption. Which of the following is the BEST way to manage the risk in this situation?
Move redundant IT infrastructure to a closer location.
Obtain insurance and ensure sufficient funds are available for disaster recovery.
Review the business continuity plan (BCP) and align it with the new business needs.
Outsource disaster recovery services to a third-party IT service provider.
Answer:
Explanation:
Updating the BCP to align with real-time recovery requirements ensures the organization’s resilience to disruptions while meeting regulatory standards. This action reflectsBusiness Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planningbest practices.
A public online information security training course is available to an organization's staff. The online course contains free-form discussion fields. Which of the following should be of MOST concern to the organization's risk practitioner?
The form may be susceptible to SQL injection attacks.
Data is not encrypted in transit to the site.
Proprietary corporate information may be disclosed.
Staff nondisclosure agreements (NDAs) are not in place.
Answer:
Explanation:
Free-form fields in public forums increase the risk of accidental or intentional disclosure of sensitive or proprietary information. This creates legal and reputational exposure. Monitoring or disabling such features is essential to mitigating data leakage risks.
A risk practitioner has received an updated enterprise risk management (ERM) report showing that residual risk is now within the organization's defined appetite and tolerance levels. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Identify new risk entries to include in ERM.
Remove the risk entries from the ERM register.
Re-perform the risk assessment to confirm results.
Verify the adequacy of risk monitoring plans.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s best course of action when the residual risk is now within the organization’s defined appetite and tolerance levels is to verify the adequacy of risk monitoring plans. Risk monitoring is the process of tracking and reviewing the risk status and performance, and ensuring that the risk responses are effective and efficient1. Risk monitoring plans are the documents that specify the objectives, scope, methods, roles, and responsibilities for the riskmonitoring activities2. By verifying the adequacy of risk monitoring plans, the risk practitioner can:
Ensure that the risk monitoring plans are aligned with the organization’s risk strategy, objectives, and policies, and that they comply with the relevant standards and regulations3.
Evaluate whether the risk monitoring plans are comprehensive and consistent, and that they cover all the key aspects and indicators of the risks and the risk responses4.
Identify and address any gaps, issues, or challenges that may affect the implementation or outcome of the risk monitoring plans, and recommend and implement appropriate improvement actions5.
The other options are not the best course of action, because:
Identifying new risk entries to include in ERM is not a relevant or necessary course of action, as it is not directly related to the residual risk or the risk responses. ERM is the process of identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and managing the risks that may affect the organization’s strategic, operational, financial, or reputational objectives6. Identifying new risk entries is a part of the risk identification process, which is the first step in ERM. It should be performedperiodically or when there are significant changes in the internal or external environment, not when the residual risk is within the appetite and tolerance levels7.
Removing the risk entries from the ERM register is not a valid or advisable course of action, as it may create a false sense of security or complacency. The ERM register is a tool that records and summarizes the key information and data about the identified risks and the risk responses. Removing the risk entries from the ERM register may imply that the risks no longer exist or matter, which is not true. The risks may still occur or change, and the risk responses may still fail or become obsolete. Therefore, the risk entries should be kept and updated in the ERM register, unless the risks are completely eliminated or transferred.
Re-performing the risk assessment to confirm results is not an efficient or effective course of action, as it may be redundant or unnecessary. Risk assessment is the process of estimating the probability and impact of the risks, and prioritizing the risks based on their significance and urgency. Re-performing the risk assessment may not provide any new or useful information or insights, and may waste time and resources. Instead, the risk practitioner should verify and validate the risk assessment results, and ensure that they are accurate and reliable.
References =
Risk Monitoring - CIO Wiki
Risk Monitoring Plan - CIO Wiki
Risk Monitoring and Reporting - ISACA
Risk Monitoring and Control - Project Management Institute
Risk Monitoring and Review - The National Academies Press
Enterprise Risk Management - CIO Wiki
Risk Identification - CIO Wiki
[Risk Register - CIO Wiki]
[Risk Register: How to Use It in Project Management - ProjectManager.com]
[Risk Assessment - CIO Wiki]
[Risk Assessment Process - ISACA]
A risk practitioner has just learned about new done FIRST?
Notify executive management.
Analyze the impact to the organization.
Update the IT risk register.
Design IT risk mitigation plans.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual1, impact analysis is the process of estimating and evaluating the potential effects of a risk event on the organization’s objectives, processes, resources, and risks. Impact analysis helps to quantify and qualify the severity and likelihood of the risk, and to identify the possible consequences and implications for the organization. Impact analysis is the first step that should be done when a risk practitioner learns about a new threat, as it helps to assess the current level of risk exposure and the urgency of the risk response. Impact analysis also helps to communicate and report the risk to the relevant stakeholders, and to facilitate risk-based decision making and action planning. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 208.
Management has noticed storage costs have increased exponentially over the last 10 years because most users do not delete their emails. Which of the following can BEST alleviate this issue while not sacrificing security?
Implementing record retention tools and techniques
Establishing e-discovery and data loss prevention (DLP)
Sending notifications when near storage quota
Implementing a bring your own device 1BVOD) policy
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the Risk and Information Systems Control documents, implementing record retention tools and techniques is the best solution in this scenario. Record retention involves managing the lifecycle of records, including their creation, usage, storage, and disposal. By implementing record retention policies, organizations can define how long emails and other data should be retained before being deleted. This helps in efficiently managing storage space and reducing unnecessary storage costs.
Establishing e-discovery and data loss prevention (DLP) (Option B) focuses more on legal and compliance aspects and may not directly address the issue of reducing storage costs. Sending notifications when near storage quota (Option C) is a reactive approach and may not prevent the exponential increase in storage costs. Implementing a bring your own device (BYOD) policy (Option D) is unrelated to the issue of email storage costs.
References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual
When establishing an enterprise IT risk management program, it is MOST important to:
review alignment with the organizations strategy.
understand the organization's information security policy.
validate the organization's data classification scheme.
report identified IT risk scenarios to senior management.
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most important thing to do when establishing an enterprise IT risk management program is to review the alignment with the organization’s strategy. The organization’s strategy is the plan or direction that the organization follows to achieve its vision, mission, and goals. The IT risk management program should be aligned with the organization’s strategy, so that it supports and enables the organization’s strategic objectives, and addresses the IT risks that could affect the organization’s performance and value. Reviewing the alignment with the organization’s strategy helps to ensure that the IT risk management program is relevant, effective, and consistent with the organization’s expectations and needs. The other options are not as important as reviewing the alignment with the organization’s strategy, although they may be useful or necessary steps or components of the IT risk management program. Understanding the organization’s information security policy, validating the organization’s data classification scheme, and reporting identified IT risk scenarios to senior management are all activities that can help to implement and improvethe IT risk management program, but they are not the initial or primary thing todo. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, page 2-12.
A web-based service provider with a low risk appetite for system outages is reviewing its current risk profile for online security. Which of the following observations would be MOST relevant to escalate to senior management?
An increase in attempted distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks
An increase in attempted website phishing attacks
A decrease in achievement of service level agreements (SLAs)
A decrease in remediated web security vulnerabilities
Answer:
Explanation:
A web-based service provider is an organization that offers online services or applications to its customers or users, such as e-commerce, social media, cloud computing, etc. A web-based service provider depends on the availability, reliability, and security of its web servers, networks, and systems to deliver its services or applications.
A low risk appetite for system outages means that the organization is not willing to accept a high level or frequency of system outages, which are interruptions or disruptions in the normal operation or functionality of the web servers, networks, or systems. System outages can cause customer dissatisfaction, revenue loss, reputation damage, or legal liability for the web-based service provider.
A current risk profile for online security is the current state or condition of the online security risks that may affect the web-based service provider’s objectives and operations. It includes the identification, analysis, and evaluation of the online security risks, and the prioritization and response to them based on their significance and urgency.
The most relevant observation to escalate to senior management is an increase in attempted distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks, which are malicious attacks that aim to overwhelm or overload the web servers, networks, or systems with a large volume or frequency of requests or traffic, and prevent them from responding to legitimate requests or traffic. An increase in attempted DDoS attacks indicates a high likelihood and impact of system outages, and a high level of threat or vulnerability for the web-based service provider’s online security. Escalating this observation to senior management can help them to understand the severity and urgency of the risk, and to decide on the appropriate risk response and allocation of resources.
The other options are not the most relevant observations to escalate to senior management, because they do not indicate a high likelihood or impact of system outages, and they may not be relevant or actionable for senior management.
An increase in attempted website phishing attacks means an increase in malicious attempts to deceive or trick the web-based service provider’s customers or users into providing their personal or financial information, such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, etc., by impersonating the web-based service provider’s website or email. An increase in attemptedwebsite phishing attacks indicates a high level of threat or vulnerability for the web-based service provider’s online security, but it may not directly cause system outages, unless thephishing attacks are used to compromise the web servers, networks, or systems. Escalating this observation to senior management may not be the most relevant, because it may not reflect the web-based service provider’s risk appetite for system outages, and it may not require senior management’s involvement or approval.
A decrease in achievement of service level agreements (SLAs) means a decrease in the extent or degree to which the web-based service provider meets or exceeds the agreed or expected standards or criteria for the quality, performance, or availability of its services or applications, as specified in the contracts or agreements with its customers or users. A decrease in achievement of SLAs indicates a low level of customer satisfaction, retention, or loyalty, and a low level of competitiveness or profitability for the web-based service provider. Escalating this observation to senior management may not be the most relevant, because it may not reflect the web-based service provider’s risk appetite for system outages, and it may not require senior management’s involvement or approval.
A decrease in remediated web security vulnerabilities means a decrease in the number or percentage of web security vulnerabilities that have been identified and resolved or mitigated by the web-based service provider. Web security vulnerabilities are weaknesses or flaws in the web servers, networks, or systems that can be exploited by malicious attackers to compromise or damage the web-based service provider’s online security. A decrease in remediated web security vulnerabilities indicates a low level of effectiveness or efficiency for the web-based service provider’s web security controls or processes. Escalating this observation to senior management may not be the most relevant, because it may not reflect the web-based service provider’s risk appetite for system outages, and it may not require senior management’s involvement or approval. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 161
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
A key performance indicator (KPI) has been established to monitor the number of software changes that fail and must be re-implemented. An increase in the KPI indicates an ineffective:
Preventive control
Administrative control
Corrective control
Deterrent control
Answer:
Explanation:
Corrective controls are designed to correct errors or deviations after they occur. If failed changes frequently require re-implementation, this means corrective measures (e.g., testing, change rollback, error correction) are not functioning effectively.
CRISC guidance defines:
Preventive controls: stop incidents from occurring.
Detective controls: identify incidents when they occur.
Corrective controls: restore systems or data after incidents occur.
An increasing KPI (failed changes) means the corrective mechanism is weak, hence C is the correct answer.
CRISC Reference: Domain 4 – Risk and Control Monitoring, Topic: Control Effectiveness Evaluation.
An internal audit report reveals that not all IT application databases have encryption in place. Which of the following information would be MOST important for assessing the risk impact?
The number of users who can access sensitive data
A list of unencrypted databases which contain sensitive data
The reason some databases have not been encrypted
The cost required to enforce encryption
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual, a list of unencrypted databases which contain sensitive data would be the most important information for assessing the risk impact, because it would help to determine the extent and severity of the potential data breach or loss. The risk impact is the effect or consequence of the risk occurrence on the business objectives and operations. A list of unencrypted databases which contain sensitive data would indicate the scope and magnitude of the risk exposure and the potential damage to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. The other options are not the most important information for assessing the risk impact, as they are less relevant or less specific than a list of unencrypted databases which contain sensitive data. The number of users who can access sensitive data would indicate the level of access control and the likelihood of unauthorized access, but it would not indicate thetype and value of the data. The reason some databases have not been encrypted would indicate the cause and rationale of the risk, but it would not indicate the effect or consequence of the risk. The cost required to enforce encryption would indicate the feasibility and affordability of the risk response, but it would not indicate the potential loss or harm of the risk. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.2, page 78.
Which of the following would BEST mitigate the risk associated with reputational damage from inappropriate use of social media sites by employees?
Validating employee social media accounts and passwords
Monitoring Internet usage on employee workstations
Disabling social media access from the organization's technology
Implementing training and awareness programs
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to mitigate the risk of reputational damage from inappropriate use of social media sites by employees is to implement training and awareness programs that educate them on the acceptable andunacceptable use of social media, the potential consequences of violating the policy, and the best practices for protecting the organization’s reputation and information. Training and awareness programs can also help to foster a culture of risk awareness and responsibility among employees, and encourage them to report any incidents or issues related to social media use. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.4, page 131.
A risk heat map is MOST commonly used as part of an IT risk analysis to facilitate risk:
communication
identification.
treatment.
assessment.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk heat map is a tool that shows the likelihood and impact of different risks on a matrix, using colors to indicate the level of risk. A risk heat map is most commonly used as part of an IT risk analysis to facilitate risk assessment, which is the process of estimating the probability and consequences of the risks, and comparing them against the risk criteria1. A risk heat map can help to visualize, communicate, and prioritize the risks, as well as to evaluate the effectiveness of the risk response actions2. The other options are not the best choices for describing the purpose of a risk heat map, as they are either less specific or less relevant than risk assessment. Risk communication is the process of sharing and exchanging information about the risks among the stakeholders3. A risk heat map can support risk communication by providing a clear and concise representation of the risks, but it is not the main objective of the tool. Riskidentification is the process of finding, recognizing, and describing the risks that may affect the organization4. A risk heat map can help to identify the risks by categorizing them into different domains or sources, but it is not the primary function of the tool. Risk treatment is the process of selecting and implementing the appropriate measures to modify the risk5. A risk heat map can help to guide the risk treatment by showing the risk ratings and thresholds, but it is not the core purpose of the tool. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.1.1, Page 47.
An organization's decision to remain noncompliant with certain laws or regulations is MOST likely influenced by:
The region in which the organization operates.
Established business culture.
Risk appetite set by senior management.
Identified business process controls.
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk appetite determined by senior management reflects the enterprise's willingness to accept certain levels of risk, including noncompliance. This decision underscores the strategic trade-offs made in risk management, a key element inGovernance and Risk Policy Alignment.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are BEST utilized to provide a high-level overview of:
control efficiency
cost effectiveness
return on investment (ROI)
changes in risk tolerance
Answer:
Explanation:
KPIs provide metrics that show whether processes and controls are meeting performance targets. CRISC explains that KPIs help identify how efficiently controls or processes are operating. They provide a leading view of performance, enabling early identification of inefficiencies that may lead to increased risk. KPIs do not measure cost effectiveness, ROI, or changes in risk tolerance—those belong to financial or strategic measurement systems. Control efficiency aligns directly with KPI use because KPIs measure operational results against objectives.
Malware has recently affected an organization. The MOST effective way to resolve this situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan would be to perform:
a gap analysis
a root cause analysis.
an impact assessment.
a vulnerability assessment.
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most effective way to resolve the situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan would be to perform a root cause analysis. A root cause analysis is a method of identifying and addressing the underlying factors or causes that led to the occurrence of a problem or incident1. In this case, the problem or incident is the malware infection that affected the organization. By performing a root cause analysis, the organization can determine how and why the malware was able to infect the systems, what vulnerabilities or weaknesses were exploited, what controls orprocesses failed or were missing, and what actions or decisions contributed to the situation. A root cause analysis can help the organization to prevent or reduce the recurrence of similar incidents, as well as to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk management process. A root cause analysis can also help the organization to define a comprehensive risk treatment plan, which is a set of actions or measures that are taken to modify the risk, such as reducing, avoiding, transferring, or accepting the risk2. Based on the findings and recommendations of the root cause analysis, the organization can select and implement the most appropriate risk treatment option for the malware risk, as well as for any other related or emerging risks. The risk treatment plan should also include the roles and responsibilities, resources, timelines, and performance indicators for the risk treatmentactions3. The other options are not the most effective ways to resolve the situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan, as they are either less thorough or less relevant than a root cause analysis. A gap analysis is a method of comparing the current state and the desired state of a process, system, or organization, and identifying the gaps or differences between them4. A gap analysis can help the organization to identify the areas of improvement or enhancement, as well as the opportunities or challenges for achieving the desired state. However, a gap analysis is not the most effective wayto resolve the situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan, as it does not address the causes or consequences of the malware infection, or the actions or measures to mitigate the risk. An impact assessment is a method of estimating the potential effects or consequences of a change, decision, or action on a process, system, or organization5. An impact assessment can help the organization to evaluate the benefits and costs, as well as the risks and opportunities, of a proposed or implemented change, decision, or action. However, an impact assessment is not the most effective way to resolve the situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan, as it does not investigate the origin or nature of the malware infection, or the solutions or alternatives to manage the risk. A vulnerability assessment is a method of identifying and analyzing the weaknesses or flaws in a process, system, or organization that can be exploited by threats to cause harm or loss6. A vulnerability assessment can help the organization to discover and prioritize the vulnerabilities, as well as to recommend and implement the controls or measures to reduce or eliminate them. However, a vulnerability assessment is not the most effective way to resolve the situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan, as it does not consider the root causes or impacts of the malware infection, or the risk treatment options or plans to address the risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.1.8, Page 61.
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY basis for deciding whether to disclose information related to risk events that impact external stakeholders?
Stakeholder preferences
Contractual requirements
Regulatory requirements
Management assertions
Answer:
Explanation:
Regulatory requirements should be the primary basis for deciding whether to disclose information related to risk events that impact external stakeholders, because they define the rules or standards that the organization must comply with to meet the expectations of the regulators, such as government agencies or industry bodies, and to avoid legal or reputational consequences. A risk event is an occurrence or incident that may cause harm or damage to the organization or its objectives, such as a natural disaster, a cyberattack, or a human error. An external stakeholder is a person or group that has an interest or influence in the organization or its activities, but is not part of the organization, such as customers, suppliers, partners, investors, or regulators. Disclosing information related to risk events that impact external stakeholders is a process of communicating or reporting the relevant facts or details of the risk events to the affected or interested parties. Disclosing information related to risk events may have benefits, such as maintaining trust, transparency, and accountability, but it may also have drawbacks, such as exposing vulnerabilities, losing competitive advantage, or inviting litigation. Therefore, regulatory requirements should be the primary basis for deciding whether to disclose information, as they provide the legal and ethical obligations and boundaries for the disclosure process. Stakeholder preferences, contractual requirements, and management assertions are all possible factors for deciding whether to disclose information related to risk events, but they are not the primary basis, as they may vary or conflict depending on the situation or context, and may not override the regulatory requirements. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.2, page 158
From a risk management perspective, which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of using automated system configuration validation tools?
Residual risk is reduced.
Staff costs are reduced.
Operational costs are reduced.
Inherent risk is reduced.
Answer:
Explanation:
From a risk management perspective, the primary benefit of using automated system configuration validation tools is that they reduce the inherent risk, which is the risk that exists before any controls are applied. Automated system configuration validation tools can help to ensure that the system settings are consistent, compliant, and secure, and that they match the predefined standards and policies. This can reduce the likelihood and impact of errors, misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, or deviations that may compromise the system’s functionality, performance, or integrity. The other options are not the primary benefits of using automated system configuration validation tools, although they may be secondary benefits or outcomes of doing so. Residual risk is the risk that remains after the controls are applied, and it may not be directly affected by the automated system configuration validation tools. Staff costs and operational costs are related to the efficiency and economy of the system configuration process, but they are not the main risk management objectives. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk Response, page 150.
An organization has identified the need to implement an asset tiering model to establish the appropriate level of impact. Which of the following is the MOST effective risk assessment methodology for a risk practitioner to use for this initiative?
Qualitative method
Industry calibration method
Threat-based method
Quantitative method
Answer:
Explanation:
Implementing an asset tiering model to establish the appropriate level of impact is best served by a quantitative risk assessment methodology. This approach provides a numeric value to the risk levels, which is crucial for accurately tiering assets.
Quantitative Risk Assessment:
Numeric Values:Quantitative methods assign numerical values to the probability and impact of risks, which allows for precise calculations of risk levels. This precision is essential when establishing tiers for assets based on their impact levels.
Data-Driven Decisions:These methods use statistical data and models to predict potential losses and the probability of various risk events, leading to more informed decision-making.
Asset Tiering Model:
Impact Assessment:Quantitative methods allow for detailed impact assessments. By using numeric values, it is easier to compare the potential impacts of different assets and categorize them into appropriate tiers.
Resource Allocation:Precise risk calculations help in the effective allocation of resources. Higher-tier assets (those with higher impact) can be allocated more resources for protection.
Which of the following would be a risk practitioner’s BEST recommendation upon learning of an updated cybersecurity regulation that could impact the organization?
Perform a gap analysis
Conduct system testing
Implement compensating controls
Update security policies
Answer:
Explanation:
 Performing a gap analysis is the best recommendation for a risk practitioner upon learning of an updated cybersecurity regulation that could impact the organization. A gap analysis can help identify the current state of compliance, the desired state of compliance, and the actions needed to achieve compliance. Conducting system testing, implementing compensating controls, and updating security policies are possible actions that may result from the gap analysis, but they arenot the best initial recommendation. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 1; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 143.
Who is MOST important lo include in the assessment of existing IT risk scenarios?
Technology subject matter experts
Business process owners
Business users of IT systems
Risk management consultants
Answer:
Explanation:
 Business process owners are the most important to include in the assessment of existing IT risk scenarios, as they have the authority and responsibility to manage the business processes and their associated risks and controls, and to provide the business perspective and requirements for the IT risk scenarios. Technology subject matter experts, business users of IT systems, and risk management consultants are not the most important to include, as they may have different roles and responsibilities related to the technical, operational, or advisory aspects of IT risk scenarios, respectively, but they do not own the business processes or the IT risk scenarios. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 101.
Which of the following is BEST measured by key control indicators (KCIs)?
Historical trends of the organizational risk profile
Cost efficiency of risk treatment plan projects
Comprehensiveness of risk assessment procedures
Effectiveness of organizational defense in depth
Answer:
Explanation:
Key control indicators are designed to measure the operational effectiveness of controls, specifically their contribution to defense-in-depth strategies. This helps assess if controls are functioning as intended to mitigate identified risks, aligning withControl Effectiveness Monitoring.
An organization's risk register contains a large volume of risk scenarios that senior management considers overwhelming. Which of the following would BEST help to improve the risk register?
Analyzing the residual risk components
Performing risk prioritization
Validating the risk appetite level
Conducting a risk assessment
Answer:
Explanation:
Performing risk prioritization would best help to improve the risk register, which is a document that records and summarizes the key information and data about the identified risks and the risk responses1. Risk prioritization is the process of ranking the risks according to their significance and urgency, based on their probability and impact2. By performing risk prioritization, the organization can:
Reduce the complexity and volume of the risk register, and focus on the most important and relevant risks that require immediate attention and action3.
Enhance the communication and understanding of the risks among the senior management and other stakeholders, and facilitate the decision-making and resource allocation for the risk responses4.
Improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the risk management process, and ensure that the risk register is aligned with the organization’s risk strategy, objectives, and appetite5.
The other options are not the best ways to improve the risk register, because:
Analyzing the residual risk components is not the best way, as it may not address the issue of the large volume of risk scenarios. Residual risk is the level of risk that remains after the implementation of risk responses6. Analyzing the residual risk components can help to measure the exposure or uncertainty of the assets, and to determine the need and extent of the risk responses. However, it may not reduce the complexity or volume of the risk register, as it may add more information or data to the risk register.
Validating the risk appetite level is not the best way, as it may not address the issue of the overwhelming risk scenarios. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept or pursue in order to achieve its objectives7. Validating the risk appetite levelcan help to ensure that the risk register is consistent and proportional to the risk level, and that the risk responses are suitable and feasible. However, it may not reduce the complexity or volume of the risk register, as it may require more information or data to validate the risk appetite level.
Conducting a risk assessment is not the best way, as it may not address the issue of the existing risk scenarios. Risk assessment is the process of estimating the probability and impact of the risks, and prioritizing the risks based on their significance and urgency. Conducting a risk assessment can help to identify and analyze new or emerging risks, and to update or revise the risk register accordingly. However, it may not reduce the complexity or volume of the risk register, as it may introduce more information or data to the risk register.
References =
Risk Register - CIO Wiki
Risk Prioritization - CIO Wiki
Risk Prioritization: A Guide for Project Managers - ProjectManager.com
Risk Prioritization: How to Prioritize Risks in Project Management - Clarizen
Risk Prioritization: A Key Step in Risk Management - ISACA
Residual Risk - CIO Wiki
Risk Appetite - CIO Wiki
[Risk Assessment - CIO Wiki]
Which of the following would be of MOST concern to a risk practitioner reviewing risk action plans for documented IT risk scenarios?
Individuals outside IT are managing action plans for the risk scenarios.
Target dates for completion are missing from some action plans.
Senior management approved multiple changes to several action plans.
Many action plans were discontinued after senior management accepted the risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
The most concerning factor for a risk practitioner reviewing risk action plans for documented IT risk scenarios is that many action plans were discontinued after senior management accepted the risk. Risk action plans are documents that define the roles, responsibilities, procedures, and resources for implementing the risk responses and strategies for the IT risk scenarios. Risk action plans help to reduce, transfer, avoid, or accept the IT risks, and to monitor and report on the IT risk performance and improvement. Discontinuing risk action plans after senior management accepted the risk is a major concern, because it may indicate that the risk acceptance decision was not based on a proper risk analysisor evaluation, or that the risk acceptance decision was not communicated or coordinated with the relevant stakeholders, such as the board, management, business units, and IT functions. Discontinuing risk action plans after senior management accepted the risk may also create challenges or risks for the organization, such as compliance, legal, reputational, or operational risks, or conflicts or inconsistencies with the organization’s risk appetite, risk objectives, or risk policies. The other options are not as concerning as discontinuing risk action plans after senior management accepted the risk, although they may also pose some difficulties or limitations for the risk management process. Individuals outside IT managing action plans for the risk scenarios, target dates for completion missing from some action plans, and senior management approving multiple changes to several action plans are all factors that could affect the quality and timeliness of the risk management process, but they donot necessarily indicate a lack of risk management accountability or oversight. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.4.1, page 4-32.
Which of the following should be the FIRST course of action if the risk associated with a new technology is found to be increasing?
Re-evaluate current controls.
Revise the current risk action plan.
Escalate the risk to senior management.
Implement additional controls.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk action plan is a document that outlines the actions to be taken to mitigate or avoid a risk. A risk action plan should be revised when the risk associated with a new technology is found to be increasing, as this indicates that the current plan is not effective or sufficient. Revising the risk action plan can help identify the root causes of the risk increase, evaluate the effectiveness of current controls, and implement additional or alternative controls as needed. Re-evaluatingcurrent controls, escalating the risk to senior management, and implementing additional controls are possible steps in the revision process, but they are not the first course of action. The first course of action should be to update the risk action plan to reflect the current risk situation and the appropriate risk response.
Which of the following would be a risk practitioner's BEST course of action when a project team has accepted a risk outside the established risk appetite?
Reject the risk acceptance and require mitigating controls.
Monitor the residual risk level of the accepted risk.
Escalate the risk decision to the project sponsor for review.
Document the risk decision in the project risk register.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Risk appetite can be expressed in qualitative or quantitative terms, and can vary depending on the context and the stakeholder. Risk appetite should be defined and communicated by the senior management or the board of directors, and should guide the risk management decisions and actions throughout the organization. When a project team has accepted a risk outside the established risk appetite, the risk practitioner’s best course of action is to escalate the risk decision to the project sponsor for review, meaning that the risk practitioner should report the risk acceptance and its rationale to the project sponsor, who is the person or group that provides the resources and support for the project, and is accountable for its success. The project sponsor should review the risk decision and determine whether it is aligned with the organization’s objectives and strategy, and whether it requires any further approval oraction. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.3.1, p. 25-26
When developing IT risk scenarios, it is MOST important to consider:
The industry's threat profile.
Incidents occurring at similar organizations.
System performance thresholds.
Organizational objectives.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Manual, developing IT risk scenarios must align with business objectives to ensure the scenarios are relevant and meaningful. A top-down approach driven by organizational objectives ensures scenarios are contextually appropriate and address what matters most to the enterprise. This ensures that risk management supports the enterprise’s ability to achieve its mission and goals.
In an organization that allows employee use of social media accounts for work purposes, which of the following is the BEST way to protect company sensitive information from being exposed?
Educating employees on what needs to be kept confidential
Implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) solution
Taking punitive action against employees who expose confidential data
Requiring employees to sign nondisclosure agreements
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to protect company sensitive information from being exposed when an organization allows employee use of social media accounts for work purposes is to require employees to sign nondisclosure agreements. Nondisclosure agreements are legal contracts that prohibit the employees from disclosing or sharing the company sensitive information with unauthorized parties, such as competitors, media, or regulators. Nondisclosure agreements also specify the scope, duration, and conditions of the nondisclosure obligation, and the penalties or remedies for breaching the agreement. Requiring employees to sign nondisclosure agreements is the best way to protect company sensitive information, as it helps to prevent or deter the employees from exposing or leaking the company sensitive information on social media, and to hold the employees accountable and liable for their actions. Requiring employees to signnondisclosure agreements also helps to comply with the legal and regulatory requirements for data protection and privacy. Educating employees on what needs to be kept confidential, implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) solution, and taking punitive action against employees who expose confidential data are also useful ways, but they are not as effective as requiring employees to sign nondisclosure agreements, as they are either dependent on the employees’ awareness or behavior, or reactive or corrective measures, rather than proactive or preventive measures. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 217.
Which of the following should be the FIRST consideration when establishing a new risk governance program?
Developing an ongoing awareness and training program
Creating policies and standards that are easy to comprehend
Embedding risk management into the organization
Completing annual risk assessments on critical resources
Answer:
Explanation:
The first consideration when establishing a new risk governance program is embedding risk management into the organization. Embedding risk management means integrating risk management principles and practices into the organization’s culture, values, processes, and decision-making. Embedding risk management helps to ensure that risk management is not seen as a separate or isolated activity, but as a part of the organization’s normal operations and strategic objectives. Embedding risk management also helps to create a risk-aware and risk-responsive organization, where risk management is shared and supported by all stakeholders. The other options are not the first consideration, although they may be important steps or components of the risk governance program. Developing an ongoing awareness and training program, creating policies and standards that are easy to comprehend, and completing annual risk assessments on critical resources are all activities that can help to embed risk management into the organization, but they are not the initial or primary consideration. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.2.1, page 1-8.
After the implementation of a remediation plan, an assessment of associated control design and operating effectiveness can determine the level of:
residual risk.
aggregated risk.
audit risk.
inherent risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to ISACA CRISC guidance)
Once remediation actions have been implemented, the risk practitioner evaluates whether the new or enhanced controls are designed appropriately and operating effectively. In the CRISC framework, this post-implementation evaluation is used to determine how much risk remains after controls are in place—this is residual risk. Inherent risk is the risk level before considering any controls; therefore it is assessed earlier in the process. Audit risk relates to assurance work, not specifically to the outcome of a remediation plan. Aggregated risk refers to a combined view of multiple risks and is not the direct output of evaluating one specific remediation initiative. By assessing control design (fit for purpose) and operating effectiveness (working as intended), the practitioner can compare the new residual risk level to risk appetite and tolerance, and determine whether additional treatment is needed.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to perform periodic vendor risk assessments?
To provide input to the organization's risk appetite
To monitor the vendor's control effectiveness
To verify the vendor's ongoing financial viability
To assess the vendor's risk mitigation plans
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary reason to perform periodic vendor risk assessments is to monitor the vendor’s control effectiveness. A vendor risk assessment is a process of evaluating the risks associated with outsourcing a service or function to a third-party vendor. The assessment should be performed periodically to ensure that the vendor is complying with the contractual obligations, service level agreements, and security standards, and that the vendor’s controls are operating effectively to mitigate the risks. Providing input to the organization’s risk appetite, verifying the vendor’s ongoing financial viability, and assessing the vendor’s risk mitigation plans are otherpossible reasons, but they are not as important as monitoring the vendor’s control effectiveness. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 11; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 144.
Which of the following is the MAIN reason to continuously monitor IT-related risk?
To redefine the risk appetite and risk tolerance levels based on changes in risk factors
To update the risk register to reflect changes in levels of identified and new IT-related risk
To ensure risk levels are within acceptable limits of the organization's risk appetite and risk tolerance
To help identify root causes of incidents and recommend suitable long-term solutions
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the main reason to continuously monitor IT-related risk is to ensure risk levels are within acceptable limits of the organization’srisk appetite and risk tolerance. The risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives, while the risk tolerance is the acceptable variation in outcomes related to specific performance measures linked to objectives. Continuous monitoring is a process that tracks the security state of an information system on an ongoing basis and maintains the security authorization for the system over time. Continuous monitoring helps to:
Provide ongoing assurance that the implemented security controls are operating effectively and efficiently
Detect changes in the risk profile of the information system and the environment of operation
Identify new or emerging threats and vulnerabilities that may affect the information system
Support risk-based decisions by providing timely and relevant risk information to stakeholders
Facilitate the implementation of corrective actions and risk mitigation strategies
Promote accountability and transparency in the risk management process
Enhance the security awareness and culture within the organization
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 4: IT Risk Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.1: IT Risk Monitoring, pp. 213-2141
Before assigning sensitivity levels to information it is MOST important to:
define recovery time objectives (RTOs).
define the information classification policy
conduct a sensitivity analyse
Identify information custodians
Answer:
Explanation:
Before assigning sensitivity levels to information, it is most important to define the information classification policy. The information classification policy is a document that establishes the criteria, categories, roles, responsibilities, and procedures for classifying information according to its sensitivity, value, and criticality. The information classification policy provides the basis, guidance, and consistency for assigning sensitivity levels to information, and ensures that the information is protected and handled appropriately. The other options are not as important as defining the information classification policy, as they are related to the specific steps, activities, or outputs of the information classification process, not the overall structure and quality of the information classification process. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.4: Key Control Indicators, page 211.
Which of the following is the BEST evidence that a user account has been properly authorized?
An email from the user accepting the account
Notification from human resources that the account is active
User privileges matching the request form
Formal approval of the account by the user's manager
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual, formal approval of the account by the user’s manager is the best evidence that a user account has been properly authorized, because it ensures that the user’s role and access rights are consistent with the business needs and the principle of least privilege. The user’s manager is responsible for verifying the user’s identity, job function, and access requirements, and for approving or rejecting the account request. The other options are not the best evidence of proper authorization, because they do not involve the user’s manager’s approval. An email from the user accepting the account is a confirmation of the account creation, but it does not indicate that the account was authorized by the user’s manager. Notification from human resources that the account is active is an administrative process that does not verify the user’s access rights and role. User privileges matching the request form is a verification of the account configuration, but it does not ensure that the request form was approved by the user’s manager. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.1.2, page 163.
Which of the following is the MOST important reason for a risk practitioner to identify stakeholders for each IT risk scenario?
To ensure enterprise-wide risk management
To establish control ownership
To enable a comprehensive view of risk
To identify key risk indicators (KRIs)
Answer:
Explanation:
Identifying stakeholders ensures that all perspectives are considered, contributing to a holistic view of risk and improving communication and response planning.
When a risk practitioner is building a key risk indicator (KRI) from aggregated data, it is CRITICAL that the data is derived from:
business process owners.
representative data sets.
industry benchmark data.
data automation systems.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Building Key Risk Indicators (KRIs):
KRIs are metrics used to provide an early signal of increasing risk exposure in various areas of an organization.
ï‚· Importance of Representative Data Sets:
To ensure KRIs are accurate and meaningful, it is critical that the data used is representative of the entire population or relevant subset of activities being monitored.
Representative data ensures that the KRIs reflect the true state of risk and are not biased or incomplete.
ï‚· Impact on KRIs:
Using representative data sets improves the reliability and validity of KRIs, enabling better risk detection and management.
It ensures that the KRIs provide a realistic view of potential risk trends and patterns.
ï‚· Comparing Other Data Sources:
Business Process Owners:While they provide valuable insights, data from them alone may not be representative.
Industry Benchmark Data:Useful for comparisons but not specific to the organization’s unique context.
Data Automation Systems:Helpful for efficiency but must ensure the data is representative.
ï‚· References:
The CRISC Review Manual emphasizes the importance of using representative data to build effective KRIs (CRISC Review Manual, Chapter 3: Risk Response and Mitigation, Section 3.11 Data Collection Aggregation Analysis and Validation) ​​.
A data privacy regulation has been revised to incorporate more stringent requirements for personal data protection. Which of the following provides the MOST important input to help ensure compliance with the revised regulation?
Gap analysis
Current control attestation
Risk profile update
Business impact analysis (BIA)
Answer:
Explanation:
Gap analysis identifies differences between existing controls and the new regulatory requirements.
CRISC guidance explains:
“When a regulatory or compliance requirement changes, the first step is to conduct a gap analysis comparing current controls to the new requirements.â€
This allows the practitioner to identify areas requiring remediation or policy enhancement.
Hence, A. Gap analysis is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 3 – Risk Response and Mitigation, Topic: Compliance and Regulatory Alignment.
Which of the following is the BEST indication of an enhanced risk-aware culture?
Users have read and agreed to comply with security policies.
Risk issues are openly discussed within the organization.
Scores have improved on risk awareness quizzes.
There is a decrease in the number of reported incidents.
Answer:
Explanation:
A strong risk-aware culture is reflected by transparent communication about risks. Open discussions signify employee engagement and ownership of risk-related issues.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of aggregating the impact of IT risk scenarios and reflecting the results in the enterprise risk register?
To ensure IT risk appetite is communicated across the organization
To ensure IT risk impact can be compared to the IT risk appetite
To ensure IT risk ownership is assigned at the appropriate organizational level
To ensure IT risk scenarios are consistently assessed within the organization
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary objective of aggregating the impact of IT risk scenarios and reflecting the results in the enterprise risk register is to ensure IT risk impact can be compared to the IT risk appetite, as it enables the organization to measure and evaluate the overall level and exposure of the IT risk, and to align and prioritize the IT risk response and strategy with the organizational objectives and regulations. The other options are not the primary objectives, as they are more related to the communication, assignment, or assessment of the IT risk scenarios, respectively, rather than the aggregation or reflection of the IT risk scenarios. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 109.
A chief risk officer (CRO) has asked to have the IT risk register integrated into the enterprise risk management (ERM) process. Which of the following will BEST facilitate the reporting of IT risk at the enterprise level?
Aggregating the IT risk scenarios into a maturity benchmark value
Using an IT risk heat map to depict likelihood and impact
Using the same risk taxonomy across the organization
Providing a summary of open IT risk-related audit findings
Answer:
Explanation:
Using aconsistent risk taxonomyensures that IT risks can be aggregated and compared with enterprise-level risks in a meaningful way. ISACA emphasizes that standardized risk language and categories are critical to integrating IT risk with ERM processes.
===========
A maturity model is MOST useful to an organization when it:
benchmarks against other organizations
defines a qualitative measure of risk
provides a reference for progress
provides risk metrics.
Answer:
Explanation:
A maturity model is a framework that describes the stages or levels of development and improvement of a certain domain, such as a process, a function, or an organization. A maturity model is most useful to an organization when it provides a reference for progress, meaning that it helps the organization to assess its current state, identify its strengths and weaknesses, set its goals and objectives, and measure itsperformance and improvement over time. A maturity model can also help the organization to compare itself with best practices and standards, but benchmarking against other organizations is not its primary purpose. A maturity model can also help the organization to manage its risks, but defining a qualitative measure of risk or providingrisk metrics is not its main function. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.3.2.1, p. 118-119
A risk practitioner's BEST guidance to help an organization develop relevant risk scenarios is to ensure the scenarios are:
based on industry trends.
mapped to incident response plans.
related to probable events.
aligned with risk management capabilities.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Understanding the Question:
The question asks for the best guidance for developing relevant risk scenarios.
ï‚· Analyzing the Options:
A. Based on industry trends:Important but may not always be directly relevant to the specific organization.
B. Mapped to incident response plans:Useful but secondary to ensuring the scenarios are probable.
C. Related to probable events:Ensures the scenarios are realistic and likely, making them more relevant and actionable.
D. Aligned with risk management capabilities:Important for managing risks but not as critical as ensuring scenarios are probable.
ï‚·
Probable Events:Developing risk scenarios that are based on probable events ensures that the organization is prepared for the most likely risks. This makes risk management efforts more practical and focused on real threats.
Relevance:By focusing on probable events, the scenarios will be more relevant to the organization's actual risk environment, making it easier to allocate resources and plan responses effectively.
Which of the following is MOST important information to review when developing plans for using emerging technologies?
Existing IT environment
IT strategic plan
Risk register
Organizational strategic plan
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important information to review when developing plans for using emerging technologies is the organizational strategic plan. The organizational strategic plan is a document that defines the vision, mission, goals, and objectives of the organization. It also outlines the strategies, actions, and resources that are needed to achieve them. The organizational strategic plan provides the direction, alignment, and guidance for the use of emerging technologies, and ensures that they are aligned with and support the organizational needs and priorities. The other options are not as important as the organizational strategic plan, as they are related to the current state, specific area, or potential issues of the use of emerging technologies, not the overall purpose and value of the use of emerging technologies. References = Risk and InformationSystems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.2: IT Risk Identification Methods, page 19.
A rule-based data loss prevention {DLP) tool has recently been implemented to reduce the risk of sensitive data leakage. Which of the following is MOST likely to change as a result of this implementation?
Risk likelihood
Risk velocity
Risk appetite
Risk impact
Answer:
Explanation:
 A rule-based data loss prevention (DLP) tool is a software solution that identifies and helps prevent unsafe or inappropriate sharing, transfer, or use of sensitive data. It can help an organization monitor and protect sensitive information across on-premises systems, cloud-based locations, and endpoint devices. It can also help an organization comply with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). A rule-based DLP tool works by comparing content to the organization’s DLP policy, which defines how the organization labels, shares, and protects data without exposing it to unauthorized users. The tool can then apply protective actions such as encryption, access restrictions, and alerts. As a result of implementing a rule-based DLP tool, the most likely change is the reduction of risk likelihood, which is the probability of a risk event occurring. By detecting and preventing data breaches, exfiltration, or unwanted destruction of sensitive data, a rule-based DLP tool can lower the chance of such incidents happening and thus decrease the risk likelihood. The other options are less likely to change as a result of implementing a rule-based DLP tool. Risk velocity is the speed at which a risk event impacts an organization, which depends on factors such as the nature of the threat, the response time, and the recovery process. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives, which depends on factors such as the organization’s culture, strategy, and stakeholder expectations. Risk impact is the potential loss or damage that a risk event can cause to an organization, which depends on factors such as the severity of the incident, the extent of theexposure, andthe resilience of the organization. While a rule-based DLP tool may have some influence on these factors, it is not the primary driver of change for them. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 13
Sensitive data has been lost after an employee inadvertently removed a file from the premises, in violation of organizational policy. Which of the following controls MOST likely failed?
Background checks
Awareness training
User access
Policy management
Answer:
Explanation:
Awareness training is the most likely control that failed in this scenario, as it is designed to educate employees on the proper handling and protection of sensitive data, and the consequences of violating the organizational policy. Awareness training can help to prevent or reduce the occurrence of human errors, such as inadvertently removing a file from the premises, that may result in data loss or breach. The other options are not the most likely controls that failed, as they are either not directly related to the scenario or not sufficient to prevent the incident. Background checks are used to verify the identity, qualifications, and trustworthiness of potential or current employees, but they do not ensure that employees will always follow the policy or avoidmistakes. User access is used to restrict the access to information systems or resources based on the identity, role, or credentials of the user, but it does not prevent the user from copying or removing the data once they have access. Policy management is used to create, communicate, and enforce the organizational policy, but it does not ensure that employees will understand orcomply with the policy. References = Sensitive Data Essentials – The Lifecycle Of A Sensitive File; Personal data breach examples | ICO; How do I prevent staff accidentally sending personal information … - GCIT; 10 Ways to Protect Sensitive Employee Information; My personal data has been lost after a breach, what are my rights …
Which of the following is MOST important for developing effective key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Engaging sponsorship by senior management
Utilizing data and resources internal to the organization
Including input from risk and business unit management
Developing in collaboration with internal audit
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics used by organizations to monitor and assess potential risks that may impact their objectives and performance. KRIs also provide early warning signals that help organizations identify, analyze, and address risks before they escalate into significant issues1. Effective KRIs are thosethat are relevant, measurable, predictable, comparable, and informational2. The most important factor for developing effective KRIs is including input from risk and business unit management, as they are the persons who have the best understanding of the risk environment, the risk appetite and tolerance, and the risk factors and impacts of the organization. By including input from risk and business unit management, the organization can ensure that the KRIs are aligned with the organization’s strategy, vision, and mission, and that they reflect the current and emerging risks and their potential consequences. Engaging sponsorship by senior management, utilizing data and resources internal to the organization, and developing in collaboration with internal audit are not the most important factors for developing effective KRIs, as they do not provide the same level of insight and relevance as including input from risk and business unit management. Engaging sponsorship by senior management is a factor that involves obtaining the support and approval of the senior leaders who have the authority and accountability for the organization’s performance and governance. Engaging sponsorship by senior management can help to promote the importance and value of KRIs, and to ensure their communication and implementation across the organization, but it does not ensure that the KRIs are appropriate and accurate for the organization’s risk profile. Utilizing data and resources internal to the organization is a factor that involves using the information and assets that are available within the organization to support or enable the development of KRIs. Utilizing data and resources internal to the organization can help to enhance the quality and reliability of KRIs, and to reduce the cost and complexity of obtaining external data and resources, but it does not ensure that the KRIs are comprehensive and consistent with the organization’s risk environment. Developing in collaboration with internal audit is a factor that involves working with the internal audit function that provides independent and objective assurance and advice on the adequacy and effectiveness of the organization’s risk management. Developing in collaboration with internal audit can help to improve the validity and compliance of KRIs, and to provide feedback and recommendations for improvement, but it does not ensure that the KRIs are relevant and realistic for the organization’s risk objectives and strategies. References = 1: Key Risk Indicators: A Practical Guide | SafetyCulture2: KRI Framework for Operational Risk Management | Workiva3: [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.1: Key Risk Indicators, pp. 181-185.]
Which of the following is the MOST effective way to reduce potential losses due to ongoing expense fraud?
Implement user access controls
Perform regular internal audits
Develop and communicate fraud prevention policies
Conduct fraud prevention awareness training.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Developing and communicating fraud prevention policies is the most effective way to reduce potential losses due to ongoing expense fraud because it creates a culture of integrity and accountability, sets clear expectations and consequences for employees, and deters fraudulent behavior. Implementing user access controls, performing regular internal audits, and conducting fraud prevention awareness training are also important controls, but they are more reactive and detective than preventive. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.2, page 4-26.
Which of the following is the MOST important factor affecting risk management in an organization?
The risk manager's expertise
Regulatory requirements
Board of directors' expertise
The organization's culture
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the organization’s culture is the most important factor affecting risk management in an organization, as it influences the riskawareness, risk attitude, risk behavior and risk communication of all stakeholders. The organization’s culture is defined as the shared values, beliefs, norms and expectations that guide the actions and interactions of the members of the organization. The organization’s culture affects how risk management is perceived, supported, implemented and integrated within the organization. A strong risk culture is one that:
Aligns with the organization’s vision, mission, strategy and objectives
Promotes a common understanding of risk and its implications for the organization
Encourages the identification, assessment, response and monitoring of risks at all levels
Fosters a proactive, collaborative and transparent approach to risk management
Empowers and rewards the stakeholders for taking ownership and accountability of risks
Enables continuous learning and improvement of risk management capabilities and maturity
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.3: IT Risk Culture, pp. 23-251
The BEST way to obtain senior management support for investment in a control implementation would be to articulate the reduction in:
detected incidents.
residual risk.
vulnerabilities.
inherent risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
Residual risk is the risk that remains after applying risk responses, such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance. It represents the level of exposure that the organisation is willing to tolerate or assume. Residual risk should be aligned with the organisation’s risk appetite and risk tolerance, which are determined by senior management. Therefore, the best way to obtain senior management support for investment in a control implementation would be to articulate the reduction in residual risk that the control would achieve. This would demonstrate how the control would help the organisation meet its riskobjectives and reduce the likelihood or impact of adverse events. References = ISACA CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, Section 1.3.2, page 25.
Which of the following is the BEST method to maintain a common view of IT risk within an organization?
Collecting data for IT risk assessment
Establishing and communicating the IT risk profile
Utilizing a balanced scorecard
Performing and publishing an IT risk analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
The best method to maintain a common view of IT risk within an organization is to establish and communicate the IT risk profile. An IT risk profile is a document that summarizes the key IT risks that the organization faces or accepts, and their likelihood, impact, and priority. An IT risk profile helps to identify and prioritize the most critical or relevant IT risks, and to align them with the organization’s objectives, strategy, and risk appetite. Establishing and communicating the IT risk profile is the best method to maintain a common view of IT risk, because it helps to create a shared understanding and awareness of the IT risks among the organization’s stakeholders, such as the board, management, business units, and IT functions. Establishing andcommunicating the IT risk profile also helps to facilitate the IT risk decision-making and reporting processes, and to monitor and control the IT risk performance and improvement. Theother options are not the best method to maintain a common view of IT risk, although they may be part of or derived from the IT risk profile. Collecting data for IT risk assessment, utilizing a balanced scorecard, and performing and publishing an IT risk analysis are all activitiesthat can help to support or update the IT risk profile, but they are not the best method to maintain a common view of IT risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.3.1, page 1-15.
Establishing and organizational code of conduct is an example of which type of control?
Preventive
Directive
Detective
Compensating
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), establishing an organizational code of conduct is an example of a directive control, which is a type of control that guides or steers the behavior of individuals or processes to achieve desired outcomes. A directive control aims toinfluence or encourage compliance with the organization’s policies, standards, procedures, and guidelines. A directive control can also communicate the organization’s values, ethics, and expectations to its stakeholders. A directive control can take various forms, such as:
Codes of conduct or ethics
Policies or manuals
Training or awareness programs
Job descriptions or roles and responsibilities
Performance appraisals or incentives
Supervision or oversight
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.4: IT Risk Scenarios, pp. 105-1061
Which of the following is MOST likely to be impacted when a global organization is required by law to implement a new data protection regulation across its operations?
Risk ownership assignments
Threat profile
Vulnerability assessment results
Risk profile
Answer:
A global company s business continuity plan (BCP) requires the transfer of its customer information….
event of a disaster. Which of the following should be the MOST important risk consideration?
The difference In the management practices between each company
The cloud computing environment is shared with another company
The lack of a service level agreement (SLA) in the vendor contract
The organizational culture differences between each country
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important risk consideration when the global company’s business continuity plan (BCP) requires the transfer of its customer information to a cloud computing environment in the event of a disaster is that the cloud computing environment is shared with another company. A cloud computing environment is a service model that provides on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources, such as servers, storage, networks, and applications. A shared cloud computing environment means that the same computing resources are used by multiple customers or tenants, and that the data and activities of one customer may affect or be affected by the data and activities of another customer. This may pose a significant risk to the security, privacy, and availability of the customer information, as it may be exposed, accessed, modified, or deleted by unauthorized or malicious parties. The other options are not as important as the cloud computing environment being shared with another company, as they are related to the differences, agreements, or cultures of the company or the country, not the environment or the platform of the customer information transfer. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: IT Risk Response Implementation, page 145.
The risk appetite for an organization could be derived from which of the following?
Cost of controls
Annual loss expectancy (ALE)
Inherent risk
Residual risk
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual1, cost of controls is the amount of money or resources that an organization is willing to spend to implement and maintain risk responses. Cost of controls is one of the factors that influences the risk appetite of an organization, as it reflects thetrade-off between the benefits and costs of risk responses. Cost of controls helps to determine the optimal level of risk that an organization can accept in pursuit of its objectives, and to align the risk responses with the organization’s strategy, goals, and culture. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 193.
Which of the following is the MOST effective way to help ensure future risk levels do not exceed the organization's risk appetite?
Establishing a series of key risk indicators (KRIs).
Adding risk triggers to entries in the risk register.
Implementing key performance indicators (KPIs).
Developing contingency plans for key processes.
Answer:
Explanation:
KRIs provide predictive metrics to monitor changes in risk levels, enabling timely interventions to maintain risks within the organization's appetite. This aligns with theRisk Monitoring and Reportingframework, which emphasizes proactive identification of risk thresholds.
Days before the realization of an acquisition, a data breach is discovered at the company to be acquired. For the accruing organization, this situation represents which of the following?
Threat event
Inherent risk
Risk event
Security incident
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk event is an occurrence or situation that has a negative impact on the objectives, operations, or resources of an enterprise. A data breach at the company to be acquired is a risk event for the acquiring organization, because it can affect the value, reputation, or performance of the acquisition. A risk event can also trigger other risks or consequences that may require further actions or responses. The other options are not the correct answers, because they do not describe the situation accurately. A threat event is an occurrence or situation that exploits a vulnerability or causes harm to an asset or process. An inherent risk is the risk that exists before applying any controls or treatments. A security incident is an event that violates the security policies or procedures of an enterprise. References = CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions
A risk practitioner recently discovered that personal information from the production environment is required for testing purposes in non-production environments. Which of the following is the BEST recommendation to address this situation?
Enable data encryption in the test environment.
Prevent the use of production data in the test environment
De-identify data before being transferred to the test environment.
Enforce multi-factor authentication within the test environment.
Answer:
Explanation:
 The best recommendation to address the situation where personal information from the production environment is required for testing purposes in non-production environments is to de-identify data before being transferred to the test environment. De-identification is the process of removing or modifying any personally identifiable information (PII) or other sensitive data from the data sets, such as names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, etc., so that the data cannot be traced back to specific individuals. De-identification protects the privacy and confidentiality of the data, while still allowing for testing, analysis, or training purposes. Enabling data encryption, preventing the use of production data, and enforcing multi-factor authentication are also useful measures, but they do not eliminate the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to PII. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.3.1, page 3-21.
Which of the following is the BEST approach to mitigate the risk associated with outsourcing network management to an external vendor who will have access to sensitive information assets?
Prepare a skills matrix to illustrate tasks and required expertise.
Require periodic security assessments of the vendor within the contract.
Perform due diligence to enable holistic assessment of the vendor.
Plan a phased approach for the transition of processes to the vendor.
Answer:
Explanation:
Performing due diligence is the most effective initial step in mitigating risks associated with outsourcing. This comprehensive assessment evaluates the vendor's capabilities, security posture, compliance with regulations, and overall suitability for handling sensitive information assets. It ensures that potential risks are identified and addressed before entering into a contractual agreement.
Which of the following BEST enables detection of ethical violations committed by employees?
Transaction log monitoring
Access control attestation
Periodic job rotation
Whistleblower program
Answer:
Explanation:
Whistleblower Program:
Definition: A whistleblower program allows employees to report unethical or illegal activities within the organization anonymously.
Detection of Ethical Violations: Employees are often in the best position to observe unethical behavior. A well-structured whistleblower program encourages them to report such behavior without fear of retaliation.
Anonymity and Protection: Providing anonymity and protection to whistleblowers increases the likelihood that employees will report violations, thus enabling the organization to detect and address ethical issues more effectively.
Comparison with Other Options:
Transaction Log Monitoring: While useful for detecting anomalies and potential fraud, it is not specifically focused on ethical violations and may not capture all types of unethical behavior.
Access Control Attestation: This ensures that users have the correct access permissions but does not directly detect unethical behavior.
Periodic Job Rotation: This can help prevent fraud by reducing the risk of collusion and providing fresh perspectives on processes, but it does not directly detect ethical violations.
Best Practices:
Clear Reporting Channels: Ensure that the whistleblower program has clear and accessible reporting channels.
Training and Awareness: Regularly train employees on the importance of reporting unethical behavior and the protections offered by the whistleblower program.
Follow-up and Action: Ensure that reports are investigated thoroughly and appropriate actions are taken to address verified violations.
A risk practitioner observed Vial a high number of pokey exceptions were approved by senior management. Which of the following is the risk practitioner’s BEST course of action to determine root cause?
Review the risk profile
Review pokey change history
interview the control owner
Perform control testing
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action to determine the root cause of the high number of policy exceptions approved by senior management is to interview the control owner. The control owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for designing, implementing, and monitoring the controls that enforce the policy. The control owner can provide insight into the reasons, circumstances, and impacts of the policy exceptions, and the effectiveness and efficiency of the controls. The control owner can also suggest possible improvements or alternatives to the policy or the controls. The other options are not as useful as interviewing the control owner, as they are related to the review, analysis, or testing of the policy or the controls, not the investigation or understanding of the policy exceptions. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.4: Key Control Indicators, page 211.
Reviewing historical risk events is MOST useful for which of the following processes within the risk management life cycle?
Risk monitoring
Risk mitigation
Risk aggregation
Risk assessment
Answer:
Explanation:
Reviewing historical risk events is most useful for the risk assessment process within the risk management life cycle. Risk assessment is the process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks that may affect the project or the organization1. Reviewing historical risk events can help to:
Identify the sources, causes, and consequences of past risks and learn from the successes and failures of previous projects or organizations
Analyze the likelihood and impact of potential risks based on historical data and trends, and use statistical methods or models to estimate the probability and severity of risk scenarios
Evaluate the level of risk exposure and compare it with the risk appetite and tolerance of the project or the organization, and prioritize the risks that need further attention or action
Use historical risk events as inputs or examples for risk identification and analysis techniques, such as brainstorming, checklists, interviews, surveys, SWOT analysis, root cause analysis, or Monte Carlo simulation2
References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Risk Assessment Process3
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern associated with the transmission of healthcare data across the internet?
Unencrypted data
Lack of redundant circuits
Low bandwidth connections
Data integrity
Answer:
Explanation:
The greatest concern associated with the transmission of healthcare data across the internet is unencrypted data, as this exposes the data to unauthorized access, interception, modification, or disclosure, which may compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. Healthcare data is sensitive and personal information that may include medical records, diagnoses, treatments, prescriptions, insurance claims, and biometric data. Healthcare data is subject to various legal and regulatory requirements, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, that mandate the protection and privacy of the data. Encryption is a method of transforming the data into an unreadable format that can only be accessed or restored by authorized parties who have the decryption key. Encryption helps to prevent or reduce the risk of data breaches, identity theft, fraud, or other malicious attacks. The other options are not the greatest concerns associated with the transmission of healthcare dataacross the internet, although they may pose some challenges or issues. Lack of redundant circuits is a concern for the reliability and continuity of the data transmission, but it does notaffect the security or privacy of the data. Low bandwidth connections is a concern for the speed andefficiency of the data transmission, but it does not affect the security or privacy of the data. Data integrity is a concern for the accuracy and completeness of the data, but it does not necessarily depend on the encryption of the data. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk Response, page 156.
Which of the following scenarios presents the GREATEST risk for a global organization when implementing a data classification policy?
Data encryption has not been applied to all sensitive data across the organization.
There are many data assets across the organization that need to be classified.
Changes to information handling procedures are not documented.
Changes to data sensitivity during the data life cycle have not been considered.
Answer:
Explanation:
Changes to data sensitivity during the data life cycle present the greatest risk for a global organization when implementing a data classification policy, as they may result in data being under-protected or over-protected, leading to potential data breaches, compliance violations, or inefficiencies. Data sensitivity refers to the level of confidentiality, integrity, and availability that the data requires, and it may changedepending on the data’s creation, storage, processing,transmission, or disposal. A data classification policy should consider the changes to data sensitivity during the data life cycle and ensure that the appropriate controls and procedures are applied at each stage. Data encryption not applied to all sensitive data, many data assets that need to be classified, and changes to information handling procedures not documented are not the greatest risks, as they do not affect the data classification policy itself, but rather the implementation or execution of the policy. References = CRISC Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control – Question211; ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 211.
An organization has outsourced its lease payment process to a service provider who lacks evidence of compliance with a necessary regulatory standard. Which risk treatment was adopted by the organization?
Acceptance
Transfer
Mitigation
Avoidance
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the ERM - Step 3 - Risk Treatment article, risk transfer is a risk treatment option that involves passing ownership and/or liability of a risk to a third party, such as an insurance company, a contractor, or a supplier. Risk transfer is usually adopted when the organization does not have the capability or the resources to manage the risk internally, or when the cost of transferring the risk is lower than the cost of retaining the risk. In this case, the organization has outsourced its lease payment process to a service provider who lacks evidence of compliance with a necessary regulatory standard. This means that the organization has transferred the risk ofnon-compliance to the service provider, who is now responsible for ensuring that the lease payment process meets the regulatory requirements. Therefore, the answer is B. Transfer. References = ERM - Step 3 - Risk Treatment
Which of the following is the MOST important component of effective security incident response?
Network time protocol synchronization
Identification of attack sources
Early detection of breaches
A documented communications plan
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important component of effective security incident response is a documented communications plan. A communications plan defines the roles and responsibilities, channels and methods, frequency and timing, and content and format of the communications that take place during and after a security incident. A communications plan helps to ensure that the relevant stakeholders are informed and updated about the incident status and outcome, and that the incident response activities are coordinated and consistent. A communications plan also helps to manage the expectations and perceptions of the stakeholders, and to maintain the trust and reputation of the enterprise. Network time protocol synchronization, identification of attack sources, and early detection of breaches are also important components of effective security incident response, but they are not as important as a documented communications plan. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1.2, page 1931
1: ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC®) Exam Guide, Answer to Question 660.
Which of the following MOST effectively limits the impact of a ransomware attack?
Cyber insurance
Cryptocurrency reserve
Data backups
End user training
Answer:
Explanation:
The most effective way to limit the impact of a ransomware attack is to have data backups. Data backups are copies of the data that are stored in a separate location or device, and can be used to restore the data in case of a loss or corruption. Data backups can help to recover the data that is encrypted or deleted by the ransomware, and to avoid paying the ransom to the attackers. Data backups also help to reduce the downtime and disruption caused by the ransomware attack, and to maintain the business continuity and availability of the data. Cyber insurance, cryptocurrency reserve, and end user training are not the most effective ways to limit the impact of a ransomware attack, as they may not prevent or recover the data loss, and may incur additional costs or risks for the enterprise. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.1.1.1, page 2281
1: ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC®) Exam Guide, Answer to Question 657.
A highly regulated organization acquired a medical technology startup company that processes sensitive personal information with weak data protection controls. Which of the following is the BEST way for the acquiring company to reduce its risk while still enabling the flexibility needed by the startup company?
Identify previous data breaches using the startup company’s audit reports.
Have the data privacy officer review the startup company’s data protection policies.
Classify and protect the data according to the parent company's internal standards.
Implement a firewall and isolate the environment from the parent company's network.
Answer:
Explanation:
Data protection is the process of safeguarding sensitive personal information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. Data protection can help to ensure the privacy and security ofthe data subjects, and to comply with the legal and regulatory requirements that apply to the data processing activities1.
A highly regulated organization that acquired a medical technology startup company that processes sensitive personal information with weak data protection controls faces a high risk of data breaches, fines, lawsuits, reputational damage, or loss of customer trust. The best way for the acquiring company to reduce its risk while still enabling the flexibility needed by the startupcompany is to classify and protect the data according to the parent company’s internal standards, because it can help to:
Identify and categorize the sensitive personal information based on its value, sensitivity, and criticality, such as confidential, restricted, internal, or public
Apply and enforce the appropriate data protection policies, procedures, and controls for each data category, such as encryption, access control, backup, retention, or disposal
Align and integrate the data protection practices and processes of the startup company with those of the parent company, and ensure the consistency and compliance across the organization
Balance and optimize the trade-off between data protection and data usability, and allow the startup company to leverage the data for innovation and growth, as long as it meets the data protection standards of the parent company23
The other options are not the best ways for the acquiring company to reduce its risk while still enabling the flexibility needed by the startup company, but rather some of the steps or aspects of data protection. Identify previous data breaches using the startup company’s audit reports is a step that can help to assess the current data protection status and gaps of the startup company, and to learn from the past incidents and mistakes, but it does not address the future data protection needs and challenges of the startup company. Have the data privacy officer review the startup company’s data protection policies is an aspect that can help to ensure the legal and regulatory compliance of the data protection activities of the startup company, and to provide guidance and oversight for the data protection issues and risks, but it does not ensure the technical and operational effectiveness and efficiency of the data protection controls of the startup company. Implement a firewall and isolate the environment from the parent company’s network is a control that can help to prevent or limit the external or internal attacks or threats to the data of the startup company, and to reduce the exposure or impact of a data breach, but it does not ensure the availability or accessibility of the data for the legitimate and authorized purposes of the startup company. References =
Data Protection - ISACA
Data Classification - ISACA
Data Protection Best Practices - ISACA
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
After mapping generic risk scenarios to organizational security policies, the NEXT course of action should be to:
record risk scenarios in the risk register for analysis.
validate the risk scenarios for business applicability.
reduce the number of risk scenarios to a manageable set.
perform a risk analysis on the risk scenarios.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the LDR514: Security Strategic Planning, Policy, and Leadership Course, after mapping generic risk scenarios to organizational security policies, the next course of action should be to validate the risk scenarios for business applicability. This is because generic risk scenarios are not specific to the organization’s context, objectives, and environment, and they may not capture the unique threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts that the organization faces. Therefore, validating the risk scenarios for business applicability will help to ensure that the risk scenarios are relevant, realistic, and consistent with the organization’s security policies. Validating the risk scenarios will also help to identify any gaps, overlaps, or conflicts between the risk scenarios and the security policies, and to resolve themaccordingly. References = LDR514: Security Strategic Planning, Policy, and Leadership Course, Risk Assessment and Analysis Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of establishing an organization's risk tolerance and appetite?
To align with board reporting requirements
To assist management in decision making
To create organization-wide risk awareness
To minimize risk mitigation efforts
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk tolerance and appetite are the expressions of the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Risk tolerance is the acceptable level of variation that the organization is willing to allow for the outcome of its risk decisions. Riskappetite is the broad-based amount of risk that the organization is willing to accept in its activities. The primary objective of establishing an organization’s risk tolerance and appetite is to assist management in decision making, as they provide guidance and boundaries for the risk management activities and decisions. By establishing the risk tolerance and appetite, the organization can align its risk exposure with its strategic goals, optimize its risk-return trade-off, and enhance its risk culture and performance. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 61.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when sharing risk management updates with executive management?
Including trend analysis of risk metrics
Using an aggregated view of organizational risk
Relying on key risk indicator (KRI) data
Ensuring relevance to organizational goals
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important consideration when sharing risk management updates with executive management is ensuring relevance to organizational goals. This means that the risk information presented should align with the strategic objectives and priorities of the organization, and demonstrate how risk management supports the achievement of those goals. Executive management is responsible for setting the direction and vision of the organization, and therefore needs to understand how risk management contributes to the value creation and protection of the organization. By ensuring relevance to organizational goals, risk management updates can help executive management make informed decisions, allocate resources, and communicate with stakeholders.
Some of the ways to ensure relevance to organizational goals are:
Linking risk management updates to the organization’s mission, vision, values, and strategy
Highlighting the key risks and opportunities that affect the organization’s performance and competitiveness
Providing clear and concise risk reports that focus on the most critical and material risks
Using a common risk language and framework that is understood by executive management
Providing actionable recommendations and solutions to address the identified risks
Aligning risk management updates with the organization’s reporting cycle and governance structure
References =
The Importance of Integrating Risk Management with Strategy
Four steps for managing risk at the CEO level
5 Key Principles of Successful Risk Management
Which of the following is the BEST way to quantify the likelihood of risk materialization?
Balanced scorecard
Threat and vulnerability assessment
Compliance assessments
Business impact analysis (BIA)
Answer:
Explanation:
A threat and vulnerability assessment is a process that identifies and evaluates the potential sources and impacts of risk events on an organization’s assets, processes, and objectives. It also estimates the probability of occurrence and the severity of consequences for each risk event. A threat and vulnerability assessment is the best way to quantify the likelihood of risk materialization, as it provides a numerical or qualitative measure of the risk exposure and the level of uncertainty associated with the risk scenarios. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.2, p. 68-69
Which of the following is the BEST way for a risk practitioner to help management prioritize risk response?
Align business objectives to the risk profile.
Assess risk against business objectives
Implement an organization-specific risk taxonomy.
Explain risk details to management.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way for a risk practitioner to help management prioritize risk response is to assess risk against business objectives. This means comparing the level and nature of the risks with the goals and strategies of the organization, and determining which risks pose the most significant threat or opportunity to the achievement of those objectives. By assessing risk against business objectives, the risk practitioner can help management identify the most critical and relevant risks, and prioritize the risk response actions accordingly. The risk response actions should be aligned with the organization’s risk appetite, which is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to take in order to meet its strategic goals1. The other options are not the best ways for a risk practitioner to help management prioritize risk response, as they are either less effective orless specific than assessing risk against business objectives. Aligning business objectives to the risk profile is a way of ensuring that the organization’s objectives are realistic and achievable, given the current and potential risks that the organization faces. However, this is not the same as prioritizing risk response, as it does not indicate which risks should be addressed first or howtheyshould be managed. Implementing an organization-specific risk taxonomy is a way of creating a common language and classification system for describing and categorizing risks. This can help improve the consistency and clarity of risk communication and reporting across the organization. However, this is not the same as prioritizing risk response, as it does not measure the likelihood and impact of the risks, or their relation to the organization’s objectives. Explaining risk details to management is a way of providing information and insight on the sources, drivers, consequences, and responses of the risks. This can help increase the awareness and understanding of the risks among the decision makers and stakeholders. However, this is not the same as prioritizing risk response, as it does not suggest or recommend the best course of action for managing the risks. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.1.6, Page 57.
Sensitive information classification and handling policies
Anti-malware controls on endpoint devices
Regular employee security awareness training
An egress intrusion detection system (IDS)
Answer:
Explanation:
Regular employee security awareness training is the most effective method to reduce unintentional disclosure of sensitive information. Training educates employees on risks, policies, and best practices, thus changing behavior and reducing human error. Classification policies provide guidelines, and technical controls like IDS and anti-malware detect or prevent some risks but do not address the human factor as directly as awareness trainingã€5:517, 5:527†CRISC_SentenceinNOTE30.pptx】.
Which of the following is a risk practitioner's MOST important responsibility in managing risk acceptance that exceeds risk tolerance?
Verify authorization by senior management.
Increase the risk appetite to align with the current risk level
Ensure the acceptance is set to expire over lime
Update the risk response in the risk register.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s most important responsibility in managing risk acceptance that exceeds risk tolerance is to verify authorization by senior management. Risk acceptance is a risk response strategy that involves acknowledging and agreeing to bear the risk and its potential consequences. Risk tolerance is the acceptable or allowable level of variation or deviation from the expected or desired outcomes or objectives. When the risk acceptance exceeds the risk tolerance, it means that the organization is taking on more risk than it can handle or afford. Therefore, the risk practitioner should verify that the risk acceptance is authorized by senior management, who have the authority and accountability for making risk management decisions and ensuring that they are aligned with the organizational strategy and objectives. The other options are not as important as verifying authorization by senior management, as they are related to the adjustments, conditions, or documentation of the risk acceptance, not the approval or validation of the risk acceptance. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.2: IT Risk Response Options, page 133.
A review of an organization s controls has determined its data loss prevention {DLP) system is currently failing to detect outgoing emails containing credit card data. Which of the following would be MOST impacted?
Key risk indicators (KRls)
Inherent risk
Residual risk
Risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
Residual risk is the risk that remains after applying controls to mitigate the inherent risk. Inherent risk is the risk that exists before considering the controls. Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metricsthat measure the level and impact of risks. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. The failure of the data loss prevention (DLP) system to detect outgoing emails containing credit card data would most impact the residual risk, because it would increase the likelihood and impact of data leakage, data loss, and data exfiltration incidents. These incidents could cause financial, reputational, legal, and regulatory damages to the organization. The failure of the DLP system would also affect the KRIs, as they would show a higher level of risk exposure and a lower level of control effectiveness. However, the KRIs are not the risk itself, but rather the indicators of the risk. The failure of the DLP system would not directly impact the inherent risk or the risk appetite, as they are independent of the controls. The inherent risk would remain the same, as it is based on the nature and value of the data and the threats and vulnerabilities that exist. The risk appetite would also remain the same, as it is based on the organization’s culture, strategy, and stakeholder expectations. Therefore, the most impacted factor would be the residual risk, as it reflects the actual risk level that the organization faces after applying the controls. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 131
For a large software development project, risk assessments are MOST effective when performed:
before system development begins.
at system development.
at each stage of the system development life cycle (SDLC).
during the development of the business case.
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk assessments are most effective when performed at each stage of the system development life cycle (SDLC). The SDLC is a framework that defines the phases and activities of developing, implementing, and maintaining a system. The SDLC typically consists of the following stages: initiation, planning, analysis, design, development, testing, implementation, and maintenance. Performing risk assessments at each stage of the SDLC helps to identify, analyze, and evaluate the risks that could affect the system objectives, requirements, functionality, quality, or performance. Performing risk assessments at each stage of the SDLC also helps to select and implement the appropriate risk responses, such as avoiding, transferring, mitigating, or accepting the risks. Performing risk assessments at each stage of the SDLC also helps to monitor and report the risk status and performance, and to update and adjust the risk assessment and response as the system changes or evolves. Performing risk assessments before system development begins, at system development, or during the development of the business case are not as effective as performing risk assessments at each stage of the SDLC, as they are either too early or too late, and they do not capture the full scope and complexity of the system risks. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 49.
Which of the following IT controls is MOST useful in mitigating the risk associated with inaccurate data?
Encrypted storage of data
Links to source data
Audit trails for updates and deletions
Check totals on data records and data fields
Answer:
Explanation:
 Check totals are IT controls that verify the accuracy and completeness of data by comparing the sum or count of data records or data fields with a predetermined or expected value. Check totals can help detect and prevent errors, omissions, or alterations in data entry, processing, or transmission. Check totals can also help identify and correct data discrepancies or anomalies. Therefore, check totals are the most useful IT controls in mitigating the risk associated with inaccurate data. The other options are not the best answers because they do not directly address the risk of inaccurate data. Encrypted storage of data is an IT control that protects the confidentiality and integrity of data by preventing unauthorized access or modification. However, encryption does not ensure the accuracy or validity of the data itself. Links to source data are IT controls that provide traceability and transparency of data by allowing users to access or view the original data from which the derived or aggregated data is obtained. However, links to source data do not verify or correct the data quality or consistency. Audit trails for updates and deletions are IT controls that record thehistory and changes of data by capturing the date, time, user, and action performed on the data. Audit trails can help monitor and review the data activities and transactions, but they do not prevent or detect the data errors or inaccuracies. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 164-1651; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 722
Which of the following would provide the MOST comprehensive information for communicating current levels of IT-related risk to executive management?
Risk register
Risk appetite
Risk dashboard
Risk action plans
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk dashboard provides a visual, real-time overview of risk levels, trends, and key metrics, making it easier for executive management to understand and act upon. It integrates data from various sources, making it comprehensive.
Which of the following is the MOST important data source for monitoring key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Directives from legal and regulatory authorities
Audit reports from internal information systems audits
Automated logs collected from different systems
Trend analysis of external risk factors
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that help organizations monitor and evaluate the level of risk they are exposed to. They provide early warning signals of potential issues that could affect the achievement of organizational goals12.
The most important data source for monitoring KRIs is automated logs collected from different systems, which are records that capture and store the details and history of the transactions or activities that are performed by the organization’s processes, systems, or controls34.
Automated logs collected from different systems are the most important data source because they provide timely and accurate data and information on the performance and status of the organization’s operations, and enable the detection and reporting of any deviations, anomalies, or issues that may indicate a risk event34.
Automated logs collected from different systems are also the most important data source because they support the accountability and auditability of the organization’s operations, and facilitate the investigation and resolution of any risk event34.
The other options are not the most important data sources, but rather possible inputs or factors that may influence or affect the KRIs. For example:
Directives from legal and regulatory authorities are documents that provide the expectations and obligations of the external authorities or bodies that govern or oversee the organization’s activities and operations, such as laws, regulations, standards, or contracts5 . However, these documents are not the most important data source becausethey do not directly measure or monitor the level of risk exposure, but rather provide the criteria or framework for risk compliance5 .
Audit reports from internal information systems audits are documents that provide the findings and recommendations of the independent and objective assessment of the adequacy and effectiveness of the organization’s information systems, processes, and controls . However, these documents are not the most important data source because they do not directly measure or monitor the level of risk exposure, but rather provide the assurance or improvement for risk management .
Trend analysis of external risk factors is a technique that involves analyzing and forecasting the changes and impacts of the external factors that influence the organization’s operations, such as technology, competition, regulation, or customer behavior . However, this technique is not themost important data source because it does not directly measure or monitor the level of risk exposure, but rather provide the insight or prediction for risk identification . References =
1: Key Risk Indicators: A Practical Guide | SafetyCulture1
2: Key risk indicator - Wikipedia2
3: Database Activity Monitoring - Wikipedia3
4: Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) | Imperva4
5: Regulatory Compliance - Wikipedia5
Regulatory Compliance Management Software | MetricStream
IT Audit and Assurance Standards, ISACA, 2014
IT Audit and Assurance Guidelines, ISACA, 2014
Trend Analysis - Investopedia
Trend Analysis: A Definition and Examples
Of the following, who is responsible for approval when a change in an application system is ready for release to production?
Information security officer
IT risk manager
Business owner
Chief risk officer (CRO)
Answer:
Explanation:
 The business owner is the person who is responsible for approval when a change in an application system is ready for release to production. The business owner is the person who has the authority and accountability for the business process or function that is supported by the application system. The business owner should approve the change to ensure that it meets the business requirements, objectives, and expectations, and that it does not introduce any adverse impacts or risks to the business operations. The information security officer, the IT risk manager, and the chief risk officer (CRO) are not responsible for the approval of the change, although they may provide input, feedback, or oversight. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.1, page 3-32.
A business unit has decided to accept the risk of implementing an off-the-shelf, commercial software package that uses weak password controls. The BEST course of action would be to:
obtain management approval for policy exception.
develop an improved password software routine.
select another application with strong password controls.
continue the implementation with no changes.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A policy exception is a deviation from the established policies, standards, or procedures of the enterprise, such as the information security policy. A policy exception may be granted by the management when there is a valid business reason or justification for the deviation, and when the risk associated with the deviation is acceptable or mitigated. The best course of action when a business unit has decided to accept the risk of implementing an off-the-shelf, commercialsoftware package that uses weak password controls is to obtain management approval for policy exception. This will ensure that the business unit is aware of the implications and consequences of the policy exception, and that the management agrees with the risk acceptance and approves the policy exception. The other options are not the best course of action, as they involve different risk response strategies or outcomes:
Develop an improved password software routine means that the business unit modifies or enhances the password controls of the software package, such as by increasing the password length, complexity, or expiration. This may not be a feasible or effective way to address the risk of weak password controls, as it may violate the terms and conditions of the software vendor, or may not be compatible or consistent with the software package.
Select another application with strong password controls means that the business unit replaces the software package with another application that has better password controls, such as by using encryption, authentication, or authorization. This may not be a desirable or efficient way to address the risk of weak password controls, as it may incur additional costs, delays, or complexities, or may not meet the business requirements or expectations of the business unit.
Continue the implementation with no changes means that the business unit proceeds with the software package without any modifications or improvements to the password controls, or without any approval or documentation of the policy exception. This may not be a responsible or ethical way to address the risk of weak password controls, as it may expose the enterprise to legal, financial, or reputational risks, or may compromise the security or compliance of the enterprise. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.1.1, pp. 121-122.
During an organization's simulated phishing email campaign, which of the following is the BEST indicator of a mature security awareness program?
A high number of participants reporting the email
A high number of participants deleting the email
A low number of participants with questions for the help desk
A low number of participants opening the email
Answer:
Explanation:
A mature program is indicated by employees recognizing phishing and actively reporting it—not just deleting it. ISACA guidance states that awareness programs should foster “threat identification and escalation actions,†not just passive compliance.
An organization has outsourced its backup and recovery procedures to a third-party cloud provider. Which of the following is the risk practitioner s BEST course of action?
Accept the risk and document contingency plans for data disruption.
Remove the associated risk scenario from the risk register due to avoidance.
Mitigate the risk with compensating controls enforced by the third-party cloud provider.
Validate the transfer of risk and update the register to reflect the change.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s BEST course of action is to validate the transfer of risk and update the register to reflect the change, because outsourcing the backup and recovery procedures to a third-party cloud provider does not eliminate the risk, but rather transfers it to the service provider. The risk practitioner should verify that the service provider has adequate controls and capabilities to handle the backup and recovery procedures, and that the contractual agreement specifies the roles and responsibilities of both parties. The risk practitioner should also update the risk register to reflect the new risk owner and the residual risk level. The other options are not the best course of action, because:
Option A: Accepting the risk and documenting contingency plans for data disruption is not the best course of action, because it implies that the risk practitioner is still responsible for the risk, even though it has been transferred to the service provider. Contingency plans are also reactive measures, rather than proactive ones.
Option B: Removing the associated risk scenario from the risk register due to avoidance is not the best course of action, because it implies that the risk has been eliminated, which is not the case. The risk still exists, but it has been transferred to the service provider. The risk register should reflect the current risk status and ownership.
Option C: Mitigating the risk with compensating controls enforced by the third-party cloud provider is not the best course of action, because it implies that the risk practitioner is still involved in the risk management process, even though the risk has been transferred to the service provider. The risk practitioner should rely on the service provider’s controls and capabilities, andmonitor their performance and compliance. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, p. 196.
Which of the following is the MOST important criteria for selecting key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Historical data availability
Implementation and reporting effort
Ability to display trends
Sensitivity and reliability
Answer:
Explanation:
Sensitivity and reliability are the most important criteria for selecting KRIs, as they indicate how well the KRIs reflect the changes in the risk level and how consistent and accurate the KRIs are in measuring the risk.Sensitivity means that the KRIs should respond quickly and proportionally to the variations in the risk exposure, and provide early warning signals of potential risk events. Reliability means that the KRIs should be based on valid and verifiable data sources, and produce consistent and comparable results over time and across different units or functions. Historical data availability, implementation and reporting effort, and ability to display trends are also useful criteria, but they are not as critical as sensitivity and reliability.
When communicating changes in the IT risk profile, which of the following should be included to BEST enable stakeholder decision making?
List of recent incidents affecting industry peers
Results of external attacks and related compensating controls
Gaps between current and desired states of the control environment
Review of leading IT risk management practices within the industry
Answer:
Explanation:
The best thing to include when communicating changes in the IT risk profile is the gaps between the current and desired states of the control environment, as this shows the stakeholders the extent and impact of the changes, and the actions and resources needed to address them. The control environment is the set of policies, processes, and systems that provide reasonableassurance that the IT risks are identified, assessed, and treated effectively and efficiently. The current state of the control environment reflects the existing level and performance of the controls, and the residual risk that remains after the controls are applied. The desired state of the control environment reflects the target level and performance of the controls, and the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization. The gaps between the current and desired states of the control environment indicate the areas of improvement or enhancement for the IT risk management process, and the priorities and strategies for risk response. The other options are not the best things to include when communicating changes in the IT risk profile, although they may be useful or relevant information. A list of recent incidents affecting industry peers can provide some context and comparison for the IT risk profile, but it does not measure or explain the changes in the IT risk level or the control environment. Results of external attacks and related compensating controls can demonstrate the security and resilience of the IT systems and networks, but they do not cover the entire scope or spectrum of the IT risk profile or the control environment. A review of leading IT risk management practices within the industry can provide some insights and benchmarks for the IT risk management process, but it does not reflect thespecific situation or needs of the organization or the stakeholders. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, page 181.
Which of the following is PRIMARILY a risk management responsibly of the first line of defense?
Implementing risk treatment plans
Validating the status of risk mitigation efforts
Establishing risk policies and standards
Conducting independent reviews of risk assessment results
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary risk management responsibility of the first line of defense is to implement risk treatment plans. The first line of defense is the operational management and staff who are directly involved in the execution of the business activities and processes. They are responsible for identifying, assessing, and responding to the risks that affect their objectives and performance. Implementing risk treatment plans means applying the appropriate risk response strategies and actions to address the identified risks, and monitoring and reporting the results and outcomes of the risk treatment. The other options are not as primary as implementing risk treatment plans, as they are related to the validation, establishment, or review of the risk management process, not the execution of the risk management process. References = Risk andInformation Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.1: IT Risk Management Process, page 15.
Which of the following is the MOST effective way to mitigate identified risk scenarios?
Assign ownership of the risk response plan
Provide awareness in early detection of risk.
Perform periodic audits on identified risk.
areas Document the risk tolerance of the organization.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A risk response plan is a document that outlines the actions to be taken to address the identified risk scenarios. A risk response plan should include the objectives, scope, roles and responsibilities, resources, timelines, and metrics for each risk response. Assigning ownership of the risk response plan is the most effective way to mitigate identified risk scenarios, as it ensures accountability, clarity, and communication among the stakeholders involved in the risk management process. Assigning ownership also helps to monitor and evaluate the progress and effectiveness of the risk response plan, and to make adjustments as needed. References =Riskand Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: Risk Response and Mitigation, Section 3.3: Risk Response Plan, p. 152-155.
An organization is analyzing the risk of shadow IT usage. Which of the following is the MOST important input into the assessment?
Business benefits of shadow IT
Application-related expresses
Classification of the data
Volume of data
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important input into the assessment of the risk of shadow IT usage is the classification of the data that is being processed, stored, or transmitted by the unauthorized applications or devices. This determines the level of confidentiality, integrity, and availability that is required for the data and the potential impact of a breach or loss. Business benefits of shadow IT, application-related expenses, and volume of data are less important inputs that may affect the risk analysis, but not as much as the data classification. References = Risk IT Framework, 2nd Edition, page 28; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 98.
Which of the following is the BEST method to ensure a terminated employee's access to IT systems is revoked upon departure from the organization?
Login attempts are reconciled to a list of terminated employees.
A list of terminated employees is generated for reconciliation against current IT access.
A process to remove employee access during the exit interview is implemented.
The human resources (HR) system automatically revokes system access.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best method to ensure a terminated employee’s access to IT systems is revoked upon departure from the organization is to have the human resources (HR) system automatically revoke system access, which is a process that involves integrating the HR system with the IT system, and triggering the removal of access rights for the employee as soon as the termination is recorded in the HR system12.
This method is the best because it provides the most timely, accurate, and consistent way of revoking access, and reduces the risk of human error, oversight, or delay that may occur in manual or semi-automated processes12.
This method is also the best because it enhances the security and compliance of the organization, and prevents the terminated employee from accessing or compromising the IT systems or data after departure12.
The other options are not the best methods, but rather alternative or supplementary methods that may have some limitations or drawbacks. For example:
Login attempts are reconciled to a list of terminated employees is a method that involves monitoring and verifying the login activities of the IT systems, and comparing them with a list of terminated employees to identify and block any unauthorized access attempts34. However, this method is not the best because it is reactive rather than proactive, and may not prevent the terminated employee from accessing the IT systems before the reconciliation is done34.
A list of terminated employees is generated for reconciliation against current IT access is a method that involves creating and maintaining a list of terminated employees, and checking it against the current IT access rights to identify and remove any access that is no longer needed34. However, this method is not the best because it is manual and labor-intensive, and may introduce errors or inconsistencies in the list or the access rights34.
A process to remove employee access during the exit interview is implemented is a method that involves conducting an exit interview with the terminated employee, and revoking the employee’s access to the IT systems during or immediately after the interview34. However, this method is not the best because it depends on the availability and cooperation of the terminated employee, and may not cover all the IT systems or access rights that the employee had34. References =
1: IT Involvement in Employee Termination, A Checklist3
2: Best Practices to Ensure Departing Employees Retain No Access5
3: User Termination Best Practices - IT Security - Spiceworks2
4: IT Security for Employee Termination - Policies, Checklists, Templates - Endsight1
Which of the following is the BEST metric to measure the effectiveness of an organization's disaster recovery program?
Percentage of applications subject to disaster recovery tests
Number of personnel dedicated to the disaster recovery program
Number of disaster recovery tests performed per year
Percentage of systems meeting defined recovery objectives
Answer:
Explanation:
Meeting defined RTOs and RPOs indicates that the DR plan can achieve its intended goals under real conditions. This metric directly reflects the effectiveness and reliability of the program.
Recent penetration testing of an organization's software has identified many different types of security risks. Which of the following is the MOST likely root cause for the identified risk?
SIEM software is producing faulty alerts.
Threat modeling was not utilized in the software design process.
The configuration management process is not applied consistently during development.
An identity and access management (IAM) tool has not been properly integrated into the software.
Answer:
Explanation:
Failure to utilize threat modeling during the design phase results in overlooked vulnerabilities. This highlights the importance ofProactive Threat Identificationin secure software development practices.
An organization wants to transfer risk by purchasing cyber insurance. Which of the following would be MOST important for the risk practitioner to communicate to senior management for contract negotiation purposes?
Most recent IT audit report results
Replacement cost of IT assets
Current annualized loss expectancy report
Cyber insurance industry benchmarking report
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important information for the risk practitioner to communicate to senior management for contract negotiation purposes when the organization wants to transfer risk by purchasing cyber insurance is the current annualized loss expectancy report, as it provides an estimate of the potential financial loss or impact that theorganization may incur due to a cyber risk event in a given year, and helps to determine the optimal coverage and premium of the cyber insurance. The other options are not the most important information, as they are more related to the audit, asset, or industry aspects of the cyber risk, respectively, rather than the financial aspect of the cyber risk. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 111.
Which of the following BEST supports ethical IT risk management practices?
Robust organizational communication channels
Mapping of key risk indicators (KRIs) to corporate strategy
Capability maturity models integrated with risk management frameworks
Rigorously enforced operational service level agreements (SLAs)
Answer:
Explanation:
 Robust organizational communication channels are the best way to support ethical IT risk management practices, as they enable transparent and consistent sharing of risk information anddecisions among all stakeholders. Ethical IT risk management requires that the risk management process and outcomes are aligned with the enterprise’s values, objectives, and obligations, and that the risk management activities are conducted with integrity, accountability, and respect. Robust organizational communication channels facilitate these aspects by ensuring that the risk management roles and responsibilities are clearly defined and communicated, that the risk management policies and procedures are widely disseminated and understood, that the risk management performance and results are regularly reported and reviewed, and that the risk management feedback and improvement suggestions are solicited and addressed. Mapping of key risk indicators (KRIs) to corporate strategy, capability maturity models integrated with risk management frameworks, and rigorously enforced operational service level agreements (SLAs) are not directly related to ethical IT risk management practices, but rather to the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk management process. References = CRISC Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control – Question201; ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 201.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective for automating controls?
Reducing the need for audit reviews
Facilitating continuous control monitoring
Improving control process efficiency
Complying with functional requirements
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary objective of automating controls is to facilitate continuous control monitoring. Automation enables real-time or near-real-time oversight of control activities, allowing for prompt detection and response to control failures or anomalies. This continuous monitoring enhances the organization's ability to maintain compliance and manage risks effectively.
Which of the following BEST indicates that an organization's risk management processes are mature?
Risk policy is approved and communicated by the risk manager
Annual risk awareness training is conducted by risk owners
Risk principles are embedded within business operations and decisions
The board regularly follows up on risk status and action plans
Answer:
Explanation:
CRISC maturity models describe high-maturity organizations as those where risk management is integrated into everyday operations and decision-making.
Supporting extract:
“An organization achieves mature risk management when risk principles are embedded within business operations, culture, and decision-making processes.â€
A and B describe compliance-level practices.
D shows oversight but not integration.
C reflects operational embedding, which defines maturity.
CRISC Reference: Domain 1 – IT Risk Governance, Topic: Risk Management Maturity Model.
An enterprise has taken delivery of software patches that address vulnerabilities in its core business software. Prior to implementation, which of the following is the MOST important task to be performed?
Assess the impact of applying the patches on the production environment.
Survey other enterprises regarding their experiences with applying these patches.
Seek information from the software vendor to enable effective application of the patches.
Determine in advance an off-peak period to apply the patches.
Answer:
Explanation:
Assessing the impact of applying the patches on the production environment is the most important task to be performed prior to implementation, because it helps to identify and mitigate any potential risks or issues that may arise from the patching process. Patching is a process ofapplying updates or fixes to software or hardware to address vulnerabilities, bugs, or performance issues. Patching is essential for maintaining the security and functionality of IT systems, but it also introduces the risk of introducing new problems or breaking existing features. Therefore, before applying patches, the organization should assess the impact of the patches on the production environment, such as compatibility, performance, availability, functionality, and security. Surveying other enterprises regarding their experiences with applying these patches, seeking information from the software vendor to enable effective application of the patches, and determining in advance an off-peak period to apply the patches are all helpful tasks to be performed prior to implementation, but they are not the most important task, as they do not directly address the impact of the patches on the production environment. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5, Section 5.4.2, page 211
A risk owner has identified a risk with high impact and very low likelihood. The potential loss is covered by insurance. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do NEXT?
Recommend avoiding the risk.
Validate the risk response with internal audit.
Update the risk register.
Evaluate outsourcing the process.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual1, the risk register is a tool that records the results of risk identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment. The risk register should be updated whenever there is a change in the risk profile, such as when a risk response is implemented or a new risk is identified. Updating the risk register allows the organization to monitor the current status of risks and the effectiveness of risk responses. Therefore, the next step for the risk practitioner after identifying a risk with high impact and very low likelihood that is covered by insurance is to update the risk register with the new information. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 191.
Which of the following should a risk practitioner review FIRST when evaluating risk events associated with the organization's data flow model?
Results of data classification activities
Recent changes to enterprise architecture (EA)
High-level network diagrams
Notes from interviews with the data owners
Answer:
In which of the following scenarios would a risk practitioner be required to provide the MOST justification for a risk assessment?
Modeling a threat-based risk event
Calculating mean time between failures (MTBF)
Using a semi-quantitative approach
Calculating adjusted loss expectancy (ALE)
Answer:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation (aligned to ISACA CRISC guidance)
Threat-based risk event modeling often involves significant expert judgment: choosing plausible threats, estimating their capability, attack paths, and motivations, and modeling multi-step attack scenarios. According to CRISC, such modeling demands strong justification and documented rationale because assumptions and inputs may be challenged by stakeholders and auditors. Semi-quantitative approaches and ALE calculations also require explanation, but they are generally based on standardized scales, historical data, or accepted formulas. MTBF is an engineering reliability metric, usually based on vendor data or operational history, requiring limited justification from a risk perspective. Threat-based modeling, however, drives critical decisions about controls and investment, and because it can be sensitive to subjective inputs, risk practitioners must carefully justify scenario selection, likelihood estimates, and impact assumptions to maintain credibility and enable informed governance decisions.
Which of the following is the BEST source for identifying key control indicators (KCIs)?
Privileged user activity monitoring controls
Controls mapped to organizational risk scenarios
Recent audit findings of control weaknesses
A list of critical security processes
Answer:
Explanation:
 Key control indicators (KCIs) are metrics that provide information on the extent to which a given control is meeting its intended objectives in terms of loss prevention, reduction, etc. In order to provide such information, the control effectiveness indicator has to have an explicit relationship to both the specific control and to the specific risk against which the control has been implemented1. Therefore, the best source for identifying KCIs is to use controls mapped to organizational risk scenarios, which can help define the control objectives, the expectedoutcomes, and the relevant indicators for each risk scenario. This approach can also help align the KCIs with the organizational goals and strategy, and enable the monitoring and reporting of the control effectiveness23.
The other options are not the best sources for identifying KCIs, because:
Privileged user activity monitoring controls are specific types of controls that aim to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive data or systems by privileged users. They are not a sourcefor identifying KCIs, but rather a possible subject of KCIs. For example, a KCI for this type of control could be the number of privileged user accounts that have not been reviewed or revoked within a specified period4.
Recent audit findings of control weaknesses are useful for identifying the gaps or deficiencies in the existing control environment, and for recommending corrective actions or improvements. However, they are not a source for identifying KCIs, but rather an input for evaluating or revising the existing KCIs. For example, if an audit finding reveals that a control is not operating as intended, or that a KCI is not providing reliable or timely information, then the control or the KCI may need to be modified or replaced5.
A list of critical security processes is a high-level overview of the key activities or functions that are essential for maintaining the security of the organization’s assets and information. It is not a source for identifying KCIs, but rather a starting point for defining the control objectives and requirements. For example, a critical security process could be incident response, which requires a set of controls to ensure the timely and effective detection, containment, analysis, and recovery of security incidents. The KCIs for this process could be the number of incidents detected, the average time to resolve incidents, or the percentage of incidents that resulted in data breaches6.
References =
Key Control Indicator (KCI) - CIO Wiki
How to Develop Key Control Indicators to Improve Security Risk Monitoring - Gartner
Indicators - Program Evaluation - CDC
Privileged User Monitoring: What Is It and Why Is It Important? - LogRhythm
Internal Audit Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) - AuditBoard
Hierarchy of Controls - NIOSH - CDC
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when determining whether to accept residual risk after security controls have been implemented on a critical system?
Cost versus benefit of additional mitigating controls
Annualized loss expectancy (ALE) for the system
Frequency of business impact
Cost of the Information control system
Answer:
Explanation:
 Residual risk is the risk that remains after security controls have been implemented on a system. Residual risk can be accepted, transferred, avoided, or further mitigated. The most important consideration when deciding whether to accept residual risk is the cost versus benefit of additional mitigating controls. This means comparing the potential impact of the residual risk with the cost and effectiveness of implementing more controls to reduce it. If the cost of additional controls outweighs the benefit of reducing the residual risk, then it may be acceptableto accept the residual risk. However, if the benefit of additional controls exceeds the cost, then it may be advisable to implement more controls to lower the residual risk to an acceptable level. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: Risk Response and Mitigation, Section 3.4: Risk Response Selection, p. 156-157.
Which of the following should be considered FIRST when managing a risk event related to theft and disclosure of customer information?
Protecting the organization from negative publicity
Performing a root cause analysis to prevent incident recurrence
Containing the impact of the incident to affected customers
Preventing further dissemination of customer information
Answer:
Explanation:
Thefirst stepis toprevent further disseminationof sensitive data to limit the impact of the breach. ISACA emphasizes that containment is the priority in risk response to minimize harm before addressing other aspects like root cause analysis or reputational management.
===========
When documenting a risk response, which of the following provides the STRONGEST evidence to support the decision?
Verbal majority acceptance of risk by committee
List of compensating controls
IT audit follow-up responses
A memo indicating risk acceptance
Answer:
Explanation:
The strongest evidence to support a risk response decision is a memo indicating risk acceptance. A memo is a formal and written document that can clearly communicate the rationale, criteria, and approval of the risk acceptance decision. Verbal majority acceptance of risk by committee, list of compensating controls, and IT audit follow-up responses are weaker evidence, as they may not be documented, verified, or aligned with the risk response decision. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 11; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 144.
Which of the following tools is MOST effective in identifying trends in the IT risk profile?
Risk self-assessment
Risk register
Risk dashboard
Risk map
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk dashboard is a graphical tool that displays the key indicators and metrics of the organization’s IT risk profile, such as the risk level, status, trend, performance, etc., using charts, graphs, tables, etc. A risk dashboard can help the organization to monitor and communicate the IT risk profile, and to support the decision making and planning for the IT risk management.
A risk dashboard is the most effective tool in identifying trends in the IT risk profile, because it provides a visual and intuitive representation of the changes and variations in the IT risk profile over time, and highlights the most significant and relevant IT risks that need to be addressed or monitored. A risk dashboard can also help to compare and contrast the IT risk profile with the organization’s IT objectives and risk appetite, and to identify the gaps or opportunities for improvement.
The other options are not the most effective tools in identifying trends in the IT risk profile, because they do not provide the same level of visibility and clarity that a risk dashboard provides, and they may not be updated or aligned with the organization’s IT objectives and risk appetite.
A risk self-assessment is a process of identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the IT risks that may affect the organization’s objectives and operations, using the input and feedback from the individuals or groups that are involved or responsible for the IT activities or functions. A risk self-assessment can help the organization to understand and document the IT risk profile, and to align it with the organization’s IT strategy and culture, but it is not the most effective tool in identifying trends in the IT risk profile, because it may not reflect the current or accurate state and performance of the IT risk profile, and it may not cover all the relevant or emerging IT risks that may exist or arise.
A risk register is a document that records and tracks the information and status of the identified IT risks and their responses. It includes the IT risk description, category, source, cause, impact, probability, priority, response, owner, action plan, status, etc. A risk register can help the organization to identify, analyze, evaluate, and communicate the IT risks and their responses, and to align them with the organization’s IT strategy and culture, but it is not the most effective tool in identifying trends in the IT risk profile, because it may not provide a visual and intuitive representation of the changes and variations in the IT risk profile over time, and it may not highlight the most significant and relevant IT risks that need to be addressed or monitored.
A risk map is a graphical tool that displays the results of the IT risk analysis in a matrix format, using colors and symbols to indicate the level and priority of the IT risks. A risk map can show the distribution and comparison of the IT risks based on various criteria, such as likelihood, impact, category, source, etc. A risk map can help the organization to assess and prioritize the IT risks, and to design and implement appropriate controls or countermeasures to mitigate or prevent the IT risks, but it is not the most effective tool in identifying trends in the IT risk profile, because it may not provide a visual and intuitive representation of the changes and variations in the IT risk profile over time, and it may not reflect the organization’s IT objectives and risk appetite. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 180
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to ensure policies and standards are properly documented within the risk management process?
It facilitates the use of a framework for risk management.
It establishes a means for senior management to formally approve risk practices.
It encourages risk-based decision making for stakeholders.
It provides a basis for benchmarking against industry standards.
Answer:
Explanation:
Policies and standards are important components of the risk management process, as they define the objectives, expectations, and requirements for managing risk within the organization. Policies and standards are also the means by which senior management formally approves and communicates the risk practices to the stakeholders, ensuring that the risk management process is aligned with the organizational strategy, culture, and values. Policies and standards also provide the authority and accountability for the risk management roles and responsibilities, as well as the criteria and metrics for measuring and reporting risk performance.
An organization has an internal control that requires all access for employees be removed within 15 days of their termination date. Which of the following should the risk practitioner use to monitor
adherence to the 15-day threshold?
Operation level agreement (OLA)
Service level agreement (SLA)
Key performance indicator (KPI)
Key risk indicator (KRI)
Answer:
Explanation:
A key performance indicator (KPI) is a metric that measures the achievement of a specific goal or objective. A KPI for the internal control that requires all access for employees be removed within 15 days of their termination date could be the percentage of employees whose access was removed within the specified time frame. This KPI would help the risk practitioner to monitor the compliance and effectiveness of the control and identify any deviations or issues.
References
•Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) - ISACA
•How to Improve Risk Awareness in the Workplace [+ Template] - AlertMedia
•[SITXWHS
Which of the following presents the GREATEST challenge to managing an organization's end-user devices?
Incomplete end-user device inventory
Unsupported end-user applications
Incompatible end-user devices
Multiple end-user device models
Answer:
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when sharing risk management updates with executive management?
Using an aggregated view of organizational risk
Ensuring relevance to organizational goals
Relying on key risk indicator (KRI) data Including
Trend analysis of risk metrics
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the most important consideration when sharing risk management updates with executive management is ensuring relevance toorganizational goals, as this helps to align risk management with business strategy and performance. The risk management updates should:
Highlight the key risks that may affect the achievement of the organizational goals and objectives
Demonstrate the value and benefits of risk management in supporting decision making and enhancing business resilience
Provide clear and concise information on the current risk profile, risk appetite, risk tolerance and risk exposure of the organization
Recommend appropriate risk response actions and resource allocation to address the identified risks
Communicate the roles and responsibilities of executive management in overseeing and governing risk management
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 4: IT Risk Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: IT Risk Reporting, pp. 221-2221
An application development team has a backlog of user requirements for a new system that will process insurance claim payments for customers. Which of the following should be the MOST important consideration for a risk-based review of the user requirements?
Number of claims affected by the user requirements
Number of customers impacted
Impact to the accuracy of claim calculation
Level of resources required to implement the user requirements
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual, one of the key objectives of risk identification is to assess the potential impact of risk events on the achievement of business objectives2. In this case, the business objective of the system is to process insurance claim payments for customers, which depends on the accuracy of claim calculation. Therefore, the impact to the accuracy ofclaim calculation should be the most important consideration for a risk-based review of the user requirements. The other options are less relevant or less critical for the business objective.
Which of the following will BEST help to ensure key risk indicators (KRIs) provide value to risk owners?
Ongoing training
Timely notification
Return on investment (ROI)
Cost minimization
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to ensure key risk indicators (KRIs) provide value to risk owners is to provide timely notification of the changes in the risk exposure. KRIs are metrics that provide an early warning of increasing risk exposure in various areas of the organization. By providing timely notification of the KRI values, the risk owners can be alerted of the risk situation and take appropriate actions to manage the risk. Ongoing training, return on investment (ROI), and cost minimization are other possible ways to ensure KRIs provide value, but they are not as effective as timely notification. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 10; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 140.
Which of the following is MOST important when developing risk scenarios?
Reviewing business impact analysis (BIA)
Collaborating with IT audit
Conducting vulnerability assessments
Obtaining input from key stakeholders
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important factor when developing risk scenarios is obtaining input from key stakeholders. A risk scenario is a description of a possible event or situation that could affect the enterprise’s objectives, processes, or resources. Obtaining input from key stakeholders, such as business owners, process owners, subject matter experts, or external parties, helps to ensure that the risk scenarios are realistic, relevant, and comprehensive. It also helps to identify the sources,drivers, indicators, likelihood, impact, and responses of the risk scenarios, and to align them with the enterprise’s risk appetite and tolerance. Obtaining input from key stakeholders also fosters a collaborative and participatory approach to risk management, and enhances the risk awareness and ownership among the stakeholders. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.1.3, page 621
Which of the following is the BEST course of action to reduce risk impact?
Create an IT security policy.
Implement corrective measures.
Implement detective controls.
Leverage existing technology
Answer:
Explanation:
To reduce risk impact, the best course of action is to implement corrective measures, which are actions taken to eliminate or minimize the negative effects of a risk event after it has occurred12.
Corrective measures can include restoring normal operations, repairing or replacing damaged assets, recovering lost data, compensating affected stakeholders, and implementing lessons learned12.
Corrective measures can reduce risk impact by minimizing the duration, severity, and scope of the consequences of a risk event, as well as preventing recurrence or escalation of similar risks in the future12.
The other options are not the best course of action to reduce risk impact, but rather different types of risk responses that may have different objectives and effects. For example:
Creating an IT security policy is an example of a preventive measure, which is an action taken to avoid or reduce the likelihood of a risk event before it occurs12. A preventive measure can reduce risk exposure, but not risk impact.
Implementing detective controls is an example of a monitoring measure, which is an action taken to identify and measure the occurrence or status of a risk event during or after it occurs12. A monitoring measure can provide timely information and feedback, but not reduce risk impact.
Leveraging existing technology is an example of a mitigation measure, which is an action taken to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk event before it occurs12. A mitigation measure can reduce risk exposure, but not necessarily risk impact. References =
1: Risk Management Guide for Information Technology Systems, NIST Special Publication 800-30, July 2002
2: Project Risk Management Handbook, California Department of Transportation, June 2011
A risk assessment has identified that an organization may not be in compliance with industry regulations. The BEST course of action would be to:
conduct a gap analysis against compliance criteria.
identify necessary controls to ensure compliance.
modify internal assurance activities to include control validation.
collaborate with management to meet compliance requirements.
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the best course of action when a risk assessment has identified that an organization may not be in compliance with industry regulations is to conduct a gap analysis against compliance criteria, which is a method of comparing the current state of compliance with the desired or required state of compliance. Conducting a gap analysis against compliance criteria helps to:
Identify and evaluate the differences or discrepancies between the compliance requirements and the actual compliance practices and capabilities
Assess the impact and severity of the compliance gaps on the organization’s objectives and performance
Prioritize the compliance gaps based on their urgency and importance
Develop and implement appropriate actions or measures to close or reduce the compliance gaps
Monitor and measure the effectiveness and efficiency of the actions or measures taken to address the compliance gaps
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.5: IT Risk Identification Methods and Techniques, pp. 34-351
A risk practitioner discovers that an IT operations team manager bypassed web filtering controls by using a mobile device, in violation of the network security policy. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
Report the incident.
Plan a security awareness session.
Assess the new risk.
Update the risk register.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC exam content outline2, one of the tasks of a risk practitioner is to “report on risk, in line with organizational reporting requirements, to enable decision making andescalationâ€. Therefore, the first thing that the risk practitioner should do after discovering apolicy violation is to report the incident to the appropriate authority, such as the IT security manager or the risk management committee. This will ensurethat the incident is properly documented, investigated, and resolved, and that any potential impact or consequences are minimized.
The other options are not the first actions that the risk practitioner should take. Planning a security awareness session (B) may be a preventive measure to avoid future incidents, but it does not address the current one. Assessing the new risk © may be part of the risk response process, but it should be done after reporting the incident and gathering more information. Updating the risk register (D) may be a result of the risk assessment and response, but it should not be done before reporting the incident and following the organizational procedures.
An organization that has been the subject of multiple social engineering attacks is developing a risk awareness program. The PRIMARY goal of this program should be to:
reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
communicate the consequences for violations.
implement industry best practices.
reduce the organization's risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the primary goal of a risk awareness program is to reduce the risk to an acceptable level by increasing the knowledge and understanding of the risk among the stakeholders. A risk awareness program should:
Educate the stakeholders about the sources, types and impacts of IT-related risks
Explain the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders in the risk management process
Promote a risk-aware culture that supports the risk appetite and risk tolerance of the organization
Provide guidance and tools for identifying, assessing, responding and monitoring IT-related risks
Encourage the reporting and escalation of risk issues and incidents
Reinforce the benefits and value of effective risk management
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 4: IT Risk Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: IT Risk Reporting, pp. 224-2251
An organization must make a choice among multiple options to respond to a risk. The stakeholders cannot agree and decide to postpone the decision. Which of the following risk responses has the organization adopted?
Transfer
Mitigation
Avoidance
Acceptance
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk avoidance is a type of risk response that involves eliminating the risk entirely by not engaging in the activity that causes the risk or changing the conditions that create the risk1. Riskavoidance is usually applied when the potential impact or likelihood of the risk is high or unacceptable, and when the benefits of avoiding the risk outweigh the costs or losses of doing so2.
In this case, the organization has adopted risk avoidance as its risk response, because it has decided to postpone the decision that could trigger the risk. By delaying the decision, the organization is avoiding therisk of making a wrong or unfavorable choice among the multiple options. However, this may not be the best or most effective risk response, as it could also result in missed opportunities, wasted resources, or increased uncertainty3. The organization shouldconsider the trade-offs and consequences of avoiding the risk, and explore other possible risk responses that could reduce or transfer the risk.
The other options are not the risk responses that the organization has adopted. Risk transfer means shifting the responsibility or burden of the risk to another party, such as a vendor or an insurer2. The organization has not transferred the risk to anyone else, but rather avoided it by postponing the decision. Risk mitigation means implementing controls or safeguards to minimize the negative effects of the risk2. The organization has not mitigated the risk by reducing its impact or likelihood, but rather avoided it by delaying the decision. Risk acceptance means acknowledging the risk and its consequences without taking any action to address it2. The organization has not accepted the risk by tolerating its potential outcomes, but rather avoided it by postponing the decision. References =
10 Risk Mitigation techniques you need to know - Stakeholdermap.com
Risk Response Strategies: Types & Examples (+ Free Template)
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
Once a risk owner has decided to implement a control to mitigate risk, it is MOST important to develop:
a process for measuring and reporting control performance.
an alternate control design in case of failure of the identified control.
a process for bypassing control procedures in case of exceptions.
procedures to ensure the effectiveness of the control.
Answer:
Explanation:
Once a risk owner has decided to implement a control to mitigate risk, it is most important to develop a process for measuring and reporting control performance. This process helps to monitor and evaluate the actual results and outcomes of the control, compare them with the expected or desired objectives and standards, identify any gaps or issues that may affect the control’s effectiveness or efficiency, and report them to the relevant stakeholders for decision making or improvement actions.
An alternate control design in case of failure of the identified control is a contingency plan that can be used to reduce the impact of a control failure or breakdown. It is not the most important thing to develop after implementing a control, but rather a backup option that can be activated when needed.
A process for bypassing control procedures in case of exceptions is a mechanism that allows authorized users to override or circumvent a control in certain situations, such as emergencies,errors, or special requests. It is not the most important thing to develop after implementing a control, but rather a risk response that can be applied when necessary.
Procedures to ensure the effectiveness of the control are the steps or actions that are required to implement, operate, and maintain the control in accordance with the risk owner’s expectations and requirements. They are not the most important thing to develop after implementing a control, but rather a part of the control design and implementation process.
The references for this answer are:
Risk IT Framework, page 13
Information Technology & Security, page 7
Risk Scenarios Starter Pack, page 5
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY focus of a disaster recovery management (DRM) framework and related processes?
Restoring IT and cybersecurity operations
Assessing the impact and probability of disaster scenarios
Ensuring timely recovery of critical business operations
Determining capacity for alternate sites
Answer:
Explanation:
Ensuring Timely Recovery of Critical Business Operations:
Primary Focus: The primary focus of a Disaster Recovery Management (DRM) framework is to ensure that critical business operations can be recovered and resumed in a timely manner after a disruption.
Business Continuity: Timely recovery of operations is essential for maintaining business continuity and minimizing the impact of disruptions on the organization’s ability to deliver products and services.
Recovery Objectives: Establishing clear recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) ensures that critical operations are prioritized and recovery efforts are aligned with business needs.
Comparison with Other Options:
Restoring IT and Cybersecurity Operations: While important, this is part of the broader goal of recovering critical business operations.
Assessing Impact and Probability of Disaster Scenarios: This is a preparatory step that informs the DRM framework but is not the primary focus.
Determining Capacity for Alternate Sites: This is a component of the DRM strategy but supports the primary focus of ensuring timely recovery.
Best Practices:
Comprehensive Planning: Develop comprehensive disaster recovery plans that prioritize the recovery of critical business operations.
Regular Testing: Regularly test and update disaster recovery plans to ensure they remain effective and aligned with business objectives.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involve all relevant business units in disaster recovery planning to ensure a coordinated and effective response.
The BEST metric to demonstrate that servers are configured securely is the total number of servers:
exceeding availability thresholds
experiencing hardware failures
exceeding current patching standards.
meeting the baseline for hardening.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best metric to demonstrate that servers are configured securely is the total number of servers meeting the baseline for hardening. Hardening is the process of applying security configurations and settings to servers to reduce their attack surface and vulnerability. A baseline is a standard or benchmark that defines the minimum level of security required for servers. By measuring the number of servers that meet the baseline, the organization can assess the effectiveness of its hardening efforts and identify any gaps or deviations. The other metrics, such as exceeding availability thresholds, experiencing hardware failures, or exceeding current patching standards, are not directly related to the security configuration of servers, but rather to their performance, reliability, or maintenance. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.3.2, page 2-25.
A recent risk workshop has identified risk owners and responses for newly identified risk scenarios. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner s NEXT step? r
Prepare a business case for the response options.
Identify resources for implementing responses.
Develop a mechanism for monitoring residual risk.
Update the risk register with the results.
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk practitioner’s next step after identifying risk owners and responses for newly identified risk scenarios in a recent risk workshop is to update the risk register with the results, as it involves documenting and communicating the risk information and decisions, and maintaining the accuracy and completeness of the risk register. Preparing a business case for the response options, identifying resources for implementing responses, and developing a mechanism for monitoring residual risk are possible steps, but they are not the next step, as they require the prior update of the risk register with the new risk information and decisions. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 109.
Which of the following is the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of IT policies? The number of:
IT policy exceptions granted.
Senior management approvals.
Key technology controls covered by IT policies.
Processes covered by IT policies.
Answer:
The MOST effective approach to prioritize risk scenarios is by:
assessing impact to the strategic plan.
aligning with industry best practices.
soliciting input from risk management experts.
evaluating the cost of risk response.
Answer:
Explanation:
The most effective approach to prioritize risk scenarios is by assessing the impact to the strategic plan, because this will help to align the risk management process with the organization’s vision, mission, and goals. The strategic plan is the document that defines the organization’s direction, priorities, and objectives, and guides the allocation of resources and efforts. By assessing theimpact to the strategic plan, the organization can determine which risk scenarios pose the greatest threat or opportunity to the achievement of the strategic objectives, and prioritize them accordingly. The other options are not as effective as assessing the impact to the strategic plan, because they do not directly relate to the organization’s specific context, needs, and expectations, as explained below:
B. Aligning with industry best practices is an approach that involves following the standards, norms, and expectations for risk management that are established and followed by the peers or competitors in the same industry or sector. Aligning with industry best practices can help to benchmark and compare the organization’s risk management performance and maturity, and identify areas for improvement or innovation. However, this approach is not as effective as assessing the impact to the strategic plan, because it does not account for the organization’s unique and customized risk scenarios, which may differ from the industry average or standard.
C. Soliciting input from risk management experts is an approach that involves seeking advice, guidance, or feedback from the professionals or specialists who have the knowledge, experience, or skills in risk management. Soliciting input from risk management experts can help to enhance the quality and validity of the risk analysis and evaluation, and provide insights and recommendations for risk mitigation. However, this approach is not as effective as assessing the impact to the strategic plan, because it does not reflect the organization’s risk appetite, preferences, and expectations, which may differ from the risk management experts’ opinions or perspectives.
D. Evaluating the cost of risk response is an approach that involves estimating the resources and efforts required to implement the risk response strategies, such as avoiding, reducing, transferring, or accepting the risk. Evaluating the cost of risk response can help to optimize the risk management efficiency and effectiveness, and balance the potential benefits and costs of taking risks. However, this approach is not as effective as assessing the impact to the strategic plan, because it does not consider the potential consequences and outcomes of the risk scenarios, which may affect the organization’s performance and reputation. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.3.1, page 45. The Ultimate Guide to Risk Prioritization - Hyperproof, Risk Prioritization: What Is It? [2021 Guide & Matrix] - ERM Software, What is Risk Prioritization | Centraleyes, Scenario Planning in Risk Management: Why It is Needed - SmartCompliance
An organization has just implemented changes to close an identified vulnerability that impacted a critical business process. What should be the NEXT course of action?
Redesign the heat map.
Review the risk tolerance.
Perform a business impact analysis (BIA)
Update the risk register.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual1, the risk register is a tool that records the results of risk identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment. It should be updated whenever there is a change in the risk profile, such as when a vulnerability is closed or a new threat is identified. Updating the risk register allows the organization to monitor the current status of risks and the effectiveness of risk responses. Therefore, the next course of action after implementing changes to close an identifiedvulnerability is to update the risk register with the new information. References = CRISC Review Manual1, page 191.
Which of the following should a risk practitioner recommend FIRST when an increasing trend of risk events and subsequent losses has been identified?
Conduct root cause analyses for risk events.
Educate personnel on risk mitigation strategies.
Integrate the risk event and incident management processes.
Implement controls to prevent future risk events.
Answer:
Explanation:
Conducting root cause analyses for risk events is the first recommendation that a risk practitioner should make when an increasing trend of risk events and subsequent losses has been identified, as this helps to identify the underlying causes and sources of the risk events, and to determine the appropriate actions to address them. Root cause analysis is a systematic process of collecting and analyzing data, finding the root causes, and implementing solutions to prevent recurrence or reduce the impact of the risk events. Educating personnel on risk mitigation strategies, integrating the risk event and incident management processes, and implementing controls to prevent future risk events are not the first recommendations, but rather the possible outcomes or actions of conducting root cause analyses for risk events. References = CRISC Certified in Riskand Information Systems Control – Question208; ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 208.
An organization uses one centralized single sign-on (SSO) control to cover many applications. Which of the following is the BEST course of action when a new application is added to the environment after testing of the SSO control has been completed?
Initiate a retest of the full control
Retest the control using the new application as the only sample.
Review the corresponding change control documentation
Re-evaluate the control during (he next assessment
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action when a new application is added to the environment after testing of the SSO control has been completed is to initiate a retest of the full control, as it may reveal any new issues or gaps that the new application may introduce to the SSO control, and ensure that the control remains effective and adequate. Retesting the control using the new application as the only sample, reviewing the corresponding change control documentation, and re-evaluating the control during the next assessment are not the best courses of action, as they may not provide sufficient assurance, evidence, or timeliness of the control testing, respectively. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 154.
Which of the following is the BEST indicator of an effective IT security awareness program?
Decreased success rate of internal phishing tests
Decreased number of reported security incidents
Number of disciplinary actions issued for security violations
Number of employees that complete security training
Answer:
Explanation:
The best indicator of an effective IT security awareness program is the decreased success rate of internal phishing tests. Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that attempts to trick the users into revealing their personal or confidential information, or clicking on malicious links or attachments, by impersonating a legitimate entity or person. Internal phishing tests are simulated phishing attacks that are conducted by the enterprise to test the awareness and behavior of the employees in response to phishing emails. A decreased success rate of internal phishing tests means that fewer employees fall victim to the phishing attempts, and that they are more aware and vigilant of the phishing threats and techniques. A decreased success rate of internal phishing tests also implies that the IT security awareness program has effectively educated and trained the employees on how to recognize and report phishing emails, and how to protect themselves and the enterprise from phishing attacks. A decreased number of reported security incidents, a number of disciplinary actions issued for security violations, and a number of employees that complete security training are not as good indicators of an effective IT security awareness program as a decreased success rate of internal phishing tests, as they do not directly measure theawareness and behavior of the employees in relation to phishing, and may be influenced by otherfactors such as reporting mechanisms, enforcement policies, and training availability. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 220.
Which of the following BEST facilitates the process of documenting risk tolerance?
Creating a risk register
Interviewing management
Conducting a risk assessment
Researching industry standards
Answer:
Explanation:
Interviewing managementis key because risk tolerance reflects leadership’s perspective on acceptable risk levels. ISACA stresses that understanding risk tolerance requires direct input from those responsible for risk decisions and strategic direction.
In order to determining a risk is under-controlled the risk practitioner will need to
understand the risk tolerance
monitor and evaluate IT performance
identify risk management best practices
determine the sufficiency of the IT risk budget
Answer:
Explanation:
 To determine if a risk is under-controlled, the risk practitioner will need to understand the risk tolerance. Risk tolerance is the acceptable or allowable level of variation or deviation from the expected or desired outcomes or objectives. Risk tolerance reflects the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing and able to take. A risk is under-controlled when the risk exposure exceeds the risk tolerance, meaning that the organization is taking on more risk than it can handle or afford. Therefore, the risk practitioner will need to understand the risk tolerance to compare it with the risk exposure and identify the gap or difference. The other options are not as relevant as understanding the risk tolerance, as they are related to the monitoring, identification, or determination of the risk or the IT performance, not the comparison or evaluation of therisk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.4: IT Risk Response, page 87.
Which of the following roles would provide the MOST important input when identifying IT risk scenarios?
Information security managers
Internal auditors
Business process owners
Operational risk managers
Answer:
Explanation:
 Business process owners would provide the most important input when identifying IT risk scenarios. IT risk scenarios are the situations or events that may affect the organization’s objectives, operations, or performance due to the use of information andtechnology1. Identifying IT risk scenarios means finding,recognizing, and describing the IT risks that the organization faces, as well as their sources, drivers, consequences, and responses2. Business process owners are the persons or entities who are responsible for the design, implementation, and operation of the business processes that support the organization’s goals and values3. Business process owners would provide the most important input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they can:
Provide the context and perspective of the business objectives, strategies, and requirements that are affected or supported by the IT risks and controls;
Identify and prioritize the IT risks that are relevant and significant to their business processes, as well as the IT assets and resources that are involved or impacted by the IT risks;
Evaluate and communicate the likelihood and impact of the IT risks on their business processes, as well as the risk appetite and tolerance of their business units;
Suggest and implement the most suitable and effective IT risk response actions or measures to mitigate the IT risks, as well as monitor and report on the IT risk and control performance;
Align and integrate the IT risk management activities and outcomes with the business risk management framework, policies, and standards. The other options are not the most important roles for providing input when identifying IT risk scenarios, as they are either less relevant or less specific than business process owners. Information security managers are the persons or entities who are responsible for the planning, implementation, and maintenance of the information security measures and controls that protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the organization’s data and systems4. Information security managers can provide input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they can:
Provide the expertise and guidance on the information security risks and controls that are related to the use of information and technology;
Identify and assess the information security vulnerabilities and threats that may affect the organization’s data and systems, as well as the information security assets and resources that are involved or impacted by the information security risks;
Recommend and implement the most appropriate and effective information security risk response actions or measures to reduce or eliminate the information security risks, as well as monitor and report on the information security risk and control performance;
Align and integrate the information security risk management activities and outcomes with the information security framework, policies, and standards. However, information security managers are not the most important roles for providing input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they may not have the full understanding or visibility of the business objectives, strategies, and requirements that are affected or supported by the IT risks and controls, or the risk appetite and tolerance of the business units. Internal auditors are the persons or entities who areresponsible for theindependent and objective assurance and consulting on the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s governance, risk management, and internal control system5. Internal auditors can provide input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they can:
Provide the assurance and validation on the design and operation of the IT risks and controls that are related to the use of information and technology;
Identify and evaluate the IT risk and control gaps or deficiencies that may affect the organization’s objectives, operations, or performance, as well as the IT risk and control objectives and activities that are involved or impacted by the IT risk and control gaps or deficiencies;
Report and recommend improvements or enhancements to the IT risks and controls, as well as follow up and verify the implementation and effectiveness of the IT risk and control improvements or enhancements;
Align and integrate the IT risk and control assurance and consulting activities and outcomes with the internal audit framework, policies, and standards. However, internal auditors are not the most important roles for providing input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they may not have the authority or responsibility to implement or operate the IT risks and controls, or to decide or prioritize the IT risk response actions or measures. Operational risk managers are the persons or entities who are responsible for the identification, analysis, evaluation, and treatment of the risks that arise from the failures or inadequacies of the organization’s people, processes, systems, or external events6. Operational risk managers can provide input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they can:
Provide the oversight and coordination of the operational risk management activities and performance across the organization, including the IT risks and controls that are related to the use of information and technology;
Identify and prioritize the operational risks that are relevant and significant to the organization, as well as the operational assets and resources that are involved or impacted by the operational risks;
Evaluate and communicate the likelihood and impact of the operational risks on the organization, as well as the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization;
Suggest and implement the most suitable and effective operational risk response actions or measures to mitigate the operational risks, as well as monitor and report on the operational risk and control performance;
Align and integrate the operational risk management activities and outcomes with the operational risk management framework, policies, and standards. However, operational risk managers are not the most important roles for providing input when identifying IT risk scenarios, because they may not have the specific knowledge or expertise on the IT risks and controls that are related to the use of information and technology, or the context and perspective of the business processes that are affected or supported by the IT risks and controls. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.1.1, Page 85.
The MAIN reason for creating and maintaining a risk register is to:
assess effectiveness of different projects.
define the risk assessment methodology.
ensure assets have low residual risk.
account for identified key risk factors.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A risk register is a tool used to identify, assess, and prioritize risks in an organization. It typically includes a detailed description of each identified risk, an assessment of its likelihood and potential impact, and a plan for managing or mitigating the risk1. A risk register is usually created at the beginning of a project or a process, and is updated regularly throughout the risk management life cycle2.
The main reason for creating and maintaining a risk register is to account for identified key risk factors. This means that the risk register helps to:
Document and track all the relevant risks that may affect the project or the organization, and their sources, causes, and consequences
Provide a comprehensive and consistent view of the risk profile and exposure of the project or the organization
Support the decision-making and prioritization of the risk responses and controls, based on the risk appetite and tolerance of the project or the organization
Communicate and report the risk information and status to the stakeholders and regulators, and ensure transparency and accountability
Enable the continuous improvement and learning from the risk management process and outcomes3
References = What is a risk register and why is it important?, Purpose of a risk register: Here’s what a risk register is used for, Risk Register: A Project Manager’s Guide with Examples [2024], Risk Register - Wikipedia
Which of the following would offer the MOST insight with regard to an organization's risk culture?
Risk management procedures
Senior management interviews
Benchmark analyses
Risk management framework
Answer:
Explanation:
Senior management interviews would offer the MOST insight with regard to an organization’s risk culture, because they can reveal the attitudes, values, beliefs, and behaviors of the seniormanagement towards risk management, and how they influence and support the risk management process and activities in the organization. Senior management interviews can also provide information on the risk appetite, tolerance, and objectives of the organization, and how they are communicated and implemented across the organization. The other options are not as insightful as senior management interviews, because:
Option A: Risk management procedures are the steps and methods that define how the risk management process and activities are performed in the organization, but they do not necessarily reflect the risk culture of the organization, which is more about the human and behavioral aspects of risk management.
Option C: Benchmark analyses are the comparisons of the performance and practices of the organization with those of similar or successful organizations, but they do not necessarily reflect the risk culture of the organization, which is more about the internal and unique aspects of risk management.
Option D: Risk management framework is the set of rules and standards that guide and support the risk management process and activities in the organization, but it does not necessarily reflect the risk culture of the organization, which is more about the leadership and commitment aspects of risk management. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, p. 82.
An organization recently implemented new technologies that enable the use of robotic process automation. Which of the following is MOST important to reassess?
Risk profile
Risk tolerance
Risk capacity
Risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk profile is the most important thing to reassess when an organization implements new technologies that enable the use of robotic process automation (RPA). The risk profile is a comprehensive and dynamic view of the organization’s risks, their ratings, responses, and status. RPA can introduce new risks or change the existing risks related to the organization’s objectives, operations, and performance. For example, RPA can create risks such as system failures, databreaches, compliance violations, human errors, or ethical dilemmas. Therefore, the organization should reassess its risk profile to identify, assess, treat, monitor, and review the risks associated with RPA, and to ensure that the risk management strategy is aligned with the business needs and expectations.
Which of the following is the MOST important characteristic of an effective risk management program?
Risk response plans are documented
Controls are mapped to key risk scenarios.
Key risk indicators are defined.
Risk ownership is assigned
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important characteristic of an effective risk management program is that risk ownership is assigned. Risk ownership is the accountability and authority to manage a risk1. Assigning risk ownership means identifying and assigning the person or entity who is responsible for evaluating, treating, monitoring, and reporting on a specific risk2. Assigning risk ownership is essential for ensuring that the risk management program works effectively and efficiently, as it helps to:
Clarify the roles and responsibilities of the different functions or groups involved in risk management and internal control;
Ensure that the risks are managed in accordance with the organization’s objectives, strategies, and risk appetite;
Provide guidance and support to the risk owners in identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risks;
Monitor and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the risk owners and the risk response actions;
Communicate and report on the risk status and issues to the relevant stakeholders and authorities. The other options are not the most important characteristic of an effective risk managementprogram, as they are either less relevant or less specific than assigning risk ownership. Risk response plans are documented. This option is a consequence or outcome of an effective risk management program, not a characteristic of it. Risk response plans are the actions or measures that are taken to modify the risk, such as reducing, avoiding, transferring, or accepting the risk3. Documenting risk response plans means recording and maintaining the details and outcomes of the risk responseactions, such as the objectives, scope, resources, timelines, performance indicators, and results4. Documenting risk response plans can help to improve the consistency and transparency of the risk management process, as well as to support the monitoring and evaluation of the risk response actions. However, documenting risk response plans is not the most important characteristic of an effective risk management program, as it does not address the accountability and authority for managing the risk. Controls are mapped to key risk scenarios. This option is a specific or narrow example of an effective risk managementprogram, not a general or broad characteristic of it. Controls are the measures or actions that are taken to reduce the likelihood or impact of a risk, or to increase the likelihood or impact of an opportunity5. Mapping controls to key risk scenarios means linking the controls to the specific situations or events that may affect the organization’s objectives, operations, or performance6. Mapping controls to key risk scenarios can help to enhance the design and implementation of the controls, as well as to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the controls in mitigating the risk. However, mapping controls to key risk scenarios is not the most important characteristic of an effective risk management program, as it does not cover the other aspects of risk management, such as risk identification, assessment, treatment, and monitoring. Key risk indicators are defined. This option is a component or element of an effective risk management program, not a characteristic of it. Key risk indicators are the metrics that measure thelevel and trend of a risk that may affect the organization’s objectives, operations, or performance7. Defining key risk indicators means establishing and maintaining the criteria and methods for measuring and reporting on the risk8. Defining key risk indicators can help to enhance the risk identification, assessment, and reporting processes, as well as to support the risk decision making and prioritization. However, defining key risk indicators is not the most important characteristic of an effective risk management program, as it does not indicate the accountability and authority for managing the risk. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.1.1, Page 85.
An organization has outsourced its billing function to an external service provider. Who should own the risk of customer data leakage caused by the service provider?
The service provider
Vendor risk manager
Legal counsel
Business process owner
Answer:
Explanation:
The business process owner should own the risk of customer data leakage caused by the service provider, as they have the responsibility and authority over the design, execution, and performance of the business process. The business process owner is also accountable for the risks and controls associated with their process, and they can provide valuable input and feedback on the likelihood and impact of customer data leakage on the process outcomes and objectives.
The other options are not the best choices for owning the risk of customer data leakage caused by the service provider. The service provider is responsible for delivering and supporting the billing function and ensuring the security and privacy of the customer data, but they may not have the full visibility or understanding of the business process and objectives. The vendor risk manager is responsible for managing and monitoring the vendor relationship and performance, but they may not have the direct involvement or influence on the business process and its risks and controls. The legal counsel is responsible for providing legal advice and guidance on the contractual and regulatory obligations and implications of the outsourcing arrangement, but they may not have the detailed knowledge or experience of the business process and its risks andcontrols. References = Guide to Vendor Risk Assessment | Smartsheet, IT Risk Resources | ISACA, Data Ownership: Considerations for Risk Management - ISACA
The cost of maintaining a control has grown to exceed the potential loss. Which of the following BEST describes this situation?
Insufficient risk tolerance
Optimized control management
Effective risk management
Over-controlled environment
Answer:
Explanation:
 The situation where the cost of maintaining a control has grown to exceed the potential loss is best described as an over-controlled environment, as it indicates that the control is not cost-effective and may be unnecessary or excessive. Insufficient risk tolerance, optimized control management, and effective risk management are not the best descriptions, as they do not reflect the imbalance between the control cost and the potential loss. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 149.
The PRIMARY advantage of involving end users in continuity planning is that they:
have a better understanding of specific business needs
can balance the overall technical and business concerns
can see the overall impact to the business
are more objective than information security management.
Answer:
Explanation:
 Continuity planning is the process of developing strategies and plans to ensure the continuity of critical business functions and processes in the event of a disruption or disaster. Continuity planning involves identifying the risks, impacts, and recovery options for various scenarios, as well as testing and updating the plans regularly. The primary advantage of involving end users in continuity planning is that they have a better understanding of specific business needs, such as the operational requirements, the customer expectations, and the dependencies and interdependencies of the business processes. End users can provide valuable input and feedback on the continuity plans, as well as participate in the testing and validation of the plans. End users can also help to ensure the alignment of the continuity plans with the business objectives and priorities, as well as the compliance with the relevant standards and regulations. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.4.1, p. 204-205
Which of the following should be included in a risk scenario to be used for risk analysis?
Risk appetite
Threat type
Risk tolerance
Residual risk
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk scenario is a hypothetical situation that describes how a risk event could adversely affect an organization’s objectives, assets, or operations. A risk scenario can be used for riskanalysis,which is the process of estimating the likelihood and impact of the risk event, and evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk response1.
One of the essential components of a risk scenario is the threat type, which is the source or cause of the risk event. The threat type can be classified into various categories, such as natural, human, technical, environmental, or legal. The threat type can help to define the characteristics, motivations, capabilities, and methods of the risk event, and to identify the potential vulnerabilities and exposures of the organization. The threat type can also help to determine the frequency and severity of the risk event, and to select the appropriate risk response strategies and controls23.
The other options are not the components of a risk scenario, but rather the outcomes or inputs of risk analysis. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Risk appetite can help to guide the risk analysis by providing a high-level statement of the desired level of risk taking and tolerance4. Risk tolerance is the acceptable variation in the outcomes related to specific objectives or risks. Risk tolerance can help to measure the risk analysis by providing quantitative or qualitative indicators of the acceptable range of risk exposure and performance4. Residual risk is the remaining risk after the risk response has been implemented. Residual risk can help to monitor the risk analysis by providing feedback on the effectiveness and efficiency of the risk response and the need for further action. References =
Risk Analysis - ISACA
Threat - ISACA
Threat Modeling - ISACA
Risk Appetite and Risk Tolerance - ISACA
[Residual Risk - ISACA]
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
An organization has contracted with a cloud service provider to support the deployment of a new product. Of the following, who should own the associated risk?
The head of enterprise architecture (EA)
The IT risk manager
The information security manager
The product owner
Answer:
Explanation:
The product owner should own the associated risk when contracting with a cloud service provider to support the deployment of a new product. The product owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for defining the product vision, requirements, and priorities. The product owner also has the accountability for the business value and outcomes of the product. Therefore, the product owner should be the one who identifies, assesses, and manages the risks related to the cloud service provider, such as security, compliance, performance, and quality. The product owner should also collaborate with the other stakeholders, such as the head of EA, the IT risk manager, and the information security manager, to ensure that the cloud service provider meets the organization’s standards and expectations. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: IT Risk Mitigation, Section 5.3: IT Risk Mitigation Strategies and Approaches, Page 254; Best Practices to Manage Risks in the Cloud - ISACA.
During a risk assessment, the risk practitioner finds a new risk scenario without controls has been entered into the risk register. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate action?
Include the new risk scenario in the current risk assessment.
Postpone the risk assessment until controls are identified.
Request the risk scenario be removed from the register.
Exclude the new risk scenario from the current risk assessment
Answer:
Explanation:
A new risk scenario without controls means that there is a potential threat or event that could adversely affect the organization’s objectives, and there are no existing measures to prevent or reduce the impact or likelihood of the risk. Therefore, the most appropriate action is to include the new risk scenario in the current risk assessment, so that the risk practitioner can analyze therisk, evaluate its severity and priority, and recommend suitable controls to mitigate the risk. By including the new risk scenario in the current riskassessment, the risk practitioner can ensure that the risk register is updated and reflects the current risk profile of the organization. The other options are not appropriate because they either ignore the new risk scenario, delay the risk assessment process, or remove valuable information from the risk register. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.1, page 95.
The analysis of which of the following will BEST help validate whether suspicious network activity is malicious?
Logs and system events
Intrusion detection system (IDS) rules
Vulnerability assessment reports
Penetration test reports
Answer:
Explanation:
 The analysis of logs and system events will best help validate whether suspicious network activity is malicious, because they provide detailed and timely information about the source, destination, content, and context of the network traffic. Logs and system events can be collected from various sources, such as firewalls, routers, switches, servers, applications, and endpoints, and can be correlated and analyzed using tools such as security information and event management (SIEM) systems. By analyzing logs and system events, an organization can identify anomalies, patterns, trends, and indicators of compromise (IOCs) that may signal malicious network activity, such as unauthorized access, data exfiltration, malware infection, denial-of-service attack, or lateral movement. Logs and system events can also help determine the scope, impact, and root cause of the malicious network activity, and support the incident response and remediation process. References = Risk IT Framework, ISACA, 2022, p. 221
Which of the following would BEST support the integrity of online financial transactions?
Developing an integrated audit facility
Implementing audit trail logs
Deploying multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Implementing blockchain technology
Answer:
Explanation:
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)significantly enhances transaction integrity by ensuring that users are who they claim to be. It is a practical, widely adopted control to prevent unauthorized access.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of maintaining an information asset inventory?
To provide input to business impact analyses (BIAs)
To protect information assets
To facilitate risk assessments
To manage information asset licensing
Answer:
Explanation:
An information asset inventory is a list of all the information assets that an organization owns or uses. It includes information such as the asset name, description, owner, location, classification,value, and dependencies. The primary objective of maintaining an information asset inventory is to provide input to business impact analyses (BIAs), which are used to identify the criticality and recovery priorities of information assets in the event of a disruption. By having an updated and accurate information asset inventory, an organization can ensure that the BIAs reflect the current state and needs of the business processes that rely on the information assets. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 74.
What can be determined from the risk scenario chart?
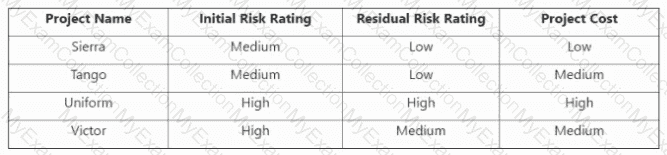
Relative positions on the risk map
Risk treatment options
Capability of enterprise to implement
The multiple risk factors addressed by a chosen response
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk scenario chart shows the initial and residual risk ratings, and the project cost, for four projects named Sierra, Tango, Uniform, and Victor. The initial risk rating is the level of risk before applying any controls or mitigation measures, while the residual risk rating is the level of risk after applying the controls or measures. The project cost is the amount of resources required to implement the project. These three factors can be used to determine the relative positions of the projects on a risk map, which is a graphical tool for displaying the risks based on their impact and likelihood. The risk map can help to prioritize and compare the risks, and to select the most appropriate risk response strategy. The other options are not the best answers, as they are not directly shown or derived from the risk scenario chart. The risk treatment options are the possible actions that can be taken to address the risks, such as accept, avoid, mitigate, or transfer. The capability of enterprise to implement is the ability of the organization to execute the risk response plan,considering the available resources, skills, and constraints. The multiple risk factors addressed by a chosen response are the various elements that contribute to or affect the risk, such as the threat sources, events, vulnerabilities, assets, and impacts. These factors are not explicitly stated or measured in the risk scenario chart, and may require further analysis or information. References = How to Write Strong Risk Scenarios and Statements - ISACA; Identifying the Right Risk Scenarios to Measure with FAIR; How to write good risk scenarios and statements
An organization is reviewing a contract for a Software as a Service (SaaS) sales application with a 99.9% uptime service level agreement (SLA). Which of the following BEST describes ownership of availability risk?
The risk is shared by both organizations.
The liability for the risk is owned by the cloud provider.
The risk is transferred to the cloud provider.
The liability for the risk is owned by the sales department.
Answer:
Explanation:
Even with SLAs in place, both parties must manage aspects of availability risk. The provider manages infrastructure, while the organization is responsible for business impact.
Which of the following provides the MOST useful information when developing a risk profile for management approval?
Residual risk and risk appetite
Strength of detective and preventative controls
Effectiveness and efficiency of controls
Inherent risk and risk tolerance
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk profile is a summary of the key risks that an organization faces, along with the corresponding risk responses, risk owners, and risk indicators1. A risk profile is a useful tool for communicating and reporting the risk status and performance to the management and other stakeholders2. When developing a risk profile for management approval, the most useful information to include is the residual risk and the risk appetite, because:
Residual risk is the level of risk that remains after the implementation of risk responses3. It indicates the degree of exposure or uncertainty that the organization still faces, and the potential impact or consequences of the risk events. Residual risk helps the management to evaluate the effectiveness and adequacy of the risk responses, and to decide whether to accept, reduce, transfer, or avoid the risk4.
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept or pursue in order to achieve its objectives5. It reflects the organization’s risk culture, strategy, and priorities, and provides a basis for setting risk thresholds and targets. Risk appetite helps the management to align the risk profile with the organizational goals and values, and to ensure that the risk responses are consistent and proportional to the risk level6.
The other options are not the most useful information when developing a risk profile for management approval, because:
Strength of detective and preventative controls is a measure of how well the controls can identify or prevent the occurrence or impact of the risk events7. It is a part of the risk response information, but it does not provide a comprehensive or holistic view of the risk profile. It does not show the residual risk or the risk appetite, which are more relevant and important for the management approval.
Effectiveness and efficiency of controls is a measure of how well the controls achieve their intended objectives and how well they use the available resources8. It is a part of the risk performance information, but it does not provide a complete or balanced view of the risk profile.It does not show the residual risk or the risk appetite, which are more significant and meaningful for the management approval.
Inherent risk and risk tolerance are related but different concepts from residual risk and risk appetite. Inherent risk is the level of risk that exists before the implementation of risk responses3. Risk tolerance is the acceptable variation or deviation from the risk appetite or the risk objectives5. They are useful for the risk assessment and analysis, but they do not provide the current or desired state of the risk profile. They do not show the residual risk or the risk appetite, which are more critical and valuable for the management approval.
References =
Risk Profile - CIO Wiki
Risk Profile: Definition, Example, and How to Create One
Residual Risk - CIO Wiki
What is Residual Risk? - Definition from Techopedia
Risk Appetite - CIO Wiki
Risk Appetite: What It Is and Why It Matters - Gartner
Preventive and Detective Controls - CIO Wiki
Control Effectiveness and Efficiency - CIO Wiki
Which of the following should be an element of the risk appetite of an organization?
The effectiveness of compensating controls
The enterprise's capacity to absorb loss
The residual risk affected by preventive controls
The amount of inherent risk considered appropriate
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. One of the elements of risk appetite is the enterprise’s capacity to absorb loss, which is the maximum amount of loss that an organization can withstand without jeopardizing its existence or strategic objectives. The effectiveness of compensating controls, the residual risk affected by preventive controls, and the amount of inherent risk considered appropriate are not elements of risk appetite, but rather factors that influence the risk assessment and responseprocesses. References = [CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version)], page 41; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, question 196.
Which of the following is the ULTIMATE objective of utilizing key control indicators (KCIs) in the risk management process?
To provide a basis for determining the criticality of risk mitigation controls
To provide early warning signs of a potential change in risk level
To provide benchmarks for assessing control design effectiveness against industry peers
To provide insight into the effectiveness of the intemnal control environment
Answer:
Explanation:
Key control indicators (KCIs) are metrics that measure the performance of a control in reducing the causes, consequences, or likelihood of a risk. They help to evaluate the adequacy and efficiency of the internal control environment, which is the set of policies, procedures, and practices that support the achievement of organizational objectives and the management of risks. By monitoring KCIs, organizations can identify and address any gaps or weaknesses in their internal controls and ensure that they are operating as intended.
References
•ISACA CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Domain 3: Risk Response, Section 3.2.2: Control Design and Implementation
•KRI Framework for Operational Risk Management | Workiva
•What is the difference between key risk indicators and key control indicators?
Which of the following is the MAIN benefit to an organization using key risk indicators (KRIs)?
KRIs provide an early warning that a risk threshold is about to be reached.
KRIs signal that a change in the control environment has occurred.
KRIs provide a basis to set the risk appetite for an organization.
KRIs assist in the preparation of the organization's risk profile.
Answer:
Explanation:
The main benefit of using key risk indicators (KRIs) for an organization is that they provide an early warning that a risk threshold is about to be reached. KRIs are metrics that measure the likelihood and impact of risks, and help monitor and prioritize the most critical risks. KRIs also help to trigger timely and appropriate risk responses, before the risk becomes unmanageable orunacceptable. The other options are not the main benefit of using KRIs, although they may be secondary benefits or outcomes. KRIs signal that a change in the control environment has occurred, provide a basis to set the risk appetite for an organization, and assist in the preparation of the organization’s risk profile. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.4.1, page 4-36.
Which of the following provides the MOST comprehensive information when developing a risk profile for a system?
Results of a business impact analysis (BIA)
Risk assessment results
A mapping of resources to business processes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Answer:
Explanation:
The most comprehensive information for developing a risk profile for a system is the risk assessment results. A risk assessment is a process that identifies, analyzes, and evaluates the risks that could affect the system’s objectives or operations. A risk assessment provides comprehensive information for developing a risk profile, because it helps to determine the likelihood and impact of the risks, and to prioritize them based on their severity and relevance. Arisk assessment also helps to select the most appropriate and effective controls to minimize the risks, such as avoiding, reducing, transferring, or accepting the risks. A risk profile is a document that summarizes the key risks that the system faces or accepts, and their likelihood, impact, and priority. A risk profile helps to identify and prioritize the most critical or relevant risks, and to align them with the system’s objectives, strategy, and risk appetite. The other options are not as comprehensive as the risk assessment results, although they may be part of or derived from the risk profile. Results of a business impact analysis (BIA), a mapping of resources to business processes, and key performance indicators (KPIs) are all factors that could affect the system’s performance and improvement, but they do not necessarily identify, analyze, or evaluate the risks that could affect the system. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1, page 4-13.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY risk management responsibility of the third line of defense?
Providing assurance of the effectiveness of risk management activities
Providing guidance on the design of effective controls
Providing advisory services on enterprise risk management (ERM)
Providing benchmarking on other organizations' risk management programs
Answer:
Which of the following is the FIRST step in risk assessment?
Review risk governance
Asset identification
Identify risk factors
Inherent risk identification
Answer:
Explanation:
The first step in risk assessment is asset identification, which is the process of identifying and documenting the assets that are relevant and valuable to the organization, such as people, information, systems, processes, or infrastructure1. Asset identification can help to:
Establish the scope and boundaries of the risk assessment, and ensure that all the assets within the scope are considered and covered2.
Determine the criticality and priority of the assets, and assign them appropriate values or ratings based on their importance and contribution to the organization’s objectives3.
Identify the potential threats and vulnerabilities that may affect the assets, and assess their likelihood and impact on the assets4.
The other options are not the first step in risk assessment, because:
Review risk governance is not the first step, but rather a prerequisite or a foundation for risk assessment. Risk governance is the system of principles, policies, roles, and responsibilities that guide and oversee the risk management activities and initiatives of the organization5. Reviewing risk governance can help to ensure that the risk assessment is aligned with the organization’sriskstrategy, culture, and appetite, and that the risk assessment process is consistent, effective, and efficient6.
Identify risk factors is not the first step, but rather a subsequent or a parallel step to asset identification. Risk factors are the elements or conditions that influence or contribute to the occurrence or outcome of a risk event7. Identifying risk factors can help to understand the causes and sources of the risks, and to analyze and evaluate the risks based on their probability and severity.
Inherent risk identification is not the first step, but rather a later or a dependent step on asset identification and risk factor identification. Inherent risk is the level of risk that exists before the implementation of risk responses. Identifying inherent risk can help to measure the exposure or uncertainty of the assets, and to determine the need and extent of the risk responses.
References =
Risk Governance - CIO Wiki
Risk Governance Framework - CIO Wiki
Asset Identification - CIO Wiki
Asset Identification and Valuation - ISACA
Asset Criticality - CIO Wiki
Threat and Vulnerability Assessment - CIO Wiki
Risk Factor - CIO Wiki
[Risk Factor Analysis - CIO Wiki]
[Inherent Risk - CIO Wiki]
[Inherent Risk Assessment - CIO Wiki]
[Risk Assessment - CIO Wiki]
After a business unit implemented an Internet of Things (IoT) solution, the organization became aware of an emerging risk from the interoperability of IoT devices. Which of the following should be done FIRST in response to this situation?
Implement new controls.
Update the risk profile.
Re-evaluate the risk tolerance.
Inform executive leadership.
Answer:
Explanation:
The first step in response to an identified risk is updating the risk profile to reflect the new exposure. This informs further actions such as treatment planning or tolerance reassessment.
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of involving business owners in risk scenario development?
Business owners have the ability to effectively manage risk.
Business owners have authority to approve control implementation.
Business owners understand the residual risk of competitors.
Business owners are able to assess the impact.
Answer:
Which of the following is MOST important to review when an organization needs to transition the majority of its employees to remote work during a crisis?
Customer notification plans
Capacity management
Access management
Impacts on IT project delivery
Answer:
Explanation:
Capacity management is crucial when transitioning employees to remote work during a crisis. It involves ensuring that the IT infrastructure can handle increased loads and that resources are available to support remote operations effectively.
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when assessing the likelihood that a recently discovered software vulnerability will be exploited?
The skill level required of a threat actor
The amount of personally identifiable information (PH) disclosed
The ability to detect and trace the threat action
The amount of data that might be exposed by a threat action
Answer:
Explanation:
When assessing the likelihood that a recently discovered software vulnerability will be exploited, the most important consideration is the skill level required of a threat actor. Here's an explanation:
Skill Level of Threat Actors:
The skill level required to exploit a vulnerability determines how accessible the exploit is to potential attackers.
If a vulnerability requires advanced technical skills to exploit, it is less likely to be targeted by less sophisticated attackers.
Conversely, if the exploit can be easily executed with minimal skills, it increases the likelihood of widespread exploitation.
Factors Influencing Likelihood of Exploitation:
Availability of Exploit Tools:If automated tools or scripts are available to exploit the vulnerability, even less skilled attackers can take advantage of it.
Publication of Exploit Details:If the vulnerability and its exploitation method are widely published, it becomes more accessible to a broader range of attackers.
Assessment of Likelihood:
Security teams assess the skill level required by analyzing whether the exploit is straightforward or complex.
They also consider the presence of exploit kits in the wild that could lower the barrier to entry for potential attackers.
Comparison with Other Factors:
Amount of PII Disclosed:While important, it relates more to the impact rather than the likelihood of exploitation.
Ability to Detect and Trace:This is crucial for response but does not directly influence the likelihood of exploitation.
Amount of Data Exposed:Similar to PII, this factor pertains to the impact rather than the likelihood of exploitation.
An internal audit report reveals that a legacy system is no longer supported Which of the following is the risk practitioner's MOST important action before recommending a risk response'
Review historical application down me and frequency
Assess the potential impact and cost of mitigation
identify other legacy systems within the organization
Explore the feasibility of replacing the legacy system
Answer:
Explanation:
A legacy system is an old or outdated IT system that is still in use by an organization. A legacy system may pose various risks to the organization, such as security vulnerabilities, compatibility issues, performance degradation, maintenance challenges, etc. When an internal audit report reveals that a legacy system is no longer supported by the vendor or the manufacturer, the risk practitioner’s most important action before recommending a risk response is to assess the potential impact and cost of mitigation, which means to estimate the consequences and expenses of the risk event if the legacy system fails or malfunctions. By assessing the potential impact andcost of mitigation, the risk practitioner can evaluate the risk exposure and determine the appropriate risk response, such as accepting, avoiding, transferring, or reducing the risk. References = 4
Which of the following is the MOST useful indicator to measure the efficiency of an identity and access management process?
Number of tickets for provisioning new accounts
Average time to provision user accounts
Password reset volume per month
Average account lockout time
Answer:
Explanation:
The average time to provision user accounts is the most useful indicator to measure the efficiency of an identity and access management (IAM) process, because it reflects how quickly and smoothly the process can grant access to the appropriate users. The average time to provision user accounts can be calculated by dividing the total time spent on provisioning user accounts by the number of user accounts provisioned in a given period. A lower average time indicates a more efficient IAM process, as it means that users can access the resources they need without unnecessary delays or errors. A higher average time may indicate problems or bottlenecks in the IAM process, such as manual steps, complex workflows, lack of automation, or insufficient resources. The average time to provision user accounts can also be compared across different applications, systems, or business units to identify areas for improvement or best practices. The other options are less useful indicators to measure the efficiency of an IAM process. The number of tickets for provisioning new accounts shows the demand for the IAM process, but not how well the process meets the demand. The password reset volume per month shows the frequency of password-related issues, but not how effectively the IAM process handles them. The average account lockout time shows the impact of account lockouts on user productivity, but not howefficiently the IAM process prevents or resolves them. References = Top Identity and Access Management MetricsÂ
An organization has determined that risk is not being adequately tracked and
managed due to a distributed operating model. Which of the following is the
BEST way to address this issue?
Increase the frequency of risk assessments.
Revalidate the organization's risk appetite
Create a centralized portfolio of risk scenarios.
Create dashboards for risk metrics.
Answer:
Which of the following activities would BEST contribute to promoting an organization-wide risk-aware culture?
Performing a benchmark analysis and evaluating gaps
Conducting risk assessments and implementing controls
Communicating components of risk and their acceptable levels
Participating in peer reviews and implementing best practices
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk-aware culture is a culture that recognizes, understands, and values the importance of risk management in achieving the organization’s objectives and goals. A risk-aware culture is also a culture that supports and encourages the identification, assessment, response, and monitoring of risks across the organization, as well as the sharing and learning of risk information and best practices. One of the activities that would best contribute to promoting an organization-wide risk-aware culture is communicating components of risk and their acceptable levels. This is a technique to inform and educate the stakeholders and decision makers about the nature and scope of the risks that the organization faces, as well as the criteria and standards that the organization uses to measure and manage the risks. Communicating components of risk and their acceptable levels can help to increase the awareness and understanding of the risks and their impact on the organization’s performance and value, as well as to align the expectations and behaviors of the stakeholders and decision makers with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. Communicating components of risk and their acceptable levels can also help to foster a transparent and collaborative environment for risk management, where the stakeholders and decision makers can openly discuss and address the risks and their implications, as well as to provide and receive feedback and support. The other options are not the best activities to promote an organization-wide risk-aware culture, although they may be relevant and useful. Performing a benchmark analysis and evaluating gaps is a technique to compare and improve the organization’s risk management process and performance with the industry standards or best practices, as well as to identify and close the gaps or weaknesses in the organization’s risk management capabilities or maturity. However, this technique does not necessarily promote a risk-aware culture, as it focuses on the process and performance of risk management, not the attitude and behavior of risk management. Conducting risk assessments and implementing controls is a technique to identify and analyze the risks that the organization faces, as well as to select and execute the appropriate actions to address the risks, such as avoiding, transferring, mitigating, or accepting the risks. However, this technique does not directly promote a risk-aware culture, as it focuses on the actions and outcomes of risk management, not the values and beliefs of risk management. Participating in peer reviews and implementing best practices is a technique to evaluate and enhance the quality and effectiveness of the organization’s risk management activities anddeliverables, as well as to adopt and apply the proven and successful methods or solutions for risk management. However, this technique does not effectively promote a risk-aware culture, as it focuses on the improvement and optimization of risk management, not the communication and collaboration of risk management. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 22-231; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 982; The 6 keyelements to creating and maintaining a good risk culture3; How to increase risk awareness - Project Management Institute4
The implementation of a risk treatment plan will exceed the resources originally allocated for the risk response. Which of the following should be the risk owner's NEXT action?
Perform a risk assessment.
Accept the risk of not implementing.
Escalate to senior management.
Update the implementation plan.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk treatment plan is a document that outlines the actions and resources required to implement the chosen risk response for a specific risk1. A risk response is a strategy or action that is taken or planned tomitigate or eliminate the risk, such as avoiding, transferring, reducing, or accepting the risk2. A risk owner is a person or entity that has the authority and accountability for a risk and its management3. If the implementation of a risk treatment plan will exceed the resources originally allocated for the risk response, the risk owner’s next action should be to escalate to senior management, which is the group of senior leaders who have the authority and accountability for the organization’s performance and governance4. By escalating to senior management, the risk owner can inform and consult them about the situation and the implications, and seek their guidance and approval for the necessary adjustments or alternatives. Escalating to senior management can also help to ensure that the risk treatment plan is aligned with the organization’s strategy, vision, and mission, and that the risk response is consistent with the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance5. Performing a risk assessment, accepting the risk of not implementing, and updating the implementation plan are not the best choices for the risk owner’s next action, as they do not provide the same level of communication and consultation as escalating to senior management. Performing a risk assessment is a process that involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating the risks and their potential impacts on the organization’s objectives and performance6. Performing a risk assessment can help to update and validate the risk information and the risk treatment plan, but it does not address the issue of the resource shortfall or the stakeholder expectations. Acceptingthe risk of not implementing is a decision that involves acknowledging and tolerating the risk or its impact without taking anyaction to reduce or eliminate it7. Accepting the risk of not implementing can help to avoid the additional cost and effort of the risk treatment plan, but it does not consider the potential consequences or the stakeholder interests. Updating the implementation plan is a process that involves revising and modifying the plan for executing the risk treatment plan, such as the scope,schedule, budget, or quality8. Updating the implementation plan can help to reflect the changes and updates in the risk treatment plan, but it does not resolve the problem of the resource gap or the stakeholder approval. References = 1: Risk Treatment and Response Plans - UNECE2: Risk Response Strategy and Contingency Plans - ProjectManagement.com3: [Risk Ownership - Risk Management] 4: [Senior Management - Definition, Roles and Responsibilities] 5: [Risk Appetite and Tolerance - ISACA] 6: [Risk Assessment - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics] 7: [Risk Acceptance - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics] 8: [Implementation Plan - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: Risk Response, Section 3.1: Risk Response Options, pp. 113-115.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.2: Risk Monitoring, pp. 189-191.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.1: Control Design, pp. 233-235.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.2: Control Implementation, pp. 243-245.] : [Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5: Information Systems Control Design and Implementation, Section 5.3: Control Monitoring and Maintenance, pp. 251-253.]
Which of the following BEST enables effective IT control implementation?
Key risk indicators (KRIs)
Documented procedures
Information security policies
Information security standards
Answer:
Explanation:
Documented procedures are the best way to enable effective IT control implementation. Documented procedures are the specific actions or steps that are performed to achieve the IT control objectives and mitigate the IT risks. Documented procedures provide clear guidance, consistency, and accountability for the IT control activities. Documented procedures also help to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the IT controls, and to identify and address any gaps or weaknesses. The other options are not as effective as documented procedures, although they may support or complement the IT control implementation. Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that measure the likelihood and impact of IT risks, but they do not specify how to implement the IT controls. Information security policies and standards are high-level statements that define the IT security goals and requirements, but they do not detail how to implement the IT controls. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.3.2, page 1-15.
What is the PRIMARY role of the application owner when changes are being introduced into an existing environment?
Determining possible losses due to downtime during the changes
Updating control procedures and documentation
Approving the proposed changes based on impact analysis
Notifying owners of affected systems after the changes are implemented
Answer:
Explanation:
The application owner must formally approve changes after reviewing impact—per ISACA's change management and governance frameworks that assign control over operational fallouts to functional owners .
Which of the following is the BEST response when a potential IT control deficiency has been identified?
Remediate and report the deficiency to the enterprise risk committee.
Verify the deficiency and then notify the business process owner.
Verify the deficiency and then notify internal audit.
Remediate and report the deficiency to senior executive management.
Answer:
Explanation:
Verifying the deficiency and then notifying the business process owner is the best response when a potential IT control deficiency has been identified. This is because verifying the deficiency can help confirm the existence, nature, and extent of the deficiency, as well as its root causes and impacts. Notifying the business process owner can help ensure that the deficiency is communicated to the person who is responsible for the process and its outcomes, and who has the authority and accountability to take appropriate actions to address the deficiency. According to the CRISC Review Manual 2022, one of the key risk response techniques is to report the risk to the relevant stakeholders, such as the business process owners1. According to the CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual 2022, verifying the deficiency and then notifying the business process owner is the correct answer to this question2.
Remediating and reporting the deficiency to the enterprise risk committee or senior executive management are not the best responses when a potential IT control deficiency has been identified. These are possible actions that can be taken after the deficiency has been verified and notified to the business process owner, but they are not the first or immediate responses. Remediating the deficiency without verifying it can lead to ineffective or inappropriate solutions, as well as wasted time and resources. Reporting the deficiency to the enterprise risk committee or senior executive management without notifying the business process owner cancreate confusion, conflict, or delay in the risk response process, as well as undermine the ownership and accountability of the business process owner.
An audit reveals that there are changes in the environment that are not reflected in the risk profile. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
Review the risk identification process.
Inform the risk scenario owners.
Create a risk awareness communication plan.
Update the risk register.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action when an audit reveals that there are changes in the environment that are not reflected in the risk profile is to review the risk identification process. This is because the risk identification process is the first step in the risk management process and it is responsible for identifying and assessing the potential risks that may affect the organization’s objectives. If the risk identification process is not effective, it may result in incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated risk profiles that do not reflect the current environment and the associated risks. Therefore, reviewing the risk identification process will help to ensure that the risk profile is updated and aligned with the changes in the environment and the organization’s strategy. References = Responding to Audit Findings
Which of the following BEST informs decision-makers about the value of a notice and consent control for the collection of personal information?
A comparison of the costs of notice and consent control options
Examples of regulatory fines incurred by industry peers for noncompliance
A report of critical controls showing the importance of notice and consent
A cost-benefit analysis of the control versus probable legal action
Answer:
Explanation:
 A cost-benefit analysis of the control versus probable legal action is the best way to inform decision-makers about the value of a notice and consent control for the collection of personal information, as it quantifies the potential benefits and costs of implementing the control and compares them with the potential consequences of not implementing the control. This helps the decision-makers to evaluate the trade-offs and the return on investment of the control.
A comparison of the costs of notice and consent control options is not sufficient to inform decision-makers about the value of the control, as it does not consider the benefits or the risks of the control.
Examples of regulatory fines incurred by industry peers for noncompliance are not the best way to inform decision-makers about the value of the control, as they are based on historical data and may not reflect the current or future situation of the enterprise.
A report of critical controls showing the importance of notice and consent is not the best way to inform decision-makers about the value of the control, as it does not provide any quantitative or comparative data to support the decision. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, page 140-1411
An organization has completed a project to implement encryption on all databases that host customer data. Which of the following elements of the risk register should be updated the reflect this change?
Risk likelihood
Inherent risk
Risk appetite
Risk tolerance
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk likelihood is the element of the risk register that should be updated to reflect the change of implementing encryption on all databases that host customer data. The risk likelihood is the probability or frequency of a risk event occurring, and it is one of the factors that determine the risk level and priority. By implementing encryption, the organization reduces the risk likelihood of unauthorized access, disclosure, or breach of the customer data, as encryption protects the data from being read or modified by anyone who does not have the decryption key. Therefore, the risk likelihood should be updated to reflect the lower probability of the risk event after applying the encryption control. The other options are not the elements that should be updated, as they are either not affected by or not related to the change of implementing encryption. The inherent risk is the level of risk before applying any controls or mitigation measures, and it does not change after implementing encryption. The risk appetite is the amount of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives, and it is not influenced by the change ofimplementing encryption. The risk tolerance is the acceptable variation between the risk thresholds and thebusiness objectives, and it is not determined by the change of implementing encryption. References = Risk Register: A Project Manager’s Guide with Examples [2023] • Asana; Risk Assessment in Project Management | PMI; Risk Assessment Process: Definition, Steps, and Examples; Risk Assessment - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The MOST essential content to include in an IT risk awareness program is how to:
define the IT risk framework for the organization
populate risk register entries and build a risk profile for management reporting
comply with the organization's IT risk and information security policies
prioritize IT-related actions by considering risk appetite and risk tolerance
Answer:
Explanation:
An IT risk awareness program shouldprimarily ensure that employees and stakeholders understand and comply with the organization's risk and information security policies. ISACA highlights that an awareness program must reinforce policy understanding to drive compliant and secure behavior across the organization.
===========
Which of the following BEST indicates effective information security incident management?
Monthly trend of information security-related incidents
Average time to identify critical information security incidents
Frequency of information security incident response plan testing
Percentage of high-risk security incidents
Answer:
Explanation:
 The average time to identify critical information security incidents is the best indicator of effective information security incident management, as it measures how quickly the organization can detect and respond to the most severe threats to its information assets. The faster the organization can identify critical incidents, the lower the potential impact and damage they can cause. The average time to identify critical incidents also reflects the efficiency and accuracy of the monitoring and reporting mechanisms, as well as the awareness and training of the staff and stakeholders. The other options are not the best indicators of effective information security incident management, as they do not directly measure the performance or quality of the incident response process. The monthly trend of information security-related incidents may show the frequency or severity of the incidents, but not how well they are managed. The frequency of information security incident response plan testing may show the preparedness or maturity of the organization, but not the actual effectiveness of the plan. The percentage of high-risk security incidents may show the risk exposure or appetite of the organization, but not the risk mitigationor treatment. References = 7 Types of Information Security Incidents and How to Respond; Annex A.16: Information Security Incident Management - ISMS.online; CISM Isaca Exam Questions and Answers - CertLibrary.com
Which of the following is MOST helpful to ensure effective security controls for a cloud service provider?
A control self-assessment
A third-party security assessment report
Internal audit reports from the vendor
Service level agreement monitoring
Answer:
Explanation:
A third-party security assessment report is the most helpful to ensure effective security controls for a cloud service provider, because it provides an independent and objective evaluation of the cloud provider’s security posture, policies, and practices. A third-party security assessment report can help to verify and validate the cloud provider’s compliance with the relevant standards, regulations, and best practices, such as ISO 27001, PCI DSS, NIST, or CSA. A third-party security assessment report can also help to identify and address any gaps, weaknesses, or vulnerabilities in the cloud provider’s security controls, and to provide recommendations and guidance for improvement. A third-party security assessment report can also help to increase the trust and confidence of the cloud customers, and to facilitate the due diligence and risk management processes. The other options are less helpful to ensure effective security controls for a cloud service provider. A control self-assessment is a process that enables the cloud provider to assess its own security controls, using a predefined framework or questionnaire. However, a control self-assessment may not be as reliable or comprehensive as a third-party security assessment report, as it may be biased, incomplete, or inaccurate, and it may not cover all the aspects or dimensions of security. Internal audit reports from the vendor are documents that provide the results and findings of the internal audits conducted by the cloud provider’s ownauditors, to verify and validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the securitycontrols. However, internal audit reports from the vendor may not be as credible or trustworthy as a third-party security assessment report, as they may be influenced by the cloud provider’s interests, objectives, or agenda, and they may not follow the same standards or criteria as the external auditors. Service level agreement monitoring is a process that measures and evaluates the performance and availability of the cloud services, based on the predefined metrics and targets agreed between the cloud provider and the cloud customer. However, service level agreement monitoring may not be sufficient or relevant to ensure effective security controls for a cloud service provider, as it may not address the security aspects or requirements of the cloud services, such as confidentiality, integrity, or accountability, and it may not reflect the actual security risks or incidents that may occur in the cloud environment. References = Cloud Security Controls: Key Elements and 4 Control Frameworks 1
Which of the following would be the result of a significant increase in the motivation of a malicious threat actor?
Increase in mitigating control costs
Increase in risk event impact
Increase in risk event likelihood
Increase in cybersecurity premium
Answer:
Explanation:
The result of a significant increase in the motivation of a malicious threat actor would be an increase in risk event likelihood. The likelihood of a risk event is influenced by the factors of threat, vulnerability, and exposure. The motivation of a threat actor is a key component of the threat factor, as it reflects the intent and capability of the actor to exploit a vulnerability. Therefore, a higher motivation would imply a higher probability of an attack. An increase in mitigating control costs, risk event impact, or cybersecurity premium are possible consequences of a risk event, but they are not directly affected by the motivation of the threat actor. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC)Certification Exam Question and Answers, question 6; CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, page 67.
An unauthorized individual has socially engineered entry into an organization's secured physical premises. Which of the following is the BEST way to prevent future occurrences?
Employ security guards.
Conduct security awareness training.
Install security cameras.
Require security access badges.
Answer:
Explanation:
Social engineering is a technique that involves manipulating or deceiving people into performing actions or divulging information that may compromise the security of an organization or its data12.
Entry into an organization’s secured physical premises is a form of physical access that allows an unauthorized individual to access, steal, or damage the organization’s assets, such as equipment, documents, or systems34.
The best way to prevent future occurrences of social engineering entry into an organization’s secured physical premises is to conduct security awareness training, which is an educational program that aims to equip the organization’s employees with the knowledge and skills they need to protect the organization’s data and sensitive information from cyber threats, such as hacking, phishing, or other breaches56.
Security awareness training is the best way because it helps the employees to recognize and resist the common and emerging social engineering techniques, such as tailgating,impersonation, or pretexting, that may be used by the attackers to gain physical access to the organization’s premises56.
Security awareness training is also the best way because it fosters a culture of security and responsibility among the employees, and encourages them to follow the best practices andpolicies for physical security, such as locking the doors, verifying the identity of visitors, or reporting any suspicious activities or incidents56.
The other options are not the best way, but rather possible measures or controls that may supplement or enhance the security awareness training. For example:
Employing security guards is a measure that involves hiring or contracting professional personnel who are trained and authorized to monitor, patrol, and protect the organization’s premises from unauthorized access or intrusion78. However, this measure is not the best way because it may not be sufficient or effective to prevent or deter all types of social engineering attacks, especially if the attackers are able to bypass, deceive, or coerce the security guards78.
Installing security cameras is a control that involves using electronic devices that capture and record the visual images of the organization’s premises, and provide evidence or alerts of any unauthorized access or activity . However, this control is not the best way because it is reactive rather than proactive, and may not prevent or stop the social engineering attacks before they cause any harm or damage to the organization .
Requiring security access badges is a control that involves using physical or electronic cards that identify and authenticate the employees or authorized visitors who are allowed to enter the organization’s premises, and restrict or deny the access to anyone else . However, this control is not the best way because it may not be foolproof or reliable to prevent or detect the social engineering attacks, especially if the attackers are able to steal, forge, or clone the security access badges . References =
1: What is Social Engineering? | Types & Examples of Social Engineering Attacks1
2: Social Engineering: What It Is and How to Prevent It | Digital Guardian2
3: What is physical Social Engineering and why is it important? - Integrity3603
4: What Is Tailgating (Piggybacking) In Cyber Security? - Wlan Labs4
5: What Is Security Awareness Training and Why Is It Important? - Kaspersky5
6: Security Awareness Training - Cybersecurity Education Online | Proofpoint US6
7: Security Guard - Wikipedia7
8: Security Guard Services - Allied Universal8
Security Camera - Wikipedia
Security Camera Systems - The Home Depot
Access Badge - Wikipedia
Access Control Systems - HID Global
A risk practitioner is advising management on how to update the IT policy framework to account for the organization s cloud usage. Which of the following should be the FIRST step in this process?
Consult with industry peers regarding cloud best practices.
Evaluate adherence to existing IT policies and standards.
Determine gaps between the current state and target framework.
Adopt an industry-leading cloud computing framework.
Answer:
Explanation:
Updating IT Policy Framework for Cloud Usage:
Gap Analysis: The first step in updating the IT policy framework is to conduct a gap analysis to identify discrepancies between the current state and the desired target framework for cloud usage.
Assessment of Current State: This involves reviewing existing policies, controls, and practices related to cloud usage to understand current capabilities and limitations.
Target Framework Definition: Define the desired state based on industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and organizational objectives.
Importance of Gap Analysis:
Focused Improvements: Identifying gaps allows the organization to focus on specific areas that need enhancement to align with best practices and compliance requirements.
Resource Allocation: Helps in allocating resources effectively to address the most critical gaps first.
Comparison with Other Options:
Consult with Industry Peers: Useful for gathering insights but should follow the gap analysis to ensure relevance to the organization’s specific context.
Evaluate Adherence to Existing Policies: Part of the gap analysis but not the initial step.
Adopt Industry-leading Framework: Important for long-term strategy but should be based on identified gaps.
Best Practices:
Comprehensive Review: Conduct a thorough review of existing policies and compare them with industry standards.
Stakeholder Involvement: Engage relevant stakeholders in the gap analysis to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration for protecting data assets m a Business application system?
Application controls are aligned with data classification lutes
Application users are periodically trained on proper data handling practices
Encrypted communication is established between applications and data servers
Offsite encrypted backups are automatically created by the application
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most important consideration for protecting data assets in a business application system is to ensure that the application controls are aligned with the data classification rules. Data classification rules define the level of sensitivity, confidentiality, and criticality of the data, andthe corresponding security requirements and controls. Application controls are the policies, procedures, and technical measures that are implemented at the application level to ensure the security, integrity, and availability of the data. Application controls should be designed and configured to match the data classification rules, so that the data is protected according to its value and risk. For example, if the data is classified as highly confidential, the application controls should enforce strong authentication, encryption, access control, logging, and auditing mechanisms. References = CRISC Review Manual, 6th Edition, ISACA, 2015, page 214.
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are MOST useful during which of the following risk management phases?
Monitoring
Analysis
Identification
Response selection
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are most useful during the monitoring phase of the risk management process, as they provide timely and relevant information on the current and future risk status and performance. KRIs are metrics that measure the level of risk exposure and the effectiveness of risk response strategies, and they have predefined thresholds that indicate the acceptable or unacceptable risk status. By monitoring the KRIs, the risk practitioner can identify and report any changes or deviations in the risk level, and take appropriate actions to manage the risk. KRIs are not most useful during the analysis, identification, or response selection phases, as they do not help to assess the likelihood or impact of the risk, to find the sources or causes of the risk, or to evaluate or choose the optimal risk response option. References = CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, question 222.
Which of the following is the BEST way to help ensure risk will be managed properly after a business process has been re-engineered?
Reassessing control effectiveness of the process
Conducting a post-implementation review to determine lessons learned
Reporting key performance indicators (KPIs) for core processes
Establishing escalation procedures for anomaly events
Answer:
Explanation:
 Business process re-engineering is the radical redesign of a business process to achieve significant improvements in performance, quality, cost, or customer satisfaction. Business process re-engineering can introduce new or modified risks to the organization, as well as affectthe existing controls and responses. Therefore, the best way to help ensure risk will be managed properly after a business process has been re-engineered is to reassess the control effectiveness of the process, meaning that the organization should evaluate whether the controls are still adequate, appropriate, and functioning as intended to mitigate the risks. Reassessing the control effectiveness can help to identify any gaps or weaknesses in the control environment, as well as to implement any necessary changes or improvements to the controls. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 5, Section 5.2.2, p. 229-230
Which of the following is the BEST approach to use when creating a comprehensive set of IT risk scenarios?
Derive scenarios from IT risk policies and standards.
Map scenarios to a recognized risk management framework.
Gather scenarios from senior management.
Benchmark scenarios against industry peers.
Answer:
Explanation:
IT risk scenarios are the descriptions or representations of the possible or hypothetical situations or events that may cause or result in an IT risk for the organization. IT risk scenarios usually consist of three elements: a threat or source of harm, a vulnerability or weakness, and an impact or consequence.
The best approach to use when creating a comprehensive set of IT risk scenarios is to map scenarios to a recognized risk management framework, which is an established or recognized model or standard that provides the principles, guidelines, and best practices for the organization’s IT risk management function. Mapping scenarios to a recognized risk management framework can help the organization to create a comprehensive set of IT risk scenarios by providing the following benefits:
It can ensure that the IT risk scenarios are relevant, appropriate, and proportional to the organization’s IT objectives and needs, and that they support the organization’s IT strategy and culture.
It can ensure that the IT risk scenarios are consistent and compatible with the organization’s IT governance, risk management, and control functions, and that they reflect the organization’s IT risk appetite and tolerance.
It can provide useful references and benchmarks for the identification, analysis, evaluation, and communication of the IT risk scenarios, and for the alignment and integration of the IT risk scenarios with the organization’s IT risk policies and standards.
The other options are not the best approaches to use when creating a comprehensive set of IT risk scenarios, because they do not provide the same level of detail and insight that mapping scenarios to a recognized risk management framework provides, and they may not be specific or applicable to the organization’s IT objectives and needs.
Deriving scenarios from IT risk policies and standards means creating or generating the IT risk scenarios based on the rules or guidelines that define and describe the organization’s IT risk management function, and that specify the expectations and requirements for the organization’s IT risk management function. Deriving scenarios from IT risk policies and standards can help the organization to create a consistent and compliant set of IT risk scenarios, but it is not the best approach, because it may not cover all the relevant or significant IT risks that may affect the organization, and it may not support the organization’s IT strategy and culture.
Gathering scenarios from senior management means collecting or obtaining the IT risk scenarios from the senior management or executives that oversee or direct the organization’s IT activities or functions. Gathering scenarios from senior management can help the organization to create a high-level and strategic set of IT risk scenarios, but it is not the best approach, because it may not reflect the operational or technical aspects of the IT risks, and it may not involve the input or feedback from the other stakeholders or parties that are involved or responsible for the IT activities or functions.
Benchmarking scenarios against industry peers means comparing and contrasting the IT risk scenarios with those of other organizations or industry standards, and identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, or threats that may affect the organization’s IT objectives oroperations. Benchmarking scenarios against industry peers can help the organization to create a competitive and innovative set of IT risk scenarios, but it is not the best approach, because it may not be relevant or appropriate for the organization’s IT objectives and needs, and it may not comply with the organization’s IT policies and standards. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 199
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Which of the following is a KEY consideration for a risk practitioner to communicate to senior management evaluating the introduction of artificial intelligence (Al) solutions into the organization?
Al requires entirely new risk management processes.
Al potentially introduces new types of risk.
Al will result in changes to business processes.
Third-party Al solutions increase regulatory obligations.
Answer:
Explanation:
Artificial intelligence (AI) solutions can offer significant benefits to an organization, such as improved efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. However, AI also poses new challenges and risks that need to be considered and addressed by senior management. Some of these risks include:
Ethical and social risks: AI solutions may have unintended or undesirable impacts on human values, rights, and behaviors, such as privacy, fairness, accountability, and transparency. For example, AI systems may exhibit bias, discrimination, or manipulation, or may infringe on personal data or autonomy.
Technical and operational risks: AI solutions may have vulnerabilities, errors, or failures that affect their performance, reliability, or security. For example, AI systems may be subject to hacking, tampering, or misuse, or may malfunction or produce inaccurate or harmful outcomes.
Legal and regulatory risks: AI solutions may have unclear or conflicting legal or regulatory implications or obligations, such as liability, compliance, or governance. For example, AI systems may raise questions about ownership, responsibility, or accountability, or may violate existing laws or regulations, or create new ones.
Therefore, a risk practitioner should communicate to senior management that AI potentially introduces new types of risk that need to be identified, assessed, and managed in alignment with the organization’s objectives, values, and risk appetite. References = ISACA CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.2, page 113.
The PRIMARY reason to implement a formalized risk taxonomy is to:
reduce subjectivity in risk management.
comply with regulatory requirements.
demonstrate best industry practice.
improve visibility of overall risk exposure.
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary reason to implement a formalized risk taxonomy is to reduce subjectivity in risk management, as it provides a common and consistent language and structure for identifying, classifying, and reporting risks, and facilitates the comparison and aggregation of risks across the organization. The other options are not the primary reasons, as they are more related to the outcomes, benefits, or drivers of risk management, respectively, rather than the reason for risk management. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 100.
Which of the following risk register updates is MOST important for senior management to review?
Extending the date of a future action plan by two months
Retiring a risk scenario no longer used
Avoiding a risk that was previously accepted
Changing a risk owner
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk register is a document that records and tracks the information and status of the identified risks and their responses. It includes the risk description, category, source, cause, impact, probability, priority, response, owner, action plan, status, etc.
A risk register update is a change or modification to the information or status of the risks and their responses in the risk register. It may be triggered by the occurrence or resolution of a risk event, the identification or evaluation of a new or emerging risk, the implementation or completion of a risk response, the monitoring or review of the risk performance, etc.
The most important risk register update for senior management to review is avoiding a risk that was previously accepted, which means that the organization has decided to eliminate or withdraw from the risk exposure or activity that may cause the risk, instead of tolerating or retaining the risk as before. This may indicate a significant change in the organization’s risk appetite, strategy, objectives, or environment, and it may have a major impact on the organization’s performance and value.
The other options are not the most important risk register updates for senior management to review, because they do not indicate a significant change or impact on the organization’s risk profile or performance.
Extending the date of a future action plan by two months means that the organization has postponed the implementation or completion of the planned actions or measures to address the risk, due to some reasons or constraints. This may indicate a delay or deviation from the expected or desired risk outcome, but it may not have a major impact on the organization’s performance and value, unless the risk is very urgent or critical.
Retiring a risk scenario no longer used means that the organization has removed or discarded the risk scenario that is no longer relevant or applicable to the organization’s objectives or operations, due to some changes or developments. This may indicate a reduction or improvement in the organization’s risk exposure or level, but it may not have a major impact on the organization’s performance and value, unless the risk scenario was very significant or influential.
Changing a risk owner means that the organization has assigned or transferred the responsibility and accountability for the risk and its response to a different person or role, due to some reasons or circumstances. This may indicate a change or improvement in the organization’s risk governance or culture, but it may not have a major impact on the organization’s performance and value, unless the risk owner was very ineffective or inappropriate. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 160
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
Which of the following is the MOST efficient method for monitoring control effectiveness?
Conduct control self-assessments (CSAs)
Review system performance logs
Compare controls to business metrics
Perform independent periodic control testing
Answer:
Explanation:
Control Self-Assessments (CSAs)provide an efficient way for process owners and staff to assess control effectiveness continuously. ISACA recognizes CSAs as a proactive approach that encourages accountability and early detection of control weaknesses, reducing the need for frequent external testing.
===========
Which of the following should a risk practitioner do NEXT after learning that Internet of Things (loT) devices installed in the production environment lack appropriate security controls for
sensitive data?
Assess the threat and associated impact.
Evaluate risk appetite and tolerance levels
Recommend device management controls
Enable role-based access control.
Answer:
Explanation:
Assessing the threat and associated impact is the next thing that a risk practitioner should do after learning that Internet of Things (IoT) devices installed in the production environment lack appropriate security controls for sensitive data. This is because assessing the threat and associated impact can help determine the level and nature of the risk posed by the IoT devices, as well as the potential consequences and costs of a security breach or incident. Assessing the threat and associated impact can also provide the basis for further risk analysis and response steps, such as evaluating risk appetite and tolerance levels, recommending device management controls, or enabling role-based access control. According to the CRISC Review Manual 2022, assessing the threat and associated impact is one of the key steps in the IT risk assessment process1. According to the web search results, assessing the threat and associated impact is a common and recommended practice for addressing the security risks of IoT devices
An IT license audit has revealed that there are several unlicensed copies of co be to:
immediately uninstall the unlicensed software from the laptops
centralize administration rights on laptops so that installations are controlled
report the issue to management so appropriate action can be taken.
procure the requisite licenses for the software to minimize business impact.
Answer:
Explanation:
An IT license audit is a process that verifies the compliance of the IT software and hardware assets with the licensing agreements and regulations. An IT license audit can reveal the existence of unlicensed copies of software, which can expose the enterprise to legal, financial, and reputational risks. The best course of action in such a situation is to report the issue to management so that appropriate action can be taken. Management can then decide on the most suitable risk response strategy, such as procuring the necessary licenses, uninstalling the unlicensed software, or negotiating with the software vendor. Reporting the issue to managementcan also help to prevent further violations, identify the root causes, and implement corrective and preventive measures. The other options are not the best course of action, as they may not address the issue effectively, efficiently, or ethically. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1.1, pp. 156-157.
Which of the following would BEST provide early warning of a high-risk condition?
Risk register
Risk assessment
Key risk indicator (KRI)
Key performance indicator (KPI)
Answer:
Explanation:
A key risk indicator (KRI) is a metric that provides information on the level of exposure to a given risk or the potential impact of a risk. KRIs are used to monitor changes in risk levels and alert management when a risk exceeds a predefined threshold or tolerance. KRIs can help provide early warning of a high-risk condition and enable timely response and mitigation actions. A risk register is a tool that records and tracks the identified risks, their likelihood, impact, and status. A risk assessment is a process that identifies, analyzes, andevaluates risks. A key performance indicator (KPI) is a metric that measures the achievement of a specific goal or objective. References = Risk IT Framework, pages 22-231; CRISC Review Manual, pages 44-452
The acceptance of control costs that exceed risk exposure MOST likely demonstrates:
corporate culture alignment
low risk tolerance
high risk tolerance
corporate culture misalignment.
Answer:
Explanation:
The acceptance of control costs that exceed risk exposure most likely demonstrates corporate culture misalignment, as it indicates that the organization is not following the principles and values of effective risk management, and that there is a lack of communication and coordination among the risk owners and stakeholders. Corporate culture misalignment can also result in inefficient and wasteful use of resources, and reduced risk-return trade-off. The organization should align its corporate culture with its risk appetite and tolerance, and ensure that the control costs are proportional and justified by the risk exposure and the expected benefits. References = Most Asked CRISC Exam Questions and Answers. CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, Question 255. ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers, Question 255. CRISC by Isaca Actual Free Exam Q&As, Question 9.
It is MOST important for a risk practitioner to have an awareness of an organization s processes in order to:
perform a business impact analysis.
identify potential sources of risk.
establish risk guidelines.
understand control design.
Answer:
Explanation:
 It is most important for a risk practitioner to have an awareness of an organization’s processes in order to identify potential sources of risk, as this enables the risk practitioner to understand the objectives, activities, resources, dependencies, and outputs of the processes, and how they may be affected by internal or external factors that create uncertainty or variability. Identifying potential sources of risk is the first step in the risk identification process, which aims to find, recognize, and describe the risks that could affect the achievement of the organization’s goals. The other options are not the most important reasons for a risk practitioner to have an awareness of an organization’s processes, although they may be related or beneficial aspects of it. Performing a business impact analysis is a part of the risk analysis process, which aims to understand the nature and extent of the risks and their consequences on the organization’s objectives and functions. Establishing risk guidelines is a part of the risk governance process, which aims to define and communicate the risk management principles, policies, and roles across the organization. Understanding control design is a part of the risk response process, which aims to select and implement the appropriate actions to modify the risk level or achieve the risk objectives. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Identification, page 47.
A bank recently incorporated Blockchain technology with the potential to impact known risk within the organization. Which of the following is the risk practitioner’s BEST course of action?
Determine whether risk responses are still adequate.
Analyze and update control assessments with the new processes.
Analyze the risk and update the risk register as needed.
Conduct testing of the control that mitigate the existing risk.
Answer:
Which of the following BEST supports the integration of IT risk management into an organization's strategic planning?
Clearly defined organizational goals and objectives
Incentive plans that reward employees based on IT risk metrics
Regular organization-wide risk awareness training
A comprehensive and documented IT risk management plan
Answer:
Explanation:
A comprehensive and documented IT risk management plan provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT risks. Integrating this plan into the organization's strategic planning ensures that IT risk considerations are aligned with business objectives and are factored into decision-making processes at the strategic level.
Which of the following is MOST helpful in providing a high-level overview of current IT risk severity*?
Risk mitigation plans
heat map
Risk appetite statement
Key risk indicators (KRls)
Answer:
Explanation:
 A heat map is a graphical tool that displays the level of risk severity for various risk scenarios or categories using different colors, shapes, or sizes. A heat map is most helpful in providing a high-level overview of current IT risk severity, as it can show the relative importance and urgency of the risks, and highlight the areas that require attention or action. A heat map can also help to communicate the risk information to the stakeholders, and facilitate the risk prioritization and decision making. References = 5
During a routine check, a system administrator identifies unusual activity indicating an intruder within a firewall. Which of the following controls has MOST likely been compromised?
Data validation
Identification
Authentication
Data integrity
Answer:
Explanation:
Authentication is a control that verifies the identity of a user or a system that tries to access a computer system or network. Authentication can be based on something the user or system knows (such as a password or a PIN), something the user or system has (such as a token or asmart card), or something the user or system is (such as a fingerprint or a retina scan). Authentication is a crucial control for preventing unauthorized or malicious access to a system or network, as well as for ensuring the accountability and traceability of the actions performed by the user or system. If the authentication control is compromised, it means that the user or system can bypass or break the verification process and gain access to the system or network without being identified or authorized. This can expose the system or network to various threats, such as data theft, data corruption, data leakage, or denial of service. Therefore, the authentication control has most likely been compromised if a system administrator identifies unusual activity indicating an intruder within a firewall. A firewall is a device or a software that monitors and filters the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules and policies. A firewall can help to protect the system or network from external or internal attacks by blocking or allowing the traffic based on the source, destination, protocol, or content. However, a firewall cannot prevent an intruder from accessing the system or network if the intruder has already authenticated or impersonated a legitimate user or system. The other options are not the most likely controls to be compromised if a system administrator identifies unusual activity indicating an intruder within a firewall, although they may be affected or related. Data validation is a control that checks the accuracy, completeness, and quality of the data that is entered, processed,or stored by a system or anetwork. Data validation can help to prevent or detect data errors, anomalies, or inconsistencies that may affect the performance, functionality, or reliability of the system or network. However, data validation does not prevent or detect unauthorized or malicious access to the system or network, as it only focuses on the data, not the user or system. Identification is a control that assigns a unique identifier to a user or a system that tries to access a computer system or network. Identification can be based on a username, an email address, a phone number, or a certificate. Identification is a necessary but not sufficient control for preventing unauthorized or malicious access to a system or network, as it only declares who or what the user or system is, but does not prove it. Identification needs to be combined with authentication to verify the identity of the user or system. Data integrity is a control that ensures that the data is accurate, consistent, and complete throughout its lifecycle. Data integrity can be achieved by implementing various controls, such as encryption, hashing, checksum, digital signature, or backup. Data integrity can help to protect the data from unauthorized or accidental modification, deletion, or corruption that may affect the value, meaning, or usability of the data. However, data integrity does not prevent or detect unauthorized or malicious access to the system or network, as it only protects the data, not the user or system. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 164-1651; CRISC Review Questions, Answers &Explanations Manual, page 952; What is Authentication? - Definition from Techopedia3; What is a Firewall? - Definition from Techopedia4
Which of the following is the BEST way to identify changes in the risk profile of an organization?
Monitor key risk indicators (KRIs).
Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs).
Interview the risk owner.
Conduct a gap analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to identify changes in the risk profile of an organization is to monitor key risk indicators (KRIs), which are metrics that provide information on the level of exposure to a given operational risk1. KRIs can help to monitor the changes in risk levels over time, identify emerging risks, and trigger risk response actions when the risk exceeds the acceptable thresholds2. KRIs can also help to align the risk management strategy with the business objectives and context. The other options are not the best ways to identify changes in the risk profile of an organization, as they do not provide the same level of insight and guidance as KRIs. Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) may show the results or outcomes of the business processes, but not the risks or uncertainties that affect them. Interviewing the risk owner may provide some subjective or qualitative information on the risk perception or attitude, but not the objective or quantitative data on the risk exposure or impact. Conducting a gap analysis may show the difference between the current and desired state of the organization, but not the causes or sources of the risk. References = Key Risk Indicators; Key Risk Indicators: A Practical Guide
The MOST important reason to aggregate results from multiple risk assessments on interdependent information systems is to:
establish overall impact to the organization
efficiently manage the scope of the assignment
identify critical information systems
facilitate communication to senior management
Answer:
Explanation:
 The interdependency of information systems means that the failure or disruption of one system can affect the performance or availability of other systems. Therefore, it is important to aggregate the results from multiple risk assessments on interdependent information systems to understand the overall impact to the organization. By aggregating the results, the risk manager can identify the potential cascading effects, the cumulative consequences, and the worst-casescenarios of interdependent risks. This can help theorganization to prioritize the risks, allocate the resources, and implement the risk response strategies accordingly. The other options are not as important as the overall impact to the organization, because they do not capture the full extent of the interdependency of information systems. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.3, page 99.
Which of the following is MOST important to ensure when reviewing an organization's risk register?
Risk ownership is recorded.
Vulnerabilities have separate entries.
Control ownership is recorded.
Residual risk is less than inherent risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
 The most important factor to ensure when reviewing an organization’s risk register is that the risk ownership is recorded, as it indicates the authority and responsibility for managing the risk and its associated controls, and facilitates the communication and accountability of the risk management process and activities. The other options are not the most important factors, as they are more related to theidentification, classification, or measurement of the risk, respectively, rather than the management of the risk. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 101.
Concerned about system load capabilities during the month-end close process, management requires monitoring of the average time to complete tasks and monthly reporting of the findings. What type of measure has been established?
Service level agreement (SLA)
Critical success factor (CSF)
Key risk indicator (KRI)
Key performance indicator (KPI)
Answer:
Explanation:
Monitoring the average time to complete tasks and monthly reporting of the findings during the month-end close process aligns with the definition of a Key Performance Indicator (KPI).
Understanding KPIs:
Performance Measurement:KPIs are used to measure how effectively a company is achieving its key business objectives. Monitoring the average time to complete tasks during the month-end close process provides a performance metric.
Tracking Efficiency:By reporting these findings monthly, management can track the efficiency and performance of the system load capabilities.
Specific Measure:
Task Completion Time:The average time to complete tasks is a specific, measurable indicator of performance. It helps in understanding how well the system handles load and identifies areas for improvement.
Continuous Improvement:Regular monitoring and reporting encourage continuous improvement, which is a core aspect of using KPIs.
An IT department has provided a shared drive for personnel to store information to which all employees have access. Which of the following parties is accountable for the risk of potential loss of confidential information?
Risk manager
Data owner
End user
IT department
Answer:
Explanation:
The data owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility to classify, label, and protect the information assets of the organization. The data owner is accountable for the risk ofpotential loss of confidential information, as they are the ones who determine the level of protection and access required for the data. The risk manager is responsible for identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risks that may affect the organization, but they are not accountable for the data itself. The end user is the person who uses the information assets for their operational tasks, but they are not accountable for the data protection or classification. The IT department is responsible for providing the technical support and infrastructure for the information assets, but they are not accountable for the data ownership or risk management. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.3: Data Classification, p. 69-70.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY goal of enterprise architecture (EA)?
To document all implemented systems reflecting the architectural views relevant to the IT team
To provide a vision of the future state and generate strategy to move from current to future state
To implement a governance framework that aligns with the desired organizational structure
To develop and design a technology framework to be used by all IT staff within the organization
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary goal of enterprise architecture is to define a future-state vision and guide the organization’s transformation to that future state. CRISC describes EA as a strategic discipline that ensures technology, processes, and capabilities support long-term business goals. Documentation of systems, governance frameworks, and standardized technology models are components of EA, but the overarching purpose is future-state planning and a structured roadmap for achieving strategic alignment. Without this vision, EA loses its strategic value and becomes merely documentation.
An organization is concerned that a change in its market situation may impact the current level of acceptable risk for senior management. As a result, which of the following is MOST important to reevaluate?
Risk classification
Risk policy
Risk strategy
Risk appetite
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Risk Appetite:
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to take in order to meet its objectives. It reflects the organization’s risk tolerance and guides decision-making at all levels.
ï‚· Impact of Market Changes:
A change in the market situation can alter the risk landscape, potentially affecting the organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. This might necessitate a reassessment of what level of risk is acceptable.
Senior management needs to ensure that the risk appetite remains aligned with the new market conditions and organizational goals.
ï‚· Reevaluation Process:
Reevaluating the risk appetite involves assessing the organization's capacity to bear risk and determining if the current acceptable risk levels are still appropriate.
This might involve more conservative or aggressive risk-taking strategies based on the new market dynamics.
ï‚· Other Considerations:
Risk Classification:This categorizes risks but does not directly address changes in acceptable risk levels.
Risk Policy:While important, the policy outlines the approach to managing risk and is influenced by the risk appetite.
Risk Strategy:This defines how risks are managed but should be aligned with the risk appetite.
ï‚· References:
The CRISC Review Manual emphasizes the importance of aligning risk appetite with the organization’s strategic objectives and market conditions (CRISC Review Manual, Chapter 1: Governance, Section 1.10 Risk Appetite, Tolerance, and Capacity) .
A zero-day vulnerability has been discovered in a globally used brand of hardware server that allows hackers to gain
access to affected IT systems. Which of the following is MOST likely to change as a result of this situation?
Control effectiveness
Risk appetite
Risk likelihood
Key risk indicator (KRI)
Answer:
Explanation:
The most likely factor to change as a result of a zero-day vulnerability being discovered in a globally used brand of hardware server that allows hackers to gain access to affected IT systems is the risk likelihood. Risk likelihood is the probability or frequency of a risk event occurring, or the possibility of a risk event occurring within a given time period. Risk likelihood is one of the key dimensions of risk analysis, along with the risk impact. Risk likelihood helps to determine the severity and priority of the risk, and to select the most appropriate and effective risk response. Risk likelihood also helps to evaluate the cost-benefit and trade-off of the risk response, and to measure the residual risk and the risk performance. The risk likelihood is likely to change as a result of a zero-day vulnerability, because a zero-day vulnerability is a security flaw that has been discovered but not yet patched by the vendor, which means that it can be exploited by hackers before the affected systems can be updated or protected. A zero-day vulnerability increases the risk likelihood, because it creates a window of opportunity for hackers to launch attacks that could compromise the affected systems, and because it may not be detected or prevented by the existing security controls or measures. The other options are not as likely to change as the risk likelihood, although they may also be affected or influenced by the zero-day vulnerability. Control effectiveness, risk appetite, and key risk indicator (KRI) are all factors that could change as a result of a zero-day vulnerability, but they are not the most likely factor to change. Control effectiveness is the extent to which the risk controls or responses achieve the intended risk objectives or outcomes. Control effectiveness could change as a result of a zero-day vulnerability, because the existing controls may not be able to detect or prevent the exploitation of the vulnerability, or because new or additional controls may be needed to address the vulnerability. However, control effectiveness is not the most likely factor to change, because it depends on the type and level of the controls that are already in place or that can be implemented, and because it may not change until the vulnerability is actually exploited or the risk response is executed. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept or pursue in order to achieve its objectives. Risk appetite could change as a result of a zero-day vulnerability, because the vulnerability could affect the organization’s objectives or operations, and because the organization may need to adjust its risk tolerance or threshold to cope with the vulnerability. However, risk appetite is not the most likely factor to change, because it is a strategic and long-term decision that is driven by the organization’s mission, vision, values, and strategy, and because it may not change until the vulnerability is resolved or the risk impact is realized. Key risk indicator (KRI) is a metric that measures thelikelihood and impact of risks, and helps monitor and prioritize the most critical risks. KRI could change as a result of a zero-day vulnerability, because the vulnerability could increase the likelihood and impact of the risks, and because the organization may need to update or revise its KRI to reflect the current risk situation. However, KRI is not the most likely factor to change,because it is a monitoring and reporting tool that is derived from the risk analysis and response, and because it may not change until the vulnerability is exploited or the risk response is implemented. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.1, page 4-25.
Which of the following controls are BEST strengthened by a clear organizational code of ethics?
Detective controls
Administrative controls
Technical controls
Preventive controls
Answer:
Explanation:
Administrative controls are the best controls to be strengthened by a clear organizational code of ethics, because they are the policies, procedures, standards, and guidelines that define the expected behavior and conduct of the employees and management. A code of ethics is an example of an administrative control that sets the ethical principles and values of the organization and helps to prevent or deter unethical or illegal actions. The other options are not the best controls to be strengthened by a clear organizational code of ethics, because they are not directly related to the ethical culture or governance of the organization. Detective controls are the controls that monitor and report the occurrence of unwanted events or incidents. Technical controls are the controls that use hardware, software, or network devices to protect the information systems and data. Preventive controls are the controls that prevent or avoid the occurrence of unwanted events or incidents. References = ISACA Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) Certification Exam Question and Answers
A risk practitioner is preparing a report to communicate changes in the risk and control environment. The BEST way to engage stakeholder attention is to:
include detailed deviations from industry benchmarks,
include a summary linking information to stakeholder needs,
include a roadmap to achieve operational excellence,
publish the report on-demand for stakeholders.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A risk practitioner is preparing a report to communicate changes in the risk and control environment, such as new or emerging risks, changes in risk levels, risk responses, or control effectiveness. The best way to engage stakeholder attention is to include a summary linking information to stakeholder needs, meaning that the report should highlight the key points and findings that are relevant and important for the stakeholder’s role, responsibility, and interest. The summary should also explain how the information affects the stakeholder’s objectives, expectations, and decisions. The summary should be concise, clear, and compelling, and should capture the stakeholder’s attention and interest. The report can also include detailed deviations from industry benchmarks, a roadmap to achieve operational excellence, or an option to publish the report on-demand for stakeholders, but these are not the best ways to engage stakeholder attention, as they may not be directly related to the stakeholder’s needs or may overwhelm the stakeholder with too much information. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.1, p. 124-125
Which of the following BEST facilities the alignment of IT risk management with enterprise risk management (ERM)?
Adopting qualitative enterprise risk assessment methods
Linking IT risk scenarios to technology objectives
linking IT risk scenarios to enterprise strategy
Adopting quantitative enterprise risk assessment methods
Answer:
Explanation:
The best way to facilitate the alignment of IT risk management with enterprise risk management (ERM) is to link IT risk scenarios to enterprise strategy, because this ensures that the IT risks are considered in the context of the enterprise’s mission, vision, and goals. Linking IT risk scenarios to enterprise strategy also helps to prioritize the IT risks based on their impact and relevance to the enterprise’s objectives, and to select the appropriate risk responses and resources. The other options are not the best ways to facilitate the alignment of IT risk management with ERM, because they do not address the integration or alignment of the IT and enterprise perspectives. Adopting qualitative or quantitative enterprise risk assessment methods, and linking IT risk scenarios to technology objectives are examples of techniques or tools that can be used to perform IT risk management or ERM, but they do not ensure the alignment or consistency of the two processes. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 1, Section 1.2.3, p. 22.
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern when using artificial intelligence (AI) language models?
The model could be hacked or exploited.
The model could be used to generate inaccurate content.
Staff could become overly reliant on the model.
It could lead to biased recommendations.
Answer:
Explanation:
Biased recommendations from AI models pose significant risks to decision-making and organizational ethics. Such biases can propagate systemic issues and impact regulatory compliance, emphasizing the need for robust controls in AI development and deployment underEmerging Technology Risks.
Which of the following should be the GREATEST concern for an organization that uses open source software applications?
Lack of organizational policy regarding open source software
Lack of reliability associated with the use of open source software
Lack of monitoring over installation of open source software in the organization
Lack of professional support for open source software
Answer:
Explanation:
Lack of organizational policy regarding open source software should be the greatest concern for an organization that uses open source software applications, as it may expose the organization to legal, security, and operational risks. Open source software is software that is freely available and can be modified and distributed by anyone, subject to certain conditions and licenses. An organizational policy regarding open source software should define the criteria and procedures for selecting, acquiring, using, and maintaining open source software, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders involved. Lack of reliability, lack of monitoring, and lack of professional support are not the greatest concerns, as they can be addressed by implementing quality assurance, configuration management, and community engagement practices for open source software. References = CRISC by Isaca Actual Free Exam Q&As, question 214; CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions, question 214.
Which of the following is MOST important when discussing risk within an organization?
Adopting a common risk taxonomy
Using key performance indicators (KPIs)
Creating a risk communication policy
Using key risk indicators (KRIs)
Answer:
Explanation:
 A common risk taxonomy is a framework that defines and categorizes the sources, types, and impacts of risks within an organization1. It helps to establish a consistent and shared understanding of risk across the organization, and to facilitate effective risk identification, assessment, reporting, and communication2. A common risk taxonomy also enables comparison and aggregation of risks at different levels and domains, and supports alignment of risk management with business objectives and strategies3. Using key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs) are important for measuring and monitoring risk and performance, but they are not the most important factor when discussing risk within an organization. KPIs and KRIs should be derived from the common risk taxonomy and aligned with theorganization’s riskappetite and tolerance4. Creating a risk communication policy is also important for ensuring that risk information is communicated to the right stakeholders at the right time and in the right format, but it is not the most important factor either. A risk communication policy should be based on the common risk taxonomy and the risk roles and responsibilities within the organization5. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1: IT Risk Identification, Section 1.2: Risk Taxonomy, pp. 25-29.
Which of the following controls will BEST detect unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator?
Reviewing database access rights
Reviewing database activity logs
Comparing data to input records
Reviewing changes to edit checks
Answer:
Explanation:
Unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator is a security risk that involves altering, deleting, or inserting data on a database without proper authorization or approval, by a person who has privileged access to the database, such as a database administrator12.
The best control to detect unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator is to review database activity logs, which are records that capture and store the details and history ofthe transactions or activities that are performed on the database, such as who, what, when, where, and how34.
Reviewing database activity logs is the best control because it provides evidence and visibility of the database operations, and enables the detection and reporting of any deviations, anomalies, or issues that may indicate unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator34.
Reviewing database activity logs is also the best control because it supports the accountability and auditability of the database operations, and facilitates the investigation and resolution of any unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator34.
The other options are not the best controls, but rather possible measures or techniques that may supplement or enhance the review of database activity logs. For example:
Reviewing database access rights is a measure that involves verifying and validating the permissions and privileges that are granted or revoked to the users or roles who can access or modify the data on the database56. However, this measure is not the best control because it does not directly detect unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator, especially if the database administrator has legitimate access rights to the data56.
Comparing data to input records is a technique that involves matching and reconciling the data on the database with the original or source data that are entered or imported into the database, and identifying and correcting any discrepancies or errors78. However, this technique is not the best control because it does not directly detect unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator, especially if the input records are also modified or compromised78.
Reviewing changes to edit checks is a technique that involves examining and evaluating the modifications or updates to the edit checks, which are rules or validations that are applied to the data on the database to ensure their accuracy, completeness, andconsistency9 . However, this technique is not the best control because it does not directly detect unauthorized modification of data by a database administrator, especially if the edit checks are bypassed or disabled9 . References =
1: Database Security: Attacks and Solutions | SpringerLink2
2: Unauthorised Modification of Data With Intent to Cause Impairment3
3: Database Activity Monitoring - Wikipedia4
4: Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) | Imperva5
5: Database Access Control - Wikipedia6
6: Database Access Control: Best Practices for Database Security7
7: Data Reconciliation - Wikipedia8
8: Data Reconciliation and Gross Error Detection9
9: Edit Check - Wikipedia
Edit Checks: A Data Quality Tool
Which of the following presents the GREATEST security risk associated with Internet of Things (IoT) technology?
The inability to monitor via network management solutions
The lack of relevant IoT security frameworks to guide the risk assessment process
The heightened level of IoT threats via the widespread use of smart devices
The lack of updates for vulnerable firmware
Answer:
Explanation:
Vulnerable firmware that lacks updates is a significant security risk, as it can be exploited by attackers. Addressing this issue aligns withSecure IoT Deployment Practicesto reduce exposure.
What should a risk practitioner do FIRST upon learning a risk treatment owner has implemented a different control than what was specified in the IT risk action plan?
Seek approval from the control owner.
Update the action plan in the risk register.
Reassess the risk level associated with the new control.
Validate that the control has an established testing method.
Answer:
Explanation:
The first thing that a risk practitioner should do upon learning that a risk treatment owner has implemented a different control than what was specified in the IT risk action plan is to reassess the risk level associated with the new control. This is because the new control may have a different effect on the likelihood and impact of the risk, and may introduce new risks or modify existing ones. The risk practitioner should evaluate the adequacy and effectiveness of the newcontrol, and compare the residual risk with the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization. The risk practitioner should also communicate the results of the risk reassessment to the relevant stakeholders, and update the risk register and action plan accordingly. The other options are not the first things that a risk practitioner should do, although they may be necessary or appropriate at a later stage. Seeking approval from the control owner is important, but it does not address the potential changes in the risk level or the alignment with the risk management objectives. Updating the action plan in the risk register is a good practice, but it should be done after the risk reassessment and with the consent of the risk owner. Validating that the control has an established testing method is a part of the control assurance process, but it does not provide information on the risk level or the risk response effectiveness. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk Response, page 151.
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for a risk practitioner to report changes and trends in the IT risk profile to senior management?
To ensure risk owners understand their responsibilities
To ensure IT risk is managed within acceptable limits
To ensure the organization complies with legal requirements
To ensure the IT risk awareness program is effective
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary reason for a risk practitioner to report changes and trends in the IT risk profile to senior management is to ensure that IT risk is managed within acceptable limits, because it helps to inform and advise the senior management on the current state and direction of IT risk, and to support the risk-based decision making and prioritization. An IT risk profile is a summary of the key IT risks that an organization faces, and their implications for the organization’s objectives and strategy. An IT risk profile may change or evolve over time, due to factors such as newtechnologies, business initiatives, or external events. Reporting changes and trends in the IT risk profile to senior management is the primary reason, as it helps to ensure that the senior management is aware of and prepared for the IT risk challenges and opportunities, and that the IT risk is managed within the acceptable limits defined by the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. To ensure risk owners understand their responsibilities, to ensure the organization complies with legal requirements, and to ensure the IT risk awareness program is effective are all possible reasons for reporting changes and trends in the IT risk profile, but they are not the primary reason, as they are not directly related to the management of IT risk within acceptable limits. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.3, page 91
An IT risk practitioner has been tasked to engage key stakeholders to assess risk for key IT risk scenarios. Which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of this activity?
Establishing the available risk mitigation budget
Verifying the relevance of risk ratings
Demonstrating compliance to regulatory bodies
Assessing IT risk management culture
Answer:
Explanation:
Stakeholders provide operational insight that enhances the accuracy and context of risk ratings. Their input ensures the ratings reflect actual risk exposure and business priorities, validating the relevance of the assessments.
An organization has committed to a business initiative with the knowledge that the risk exposure is higher than the risk appetite. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's MOST important action related to this decision?
Recommend rejection of the initiative.
Change the level of risk appetite.
Document formal acceptance of the risk.
Initiate a reassessment of the risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
Formal acceptance of the risk is critical when the risk exposure exceeds the risk appetite, as it ensures accountability and acknowledges the decision at the appropriate level. Documenting acceptance involves communicating the potential impacts and obtaining agreement from senior stakeholders. This process aligns with theRisk Response and Reportingdomain in CRISC, emphasizing clear documentation and communication of risks for decision-making.
Which of the following enterprise architecture (EA) controls BEST mitigates the risk of increasingly complex systems becoming compromised by unauthorized network access?
Requirements to change default settings on network devices
Continuous network vulnerability scanning and remediation
Complex password policy and procedures
Continuous access verification and authentication
Answer:
A business is conducting a proof of concept on a vendor’s AI technology. Which of the following is the MOST important consideration for managing risk?
Use of a non-production environment
Regular security updates
Third-party management plan
Adequate vendor support
Answer:
Explanation:
Conducting a proof of concept in a non-production environment ensures that any potential issues or vulnerabilities in the AI technology do not affect live systems or data. This approach allows for thorough testing and evaluation without risking operational disruptions or data breaches.
During implementation of an intrusion detection system (IDS) to monitor network traffic, a high number of alerts is reported. The risk practitioner should recommend to:
reset the alert threshold based on peak traffic
analyze the traffic to minimize the false negatives
analyze the alerts to minimize the false positives
sniff the traffic using a network analyzer
Answer:
Explanation:
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a network security tool that monitors network traffic and devices for known malicious activity, suspicious activity or security policy violations1. An IDS can generate alerts when it detects any potential threats, but not all alerts are accurate or relevant. There are two types of errors that can affect the performance and reliability of an IDS: false positives and false negatives2.
A false positive is when an IDS incorrectly flags a benign or normal activity as malicious or suspicious. For example, an IDS may alert on a legitimate network scan or a harmless software update. False positives can reduce the credibility and efficiency of an IDS, as they can overwhelm the security team with unnecessary alerts, distract them from the real threats, and cause them to ignore or disable the IDS3.
A false negative is when an IDS fails to flag a malicious or suspicious activity as such. For example, an IDS may miss a stealthy or novel attack that does not match any known signatures or patterns. False negatives can compromise the security and integrity of the network, as they can allow attackers to bypass the IDS and cause damage or steal data without being detected4.
The risk practitioner should recommend to analyze the alerts to minimize the false positives, because this is the best way to improve the accuracy and usefulness of the IDS. By analyzing the alerts, the risk practitioner can:
Identify the sources and causes of the false positives, such as misconfigured or outdated IDS rules, network anomalies, or legitimate traffic that resembles malicious traffic5.
Adjust or fine-tune the IDS settings, such as the alert threshold, the sensitivity level, the detection method, or the rule base, to reduce the number of false positives without increasing the risk of false negatives.
Validate or verify the alerts with other sources of information, such as logs, network traffic analysis, or threat intelligence, to confirm or dismiss the alerts as true or false positives.
Prioritize or classify the alerts based on their severity, impact, or likelihood, to focus on the most critical or relevant alerts and avoid alert fatigue.
The other options are not the best course of action, because:
Resetting the alert threshold based on peak traffic is not a reliable or effective way to minimize the false positives, as it may also increase the risk of false negatives. The alert threshold is the level of activity or deviation that triggers an alert from the IDS. If the threshold is set too high, the IDS may miss some malicious or suspicious activity that occurs below the threshold. If the threshold is set too low, the IDS may generate too many alerts for normal or benign activity that exceeds the threshold. The optimal threshold depends on various factors, such as the network size, topology, traffic volume, and baseline. Peak traffic is not a good indicator of the optimal threshold, as it may vary depending on the time, day, or season, and it may not reflect the normal or expected network behavior.
Analyzing the traffic to minimize the false negatives is not the main issue or goal in this scenario, as the problem is the high number of alerts, not the low number of alerts. Analyzing thetraffic can help to identify the malicious or suspicious activity that the IDS may have missed, but it does not address the root cause of the false positives or improve the IDS performance. Moreover, analyzing the traffic can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for large or complex networks, and it may require specialized tools or skills that the risk practitioner may not have.
Sniffing the traffic using a network analyzer is not a suitable or feasible option in this scenario, as it may violate the privacy or security policies of the network or the organization. Sniffing the traffic means capturing and inspecting the network packets that are transmitted or received by the devices on the network. A network analyzer is a tool that can perform this function and display the packet data in a readable format. However, sniffing the traffic can also expose sensitive or confidential information, such as passwords, usernames, or credit card numbers, that may be contained in the packets. Therefore, sniffing the traffic may require authorization or consent from the network owners or users, and it may be restricted or prohibited by law or regulation.
References =
What is an intrusion detection system (IDS)? - IBM
Intrusion detection system - Wikipedia
What Are Intrusion Detection Systems? - MUO
12 Best Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Software 2024 - Comparitech
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)? - Fortinet
[False Positive and False Negative in Intrusion Detection System]
[False Positives and False Negatives in Intrusion Detection Systems]
[How to Reduce False Positives for Your IDS/IPS]
[How to Set the Right Alert Thresholds for Your IDS/IPS]
[Network Traffic Analysis: What It Is and How It Works]
[What is a Network Analyzer? - Definition from Techopedia]
When developing a risk awareness training program, which of the following training topics would BEST facilitate a thorough understanding of risk scenarios?
Mapping threats to organizational objectives
Reviewing past audits
Analyzing key risk indicators (KRIs)
Identifying potential sources of risk
Answer:
Explanation:
Identifying potential sources of risk is the first step in the risk identification process, which is essential for developing a thorough understanding of risk scenarios. Sources of risk can be internal or external, and can include factors such as people, processes, technology, environment, regulations, and events. Identifying potential sources of risk can help to generate a comprehensive list of risk scenarios that can affect the organization’s objectives and operations. Identifying potential sources of risk can also help to raise risk awareness among the employees and to foster a risk culture within the organization. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.2.1, p. 66-67
Reviewing which of the following would provide the MOST useful information when preparing to evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls?
Previous audit reports
Control objectives
Risk responses in the risk register
Changes in risk profiles
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Understanding the Question:
The question seeks to identify which source provides the most useful information for evaluating the effectiveness of existing controls.
ï‚· Analyzing the Options:
A. Previous audit reports:Provide historical data but might not reflect current risks.
B. Control objectives:These are standards to be achieved, not current evaluations.
C. Risk responses in the risk register:Useful but focused on specific responses rather than overall effectiveness.
D. Changes in risk profiles:Reflect current and emerging risks, providing a dynamic view of control effectiveness.
ï‚·
Risk Profiles:Evaluating changes in risk profiles helps understand how effective existing controls are against current threats. If risk levels are increasing, it may indicate that controls are insufficient or need updating.
Proactive Adjustment:By monitoring changes in risk profiles, organizations can proactively adjust their controls to address new or evolving risks.
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when developing an organization's risk management strategy?
Complexity of technology architecture
Disaster recovery strategy
Business operational requirements
Criteria for assessing risk
Answer:
Explanation:
Thebusiness operational requirementsshould be the central consideration when crafting a risk management strategy. This ensures that risk management aligns with and supports business objectives, a core principle in ISACA’s risk management framework.
===========
Which of the following practices would be MOST effective in protecting personality identifiable information (Ptl) from unauthorized access m a cloud environment?
Apply data classification policy
Utilize encryption with logical access controls
Require logical separation of company data
Obtain the right to audit
Answer:
Explanation:
The most effective practice in protecting personally identifiable information (PII) from unauthorized access in a cloud environment is to utilize encryption with logical access controls. Encryption is a technique that transforms the data into an unreadable or unintelligible form, making it inaccessible or unusable by unauthorized parties. Logical access controls are the mechanisms or rules that regulate who can access, view, modify, or delete the data, based on their identity, role, or privilege. By utilizing encryption with logical access controls, the PII can be protected from unauthorized access, disclosure, or theft, both in transit and at rest, in a cloud environment. The other options are not as effective as utilizing encryption with logical access controls, as they are related to the classification, separation, or audit of the data, not the protection or security of the data. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: IT Risk Response Implementation, page 145.
Which of the following is the MOST important characteristic of a key risk indicator (KRI) to enable decision-making?
Monitoring the risk until the exposure is reduced
Setting minimum sample sizes to ensure accuracy
Listing alternative causes for risk events
Illustrating changes in risk trends
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important characteristic of a key risk indicator (KRI) to enable decision-making is illustrating changes in risk trends, as it provides a clear and timely indication of the direction and magnitude of the risk level and exposure, and enables the stakeholders to take proactive andappropriate actions to address the risk. The other options are not the most important characteristics, as they are more related to the monitoring, measurement, or identification of the risk, respectively, rather than the illustration of the risk trends. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 110.
When evaluating enterprise IT risk management it is MOST important to:
create new control processes to reduce identified IT risk scenarios
confirm the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance
report identified IT risk scenarios to senior management
review alignment with the organization's investment plan
Answer:
Explanation:
 Enterprise IT risk management is the process of identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and treating the IT-related risks that may affect the organization’s objectives, operations, or assets1. Enterprise IT risk management should be aligned with the organization’s overall riskmanagement framework and strategy, and support the organization’s value creation and protection2.
When evaluating enterprise IT risk management, it is most important to confirm the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to take in order to meet its strategic objectives3. Risk tolerance is the acceptable level of variation that an organization is willing to accept around its risk appetite4. By confirming the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance, the evaluation can:
Ensure that the enterprise IT risk management is consistent and compatible with the organization’s risk culture and vision
Provide clear and measurable criteria and boundaries for assessing and prioritizing the IT risks and their impacts
Guide the selection and implementation of the appropriate risk responses and controls that balance the costs and benefits of risk mitigation
Enable the monitoring and reporting of the IT risk performance and outcomes, and the adjustment of the IT risk strategy and objectives as needed5
References = Enterprise IT Risk Management - ISACA, Enterprise Risk Management - Wikipedia, Risk Appetite - COSO, Risk Tolerance - COSO, Risk Appetite and Tolerance - IRM
During the control evaluation phase of a risk assessment, it is noted that multiple controls are ineffective. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner's FIRST course of action?
Recommend risk remediation of the ineffective controls.
Compare the residual risk to the current risk appetite.
Determine the root cause of the control failures.
Escalate the control failures to senior management.
Answer:
Explanation:
The control evaluation phase of a risk assessment is the phase where the risk practitioner evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the existing or planned controls that mitigate the identified risks. Controls are the actions or measures that reduce the likelihood or impact of the risks to an acceptable level. The control evaluation phase involves testing, reviewing, and auditing the controls, and identifying any gaps or weaknesses that need to be addressed. If the control evaluation phase reveals that multiple controls are ineffective, the risk practitioner’s first course of action should be to determine the root cause of the control failures. The root cause is the underlying or fundamental reason that leads to the problem or issue, such as the controlfailure. By determining the root cause of the control failures, the risk practitioner can understand why the controls are not working as intended, and what factors or variables are influencing the control performance. This will help the risk practitioner to identify and implement the most appropriate and effective risk response strategy and actions, such as recommending risk remediation, comparing the residual risk, or escalating the control failures. The other options are not the first course of action, as they involve different steps or outcomes of the risk management process:
Recommend risk remediation of the ineffective controls means that the risk practitioner suggests the actions or measures that can improve or restore the effectiveness of the controls, such as by modifying, replacing, or adding the controls. This may be a useful step in the risk management process, but it is not the first course of action, as it may not address the root cause of the control failures, or may not be feasible or efficient for the enterprise’s needs.
Compare the residual risk to the current risk appetite means that the risk practitioner evaluates the level of risk that remains after considering the existing or planned controls, and compares it with the amount and type of risk that the enterprise is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. This may be a helpful step in the risk management process, but it is not the first course of action, as it may not reflect the true or current level of risk exposure, or may not account for the uncertainties or complexities of the risks or the controls.
Escalate the control failures to senior management means that the risk practitioner communicates the control failures to the senior leaders of the enterprise, who oversee the enterprise-wide risk management program, and provide guidance and direction to the risk owners and practitioners. This may be a necessary step in the risk management process, but it is not the first course of action, as it may not provide sufficient or timely information or action to address the control failures, or may not reflect the urgency or priority of the control failures. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.3.3.1, pp. 62-63.
Develop policies with less restrictive requirements to ensure consistency across the organization.
Develop a global policy to be applied uniformly by each country.
Develop country-specific policies to address local regulations.
Develop a global policy that accommodates country-specific requirements.
Answer:
Explanation:
A global policy that accommodates country-specific requirements balances consistency and compliance. It establishes a baseline of controls while allowing adaptation to local laws and cultural differences. Uniform application without adaptation risks non-compliance. Country-specific policies alone may lack global coherence. Therefore, accommodating local requirements within a global policy framework is best practice.
Which of the following can be affected by the cost of risk mitigation alternatives?
Risk appetite
Risk factors
Risk tolerance
Current risk rating
Answer:
Explanation:
When the cost of mitigating a risk exceeds the benefit,organizations may adjust their risk toleranceto accept a higher level of risk. Thus, financial feasibility influences how much risk the organization is willing to accept.
Which of the following BEST helps to balance the costs and benefits of managing IT risk?
Prioritizing risk responses
Evaluating risk based on frequency and probability
Considering risk factors that can be quantified
Managing the risk by using controls
Answer:
Explanation:
Prioritizing risk responses helps to balance the costs and benefits of managing IT risk by ensuring that the most significant risks are addressed first and that the resources allocated to risk management are used efficiently and effectively. Evaluating risk based on frequency and probability is a part of risk analysis, not risk response. Considering risk factors that can be quantified is also a part of risk analysis, and it does not necessarily capture all the relevant aspects of risk. Managing the risk by using controls is a possible risk response, but it does not guarantee that the costs and benefits of risk management are balanced, as some controls may be too expensive or ineffective for the level of risk they mitigate. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk Response, page 145.
Which of the following should be given the HIGHEST priority when developing a response plan for risk assessment results?
Risk that has been untreated
Items with a high inherent risk
Items with the highest likelihood of occurrence
Risk that exceeds risk appetite
Answer:
A risk practitioner has observed that there is an increasing trend of users sending sensitive information by email without using encryption. Which of the following would be the MOST effective approach to mitigate the risk associated with data loss?
Implement a tool to create and distribute violation reports
Raise awareness of encryption requirements for sensitive data.
Block unencrypted outgoing emails which contain sensitive data.
Implement a progressive disciplinary process for email violations.
Answer:
Explanation:
 According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the most effective approach to mitigate the risk associated with data loss due to users sending sensitive information by email without using encryption is to block unencrypted outgoing emails which contain sensitive data. This is an example of a risk avoidance strategy, which aims to eliminate the risk by removing the source of the risk or the activity that causes the risk. Blocking unencrypted outgoing emails which contain sensitive data can prevent unauthorized access, disclosure, modification or destruction of the sensitive information, and thus protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the data. This approach can also deter users from violating the encryption policy and enforce compliance with the security standards and regulations.
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 3: IT Risk Response, Section 3.3: Risk Response Options, pp. 167-1681
The MAIN purpose of conducting a control self-assessment (CSA) is to:
gain a better understanding of the control effectiveness in the organization
gain a better understanding of the risk in the organization
adjust the controls prior to an external audit
reduce the dependency on external audits
Answer:
Explanation:
 A control self-assessment (CSA) is a technique that allows managers and work teams directly involved in business units, functions, or processes to participate in assessing the organization’s risk management and control processes. The main purpose of conducting a CSA is to gain a better understanding of the control effectiveness in the organization, which means how well the controls are designed, implemented, and operated to achieve the desired outcomes and mitigate the risks. A CSA can help to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the existing controls, as well as the gaps and opportunities for improvement. A CSA can also help to enhance the awareness, ownership, and accountability of the control environment among the managers and staff. The other options are not the main purpose of conducting a CSA, although they may be related or beneficial. Gaining a better understanding of the risk in the organization is a result of conducting a CSA, but it is not the primary goal. The primary goal is to evaluate the controls that address the risks, not the risks themselves. Adjusting the controls prior to an external audit is a possible action that may follow a CSA, but it is not the reason for conducting a CSA. The reasonfor conducting a CSA is to improve the control effectiveness, not to prepare for an audit. Reducing the dependency on external audits is a potential benefit of conducting a CSA, but it is not the objective of conducting a CSA. The objective of conducting a CSA is to enhance the internal control assurance, not to replace the external audit assurance. References = CRISC Review Manual, pages 153-1541; CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Manual, page 802
Which of the following scenarios is MOST likely to cause a risk practitioner to request a formal risk acceptance sign-off?
Residual risk in excess of the risk appetite cannot be mitigated.
Inherent risk is too high, resulting in the cancellation of an initiative.
Risk appetite has changed to align with organizational objectives.
Residual risk remains at the same level over time without further mitigation.
Answer:
Explanation:
Requesting a formal risk acceptance sign-off is the most likely scenario when the residual risk in excess of the risk appetite cannot be mitigated, because it indicates that the organization is willing to tolerate a higher level of risk than it normally would, and that the risk owner has the authority and accountability to accept the risk and its consequences. Risk acceptance is a risk response strategy that involves acknowledging the existence ofa risk and deciding not to take any action to reduce it. Risk acceptance is usually chosen when the cost or effort of mitigating therisk outweighs the potential benefits, or when no feasible mitigation options are available. Residual risk is the risk that remains after applying controls or mitigating factors. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Inherent risk, cancellation of an initiative, change of risk appetite, and constant residual risk are all possible scenarios that may affect the risk management process, but they are not the most likely to cause a risk practitioner to request a formal risk acceptance sign-off, as they do not necessarily involve a risk owner accepting a higher level of risk than the organization’s risk appetite. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.2, page 103
A company has located its computer center on a moderate earthquake fault. Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when establishing a contingency plan and an alternate processing site?
The contingency plan provides for backup media to be taken to the alternative site.
The contingency plan for high priority applications does not involve a shared cold site.
The alternative site is a hot site with equipment ready to resume processing immediately.
The alternative site does not reside on the same fault no matter how far the distance apart.
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important consideration when establishing a contingency plan and an alternate processing site for a company that has located its computer center on a moderate earthquake fault is that the alternative site does not reside on the same fault no matter how far the distance apart, as it ensures that the alternative site is not affected by the same earthquake event that may disrupt the primary site, and that the business continuity and recovery objectives can be met. The other options are not the most important considerations, as they are more related to the backup, priority, or readiness of the alternative site, respectively, rather than the location of the alternative site. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 111.
An organization is measuring the effectiveness of its change management program to reduce the number of unplanned production changes. Which of the following would be the BEST metric to determine if the program is performing as expected?
Decrease in the time to move changes to production
Ratio of emergency fixes to total changes
Ratio of system changes to total changes
Decrease in number of changes without a fallback plan
Answer:
Explanation:
 The ratio of emergency fixes to total changes is the best metric to determine if the change management program is performing as expected, because it reflects the quality and stability of the changes that are implemented in the production environment. A high ratio of emergency fixes to total changes indicates that the change management program is not effective, as it means that many changes are causing problems or failures that require urgent correction. A low ratio of emergency fixes to total changes indicates that the change management program is effective, as it means that most changes are well-planned, tested, and approved, and do not cause significant disruptions or defects. The ratio of emergency fixes to total changes can also help identify the root causes of the problems, the gaps in the change management process, and the areas for improvement. For example, if the ratio of emergency fixes to total changes is high, it may indicate that the change management program has issues with the following aspects: - Change request and approval: The change management program may not have a clear and consistent process for requesting, reviewing, and approving changes, or the process may not be followed by all stakeholders. - Change impact analysis: The change management program may not have acomprehensive and systematic method for assessing the potential impact of the changes on thebusiness processes, the IT systems, the users, and the customers. - Change testing and validation: The change management program may not have adequate testing and validation procedures to ensure that the changes meet the requirements and specifications, and do not introduce errors or vulnerabilities. - Change communication and training: The change management program may not have effective communication and training strategies to inform and educate the affected parties about the changes and their implications. - Change implementation and monitoring: The change management program may not have proper implementation and monitoring plans or tools to ensure that the changes are executed smoothly and successfully, and that any issues or incidents are detected and resolved promptly. Therefore, the ratio of emergency fixes to total changes is the best metric to determine if the change management program is performing as expected, as it can provide valuable feedback and insights for the change management program and its improvement. References = How to Measure Change Management Effectiveness: Metrics, Tools & Processes1, Metrics for Measuring Change Management2, Driving Value with Change Management Metrics3, Must-Know Organizational Change Management Metrics
Which of the following would BEST facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements?
Assigning a data owner
Scheduling periodic audits
Implementing technical controls over the assets
Implementing a data loss prevention (DLP) solution
Answer:
Explanation:
Assigning a data owner ensures accountability and responsibility for classifying and protecting data according to its sensitivity. This role is critical in implementing effectiveData Governance Practices.
The operational risk associated with attacks on a web application should be owned by the individual in charge of:
network operations.
the cybersecurity function.
application development.
the business function.
Answer:
Explanation:
The operational risk associated with attacks on a web application should be owned by the individual in charge of the business function, because they are the primary stakeholder and beneficiary of the web application, and they are responsible for defining and achieving the business objectives and requirements that the web application supports or enables. Anoperational risk is a risk of loss or damage resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, or systems, or from external events. An attack on a web application is a type of operational risk that involves a malicious or unauthorized attempt to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the web application, such as a denial-of-service attack, a SQL injection attack, or a cross-site scripting attack. A web application is an application that runs on a web server and can be accessed or used through a web browser, such as an online shopping site, a social media platform, or a web-based email service. A business function is a set of activities or tasks that support or enable the organization’s vision, mission, and strategy, such as marketing, sales, or customer service. A risk owner is a person or role that has the authority and accountability to manage a specific risk, and to implement and monitor the risk response and controls. The individual in charge of the business function should be the risk owner, as they have the best understanding and interest of the web application and its business value and impact, and they have the ability and responsibility to manage the operational risk associated with the attacks on the web application. The individual in charge of network operations, the cybersecurity function, or application development are all possible candidates for the risk owner, but they are not the best choice, as they may not have the same level of stake and influence in the web application and its business objectives and requirements, and they may have different orconflicting priorities or perspectives on the operational risk and its management. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.4.1, page 101
Which of the following BEST facilitates the development of effective IT risk scenarios?
Utilization of a cross-functional team
Participation by IT subject matter experts
Integration of contingency planning
Validation by senior management
Answer:
Explanation:
 The best way to facilitate the development of effective IT risk scenarios is to utilize a cross-functional team. A cross-functional team is a group of people with different skills, expertise, and perspectives who work together to achieve a common goal. A cross-functional team can help to create realistic, comprehensive, and relevant IT risk scenarios by bringing diverse knowledge, experience, and insights from various domains and functions. A cross-functional team can alsohelp to identify and address the interdependencies, interactions, and impacts of IT risks across the organization. The other options are not the best ways to facilitate the development of effective IT risk scenarios, although they may be useful or necessary depending on the context and nature of the IT risks. Participation by IT subject matter experts is important, but it is notsufficient, as IT risks may affect or be affected by non-IT factors and stakeholders. Integration of contingency planning is a part of the risk response process, which follows the risk scenario development process, but it is not the same as creating the risk scenarios. Validation by senior management is a quality assurance step that ensures the accuracy and completeness of the risk scenarios, but it is not the same as facilitating the development of the risk scenarios. References = Six Steps to Using Risk Scenarios for Improved Risk Management, IT Risk Scenarios - Morland-Austin, IT Risk Resources | ISACA
Which of the following should be done FIRST when developing a data protection management plan?
Perform a cost-benefit analysis.
Identify critical data.
Establish a data inventory.
Conduct a risk analysis.
Answer:
Explanation:
A data protection management plan is a document that outlines how an organization will protect its sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or loss. A data protection management plan should include the following components1:
The scope and objectives of the data protection management plan, and how it aligns with the organization’s data protection policy and strategy
The roles and responsibilities of the data protection team and other stakeholders, and how they will communicate and coordinate
The data protection risks and threats that the organization faces, and how they will be assessed and prioritized
The data protection controls and measures that the organization will implement and maintain, and how they will be monitored and evaluated
The data protection incidents and breaches that the organization may encounter, and how they will be reported and resolved
The data protection training and awareness programs that the organization will provide and conduct, and how they will be measured and improved
The first step that should be done when developing a data protection management plan is to identify critical data. This means that the organization should:
Define what constitutes sensitive data in the organization, such as personal data, confidential data, or regulated data
Identify and classify the sensitive data that the organization collects, processes, stores, or transfers, and assign appropriate labels or tags
Determine the value and importance of the sensitive data to the organization and its stakeholders, and the potential impacts or consequences of data loss or compromise
Map the data flows and locations of the sensitive data within the organization and across its partners or vendors, and document the data lifecycle stages and activities
By identifying critical data, the organization can:
Establish a clear and consistent understanding of the data protection scope and objectives, and ensure that they are relevant and realistic
Provide a comprehensive and accurate data inventory that can support the data protection risk assessment and control implementation
Identify and prioritize the data protection needs and requirements of the organization and its stakeholders, and align them with the data protection laws and standards
Communicate and report the data protection status and performance to the stakeholders and regulators, and ensure transparency and accountability
References = Guide to Developing a Data Protection Management Programme
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for logging in a production database environment?
To provide evidence of activities
To prevent illicit actions of database administrators (DBAs)
To ensure that changes are authorized
To ensure that changes made are correctly applied
Answer:
Explanation:
The primary reason for logging is to provide evidence of activities, ensuring accountability and traceability. This supports investigations, audits, and compliance requirements, aligning withControl Monitoring and Reportingstandards.
Who is MOST likely to be responsible for the coordination between the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy?
Chief financial officer
Information security director
Internal audit director
Chief information officer
Answer:
Explanation:
 The chief information officer (CIO) is the most likely person to be responsible for the coordination between the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy, because the CIO is the senior executive who oversees the information technology (IT) function and aligns it with the organization’s strategy, objectives, and operations. The CIO is also responsible for ensuring that the IT function delivers value, supports innovation, and manages IT risks effectively and efficiently. The CIO can coordinate the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy by communicating and collaborating with other business leaders, establishing and implementing IT governance frameworks and policies, and monitoring and reporting on IT performance and risk indicators. The other options are not as likely as the CIO to be responsible for the coordination between the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy, because they have different or limited roles and responsibilities in relation to IT and business risk management, as explained below:
A. Chief financial officer (CFO) is the senior executive who oversees the financial function and manages the financial risks of the organization. The CFO may be involved in the coordination between the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy, especially when it comes to budgeting, funding, or reporting on IT-related projects and initiatives, but the CFO is not the primary person who oversees the IT function and aligns it with the organization’s strategy and objectives.
B. Information security director is the senior manager who oversees the information security function and manages the information security risks of the organization. The information security director may be involved in the coordination between the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy, especially when it comes to protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the information assets and systems, but the information security director is not the primary person who oversees the IT function and aligns it with the organization’s strategy and objectives.
C. Internal audit director is the senior manager who oversees the internal audit function and provides independent assurance on the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s governance, risk management, and control processes. The internal audit director may be involved in the coordination between the IT risk strategy and the business risk strategy, especially when it comes to auditing, reviewing, or testing the IT-related processes and controls, but the internal audit director is not the primary person who oversees the IT function and aligns it with the organization’s strategy and objectives. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 1, Section 1.1.1, page 7. The Strategic CIO: Balancing Business and ITPriorities, Technology’s Role in Enterprise Risk Management, Aligning Enterprise Cyber Risk and Business Strategy
Which of the following is MOST helpful to review when assessing the risk exposure associated with ransomware?
Potentially impacted business processes
Recent changes in the environment
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Suspected phishing events
Answer:
Which of the following is the BEST recommendation of a risk practitioner for an organization that recently changed its organizational structure?
Communicate the new risk profile.
Implement a new risk assessment process.
Revalidate the corporate risk appetite.
Review and adjust key risk indicators (KRIs).
Answer:
Explanation:
Communicating the new risk profile is the best recommendation for a risk practitioner for an organization that recently changed its organizational structure, because it helps to inform and align the stakeholders on the current state of risks and their implications for the organization’s objectives and strategy. A risk profile is a summary of the key risks that an organization faces, along with their likelihood, impact, and response strategies. An organizational structure is the way that an organization arranges its people, roles, and responsibilities to achieve its goals and deliver its value proposition. A change in the organizational structure may affect the risk profile, as it may introduce new sources or types of risk, or alter the existing risk levels orresponses. Therefore, communicating the new risk profile is the best recommendation, as it helps to ensure that the stakeholders are aware of and prepared for the changes and challenges that the new organizational structure may bring. Implementing a new risk assessment process, revalidating the corporate risk appetite, and reviewing and adjusting key risk indicators (KRIs) are all important tasks to perform after communicating the new risk profile, but they are not the best recommendation, as they depend on the communication and understanding of the new risk profile. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 3, Section 3.2.3, page 91
Which of the following would be the GREATEST risk associated with a new implementation of single sign-on?
Inability to access key information
Complex security administration
User resistance to single sign-on
Single point of failure
Answer:
Explanation:
Single sign-on (SSO)simplifies authentication but introduces asingle point of failure. If the SSO mechanism is compromised or goes down, it can result in the loss of access across multiple systems, leading to widespread business disruption or security breaches.
For no apparent reason, the time required to complete daily processing for a legacy application is approaching a risk threshold. Which of the following activities should be performed FIRST?
Temporarily increase the risk threshold.
Suspend processing to investigate the problem.
Initiate a feasibility study for a new application.
Conduct a root-cause analysis.
Answer:
Explanation:
The first activity that should be performed when the time required to complete daily processing for a legacy application is approaching a risk threshold is to conduct a root-cause analysis. This will help to identify the source of the problem and the factors that are contributing to the increased processing time. By conducting a root-cause analysis, the enterprise can determine the most appropriate and effective solution to address the problem and prevent it from recurring. Temporarily increasing the risk threshold, suspending processing to investigate the problem, and initiating a feasibility study for a new application are not the first activities that should be performed, as they may not resolve the underlying issue and may introduce additional risks or costs. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 4, Section 4.2.1.2, page 193.
Which of the following deficiencies identified during a review of an organization's cybersecurity policy should be of MOST concern?
The policy lacks specifics on how to secure the organization's systems from cyberattacks.
The policy has gaps against relevant cybersecurity standards and frameworks.
The policy has not been reviewed by the cybersecurity team in over a year.
The policy has not been approved by the organization's board.
Answer:
Explanation:
The policy has not been approved by the organization’s board should be of most concern, as it indicates a lack of governance and oversight for the organization’s cybersecurity posture. The board is ultimately responsible for setting the strategic direction, objectives, and risk appetite of the organization, and for ensuring that the cybersecurity policy aligns with them. Without the board’s approval, the policy may not reflect the organization’s vision, mission, values, and culture, and may not be communicated, implemented, or enforced effectively. The board’s approval also demonstrates the commitment and support of the senior management for the cybersecurity program, and enhances the accountability and responsibility of the stakeholders involved.
An organization automatically approves exceptions to security policies on a recurring basis. This practice is MOST likely the result of:
a lack of mitigating actions for identified risk
decreased threat levels
ineffective service delivery
ineffective IT governance
Answer:
Explanation:
IT governance is the process of ensuring that IT supports the organization’s objectives and strategies, and that IT risks are managed appropriately. IT governance involves defining the roles, responsibilities, and accountabilities of the IT stakeholders, establishing the IT policies, standards, and procedures, and monitoring and evaluating the IT performance and outcomes1.
An organization that automatically approves exceptions to security policies on a recurring basis is most likely the result of ineffective IT governance, because it indicates that the organization:
Lacks a clear and consistent IT strategy and direction, and does not align IT with the business goals and needs
Fails to implement and enforce the IT policies, standards, and procedures, and does not ensure the compliance and accountability of the IT users and providers
Neglects to identify and assess the IT risks, and does not implement the appropriate risk responses and controls
Does not monitor and measure the IT performance and outcomes, and does not review and improve the IT processes and practices23
The other options are not the most likely results of ineffective IT governance, but rather some of the possible causes or consequences of it. A lack of mitigating actions for identified risk is a possible consequence of ineffective IT governance, as it implies that the organization does not have a systematic and proactiveapproach to IT risk management, and does not address the IT risks in a timely and effective manner. Decreased threat levels is a possible cause of ineffective IT governance, as it may create a false sense of security and complacency, and reduce the motivation and urgency to implement and follow the IT policies, standards, and procedures. Ineffective service delivery is a possible consequence of ineffective IT governance, as it means that the organization does not deliver the IT services that meet the expectations and requirements of the customers and stakeholders, and does not ensure the quality and reliability of the IT services. References =
IT Governance - ISACA
IT Governance: What It Is and Why You Need It
IT Governance: The Benefits of an Effective Enterprise IT Governance Framework
[CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition]
An organization maintains independent departmental risk registers that are not automatically aggregated. Which of the following is the GREATEST concern?
Management may be unable to accurately evaluate the risk profile.
Resources may be inefficiently allocated.
The same risk factor may be identified in multiple areas.
Multiple risk treatment efforts may be initiated to treat a given risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
The greatest concern of maintaining independent departmental risk registers that are not automatically aggregated is that management may be unable to accurately evaluate the risk profile. The risk profile is the overall view of the risks that the organization faces and their impact on the organization’s objectives. It helps management to prioritize and allocate resources for risk management and to align the risk appetite and strategy. If the departmental risk registers are not aggregated, management may not have a complete and consistent picture of the risks across the organization. They may miss some important risks, overestimate or underestimate some risks, or have conflicting or redundant risk information. This may lead to poor risk management decisions and outcomes. The other options are also concerns, but they are not ascritical as the inability to evaluate the risk profile. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.2: IT Risk Analysis, page 63.
What is a risk practitioner's BEST approach to monitor and measure how quickly an exposure to a specific risk can affect the organization?
Create an asset valuation report.
Create key performance indicators (KPls).
Create key risk indicators (KRIs).
Create a risk volatility report.
Answer:
Explanation:
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are metrics that measure the exposure to a given risk at a particular time. They can also provide early warning signs of a potential change in risk level. By monitoring KRIs, risk practitioners can assess how quickly an exposure to a specific risk can affect the organization and take appropriate actions.
References
•Risk management at the speed of business - PwC
•Risk velocity measures how fast an exposure can affect an organization | Business Insurance
A control for mitigating risk in a key business area cannot be implemented immediately. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action when a compensating control needs to be applied?
Obtain the risk owner's approval.
Record the risk as accepted in the risk register.
Inform senior management.
update the risk response plan.
Answer:
Explanation:
 A compensating control is a temporary or alternative control that is implemented when the primary control for mitigating a risk is not feasible or available. A compensating control should provide a similar level of protection and assurance as the primary control, and should be aligned with the risk appetite and tolerance of the organization. The risk practitioner’s best course of action when a compensating control needs to be applied is to obtain the risk owner’s approval. The risk owner is the person who has the authority and accountability for managing a specific risk, and who is responsible for ensuring that the risk is within the acceptable level. The risk practitioner should consult with the risk owner to explain the situation, proposethe compensating control, and seek their approval before implementing it. This way, the risk practitioner can ensure that the compensating control is appropriate, effective, and acceptable for the risk owner, and that the risk owner is aware of and agrees with the change in the risk treatment. The other options are not the best course of action, as they do not involve the risk owner’s approval or input. Recording the risk as accepted in the risk register implies that the risk is not treated or reduced, which may not be the case with a compensating control. Informing senior management may be a good practice, but it does not ensure that the risk owner is involved or agrees with the compensating control. Updating the risk response plan may be a necessary step after implementing the compensating control, but it does not require the risk owner’s approval or consultation. References = 5 Key Risk Mitigation Strategies (With Examples), Risk Management 101: Process, Examples, Strategies
An organization is outsourcing a key database to be hosted by an external service provider. Who is BEST suited to assess the impact of potential data loss?
Public relations manager
Data privacy manager
Business manager
Database manager
Answer:
Explanation:
The business manager understands how data loss affects operations, revenue, and compliance — making them best positioned to assess impact.
ISACA guidance:
“Business process owners or business managers are responsible for identifying and assessing business impacts resulting from data loss or system unavailability.â€
Technical roles may estimate likelihood or technical details, but impact assessment is a business responsibility.
Hence, C is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 2 – IT Risk Assessment, Topic: Business Impact Assessment.
Which of the following has the GREATEST influence on an organization's risk appetite?
Threats and vulnerabilities
Internal and external risk factors
Business objectives and strategies
Management culture and behavior
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives. Risk appetite is influenced by various factors, such as the organization’s mission, vision, values, culture, stakeholders, resources, capabilities, etc. However, the factor that has the greatest influence on the organization’s risk appetite is the business objectives and strategies, which are the desired outcomes and the plans to achieve them. The business objectives and strategies define the direction and scope of the organization, and the risk appetite reflects the level of risk that the organization is prepared to take to accomplish them. The risk appetite should be aligned with the business objectives and strategies, andshould provide guidance for the risk management activities and decisions. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 61.
When collecting information to identify IT-related risk, a risk practitioner should FIRST focus on IT:
risk appetite.
security policies
process maps.
risk tolerance level
Answer:
Explanation:
When collecting information to identify IT-related risk, a risk practitioner should first focus on IT risk appetite, which is the amount of risk that the organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its IT objectives, before action is deemed necessary to reduce the risk1. IT risk appetite reflects the organization’s IT risk attitude and its willingness to accept risk in specific scenarios, with a governance model in place for IT risk oversight. IT risk appetite helps to guide the organization’s approach to IT risk and IT risk management, and to align its IT risk decisions with its business objectives and context. The other options are not the best answers, as they are either derived from or dependent on the IT risk appetite. IT security policies are the rules and guidelines that define the organization’s IT security objectives, requirements, and responsibilities, and they are based on the IT risk appetite. IT process maps are the graphical representations of the IT processes, activities, and tasks that support the organization’s IT objectives, and they are influenced by the IT risk appetite. IT risk tolerance level is the acceptable variation between the IT risk thresholds and the IT objectives, and it is determined by the IT risk appetite. References = IT Risk Resources | ISACA; RiskAppetite vs. Risk Tolerance: What is the Difference?; IT Risk Management - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics; IT Risk Management Framework - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
A risk practitioner has been notified of a social engineering attack using artificial intelligence (Al) technology to impersonate senior management personnel. Which of the following would BEST mitigate the impact of such attacks?
Training and awareness of employees for increased vigilance
Increased monitoring of executive accounts
Subscription to data breach monitoring sites
Suspension and takedown of malicious domains or accounts
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚· Understanding the Question:
The question is about mitigating the impact of social engineering attacks that use AI technology to impersonate senior management personnel.
ï‚· Analyzing the Options:
A. Training and awareness of employees for increased vigilance:This is the most proactive approach. Educating employees about the risks and signs of social engineering attacks enhances their ability to recognize and respond appropriately to such threats.
B. Increased monitoring of executive accounts:Useful but reactive; it doesn't prevent initial attempts.
C. Subscription to data breach monitoring sites:Helps detect breaches but doesn’t directly mitigate impersonation attacks.
D. Suspension and takedown of malicious domains or accounts:Reactive measure and might not be immediate or comprehensive.
ï‚·
Importance of Training:Employees are often the first line of defense against social engineering attacks. Regular training ensures they are aware of the tactics used in such attacks, including those leveraging AI, and how to respond effectively.
Proactive Measure:Training increases vigilance and the likelihood of early detection, reducing the potential impact of the attack.
Changes in which of the following are MOST likely to trigger the need to reassess inherent risk?
Risk tolerance
Regulatory requirements
Key risk indicators (KRIs)
Industry benchmarks
Answer:
Explanation:
Inherent risk reflects exposure before controls. When regulatory requirements change, they can alter compliance obligations, legal exposure, and the baseline inherent risk of processes.
ISACA’s CRISC framework specifies:
“Significant changes to regulatory or legal environments are triggers for reassessing inherent and residual risk.â€
A (risk tolerance) affects acceptance, not inherent risk itself.
C (KRIs) and D (benchmarks) measure and compare risk but do not trigger reassessment directly.
Hence, B is correct.
CRISC Reference: Domain 2 – IT Risk Assessment, Topic: Risk Triggers and Environmental Changes.
Which of the following is the BEST method for assessing control effectiveness against technical vulnerabilities that could be exploited to compromise an information system?
Vulnerability scanning
Systems log correlation analysis
Penetration testing
Monitoring of intrusion detection system (IDS) alerts
Answer:
Explanation:
Penetration testing is the best method for assessing control effectiveness against technical vulnerabilities that could be exploited to compromise an information system, as it simulates areal-world attack scenario and evaluates the security posture of the system. Penetration testing is a type of security testing that involves performing authorized and ethical hacking activities on a system to identify and exploit its vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Penetration testing can help to measure and improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the controls implemented to protect the system from unauthorized access, modification, or damage.
The other options are not the best methods for assessing control effectiveness against technical vulnerabilities that could be exploited to compromise an information system. Vulnerability scanning is an automated process that uncovers potential vulnerabilities in systems and software, but it does not provide information on the impact and severity of the vulnerability or how they can be exploited using different exploitation techniques1. Systems log correlation analysis is a process of examining and analyzing the records of system activities and events, but it does not directly test the controls or simulate the attack scenarios. Monitoring of intrusion detection system (IDS) alerts is a process of tracking and auditing the system or network for any signs of malicious or anomalous activities, but it does not evaluate the control performance or identify the root causes of the vulnerabilities. References = Vulnerability Assessment Principles | Tenable®, A Complete Guide on Vulnerability Assessment Methodology, Karen Scarfone Scarfone Cybersecurity - NIST Computer Security Resource …
A department allows multiple users to perform maintenance on a system using a single set of credentials. A risk practitioner determined this practice to be high-risk. Which of the following is the MOST effective way to mitigate this risk?
Single sign-on
Audit trail review
Multi-factor authentication
Data encryption at rest
Answer:
Explanation:
Multi-factor authentication is the most effective way to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to the system, as it requires the users to provide more than one piece of evidence to prove their identity, such as a password, a token, a biometric feature, etc. This reduces the likelihood of compromising the credentials and ensures that only authorized users can perform maintenance on the system.
Single sign-on is a convenience feature that allows users to access multiple systems with one set of credentials, but it does not address the risk of sharing credentials among multiple users.
Audit trail review is a detective control that can help identify and investigate unauthorized access to the system, but it does not prevent or mitigate the risk of credential compromise.
Data encryption at rest is a security measure that protects the data stored on the system from unauthorized access, but it does not prevent or mitigate the risk of credential compromise. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, ISACA, 2020, page 107-108.
An organization has adopted an emerging technology without following proper processes. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action to address this risk?
Accept the risk because the technology has already been adopted.
Propose a transfer of risk to a third party with subsequent monitoring.
Conduct a risk assessment to determine risk exposure.
Recommend to senior management to decommission the technology.
Answer:
Explanation:
Conducting a risk assessment allows the organization to evaluate the exposure created by adopting the technology. This step ensures informed decision-making and aligns with the principles ofRisk Identification and Assessmentfor managing emerging risks effectively.
Who should be responsible (of evaluating the residual risk after a compensating control has been
Compliance manager
Risk owner
Control owner
Risk practitioner
Answer:
Explanation:
 The control owner should be responsible for evaluating the residual risk after a compensating control has been implemented. A compensating control is a control that provides an alternative or additional measure of protection when the primary or preferred control is not feasible or effective. A residual risk is the risk that remains after the risk response or mitigation has beenapplied. The control owner is the person who has the authority and responsibility for designing, implementing, and monitoring the controls that enforce the policy. The control owner can assess the impact and effectiveness of the compensating control on the residual risk, and report the results and recommendations to the risk owner or the risk practitioner. The other options are not as responsible as the control owner, as they are related to the compliance, ownership, or management of the risk, not the evaluation of the control. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4: Risk and Control Monitoring and Reporting, Section 4.4: Key Control Indicators, page 211.
Risk appetite should be PRIMARILY driven by which of the following?
Enterprise security architecture roadmap
Stakeholder requirements
Legal and regulatory requirements
Business impact analysis (BIA)
Answer:
Explanation:
Risk appetite should be primarily driven by stakeholder requirements. Stakeholder requirements are the needs and expectations of the internal and external parties that have an interest or influence in the organization’s objectives or operations, such as the board, management, employees, customers, regulators, investors, etc. Risk appetite is the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing to accept or pursue in order to achieve its objectives. Risk appetite should be driven by stakeholder requirements, because they reflect the organization’s mission, vision, values, and strategy, and they provide the basis and direction for the organization’s risk management activities. Risk appetite should also be aligned and communicated with stakeholder requirements, because they affect the organization’s performance and reputation, and they require the organization’s accountability and transparency. The other options are not the primary drivers of risk appetite, although they may be considered or influenced by risk appetite. Enterprise security architecture roadmap, legal and regulatory requirements, and businessimpactanalysis (BIA) are all factors that could affect the organization’s risk profile, risk assessment, or risk response, but they do not necessarily determine or reflect the organization’s risk appetite. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 2, Section 2.3.1, page 2-23.
A risk practitioner is reviewing the status of an action plan to mitigate an emerging IT risk and finds the risk level has increased. The BEST course of action would be to:
implement the planned controls and accept the remaining risk.
suspend the current action plan in order to reassess the risk.
revise the action plan to include additional mitigating controls.
evaluate whether selected controls are still appropriate.
Answer:
Explanation:
The best course of action when a risk practitioner finds that the risk level of an emerging IT risk has increased, despite having an action plan to mitigate it, is to evaluate whether the selected controls are still appropriate. This is because the increase in the risk level may indicate that the current controls are not effective or sufficient to reduce the impact or likelihood of the risk, or that the risk environment has changed and new threats or vulnerabilities have emerged. By evaluating the appropriateness of the selected controls, the risk practitioner can identify the gaps or weaknesses in the control design or implementation, and determine the need for corrective actions or improvements. The other options are not the best course of action, because they do not address the root cause of the problem, but rather assume or ignore the effectiveness of the controls, as explained below:
A. Implement the planned controls and accept the remaining risk is not the best course of action, because it assumes that the planned controls are adequate and aligned with the organization’s risk appetite, which may not be the case if the risk level has increased. Implementing the planned controls without evaluating their appropriateness may result in wasting resources, exposing the organization to more risk, or missing opportunities to enhance the risk mitigation effectiveness.
B. Suspend the current action plan in order to reassess the risk is not the best course of action, because it ignores the effectiveness of the current controls, which may still provide some level ofrisk mitigation, even if they are not optimal. Suspending the current action plan may also delay the risk response and increase the risk exposure, especially if the risk is time-sensitive or dynamic. Reassessing the risk without evaluating the appropriateness of the current controls may also lead to inaccurate or incomplete risk information and analysis.
C. Revise the action plan to include additional mitigating controls is not the best course of action, because it assumes that the current controls are ineffective or insufficient, which may not be the case if the risk level has increased due to other factors, such as changes in the risk environment or the organization’s objectives. Revising the action plan without evaluating the appropriateness of the current controls may result in overcompensating, duplicating, or conflicting the controls, which may affect the risk mitigation efficiency and performance. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, Chapter 4, Section 4.3.3, page 130. How to Mitigate Emerging Technology Risk - ISACA, Risk Mitigation Strategies: Types & Examples (+ Free Template), 5 Key Risk Mitigation Strategies (With Examples) | Indeed.com
Which of the following is the BEST indication of the effectiveness of a business continuity program?
Business continuity tests are performed successfully and issues are addressed.
Business impact analyses are reviewed and updated in a timely manner.
Business continuity and disaster recovery plans are regularly updated.
Business units are familiar with the business continuity plans and process.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the Section 4: Quiz 40 - Business Continuity Plan Flashcards, the best indication of the effectiveness of a business continuity program is the successful performance of business continuity tests and the resolution of any issues that arise. Business continuity tests are exercises that simulate various scenarios of disruption or disaster and evaluate the organization’s ability to recover and resume its critical functions. Business continuity tests can help to validate the assumptions, objectives, and strategies of the business continuity program, as well as to identify and address any gaps, weaknesses, or errors in the business continuity and disaster recovery plans. By performing business continuity tests regularly and effectively, the organization can ensure that its business continuity program is aligned with its needs andexpectations, and that it can cope with any potential crisis. References = Section 4: Quiz 40 - Business Continuity Plan Flashcards
Which of the following situations presents the GREATEST challenge to creating a comprehensive IT risk profile of an organization?
Manual vulnerability scanning processes
Organizational reliance on third-party service providers
Inaccurate documentation of enterprise architecture (EA)
Risk-averse organizational risk appetite
Answer:
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of analyzing logs collected from different systems?
A record of incidents is maintained.
Forensic investigations are facilitated.
Security violations can be identified.
Developing threats are detected earlier.
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual, the greatest benefit of analyzing logs collected from different systems is to detect developing threats earlier, because it helps to identify and correlate the patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate a potential attack or compromise. Log analysis is the process of examining and interpreting the log data generated by various systems, such as firewalls, servers, routers, and applications. Log analysis can provide valuable insights into the activities and events that occur on the systems, and can enable the timely detection and response to the emerging threats. The other options are not the greatest benefits of analyzing logs, as they are less proactive or less strategic than detecting developing threats earlier. Maintaining a record of incidents is a benefit of logging, but not of analyzing logs, as it involves storing and preserving the log data for future reference. Facilitating forensic investigations is a benefit of analyzing logs, but it is a reactive and tactical activity that occurs after an incident has happened. Identifying security violations is a benefit of analyzing logs, but it is a specific and operational activity that focuses on the compliance and enforcement of the security policies and standards. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 5, Section 5.3.2, page 263.
The PRIMARY benefit of maintaining an up-to-date risk register is that it helps to:
implement uniform controls for common risk scenarios.
ensure business unit risk is uniformly distributed.
build a risk profile for management review.
quantify the organization's risk appetite.
Answer:
Explanation:
A risk register is a document that records and tracks the information and status of the identified risks and their responses. It includes the risk description, category, source, cause, impact, probability, priority, response, owner, action plan, status, etc.
A risk profile is a summary or representation of the organization’s exposure or level of risk, based on the results of the risk assessment and evaluation. A risk profile can show the distribution and comparison of the risks based on various criteria, such as likelihood, impact, category, source, etc. A risk profile can also indicate the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance, and the gaps or opportunities for improvement.
The primary benefit of maintaining an up-to-date risk register is that it helps to build a risk profile for management review, because it provides the data and information that are necessary and relevant for creating and updating the risk profile, and for communicating and reporting the risk profile to the management. Maintaining an up-to-date risk register can help to build a risk profile for management review by providing the following benefits:
It can ensure that the risk profile reflects the current and accurate state and performance of the organization’s risk management function, and that it covers all the relevant and significant risks that may affect the organization’s objectives and operations.
It can provide useful references and benchmarks for the identification, analysis, evaluation, and communication of the risks and their responses, and for the alignment and integration of the risks and their responses with the organization’s strategy and culture.
It can support the decision making and planning for the risk management function, and for the allocation and optimization of the resources, time, and budget for the risk management function.
The other options are not the primary benefits of maintaining an up-to-date risk register, because they do not address the main purpose and benefit of building a risk profile for management review, which is to summarize and represent the organization’s exposure or level of risk, and to communicate and report it to the management.
Implementing uniform controls for common risk scenarios means applying and enforcing the same or similar controls or countermeasures for the risks that have the same or similar characteristics or features, such as source, cause, impact, etc. Implementing uniform controls for common risk scenarios can help to ensure the consistency and efficiency of the risk management function, but it is not the primary benefit of maintaining an up-to-date risk register, because itdoes not summarize or represent the organization’s exposure or level of risk, and it may not be relevant or appropriate for the organization’s objectives and needs.
Ensuring business unit risk is uniformly distributed means ensuring that the risks that are associated with the different business units or divisions of the organization are balanced or equalized, and that they do not exceed or fall below the organization’s risk appetite and tolerance. Ensuring business unit risk is uniformly distributed can help to optimize the performance and profitability of the organization, but it is not the primary benefit of maintaining an up-to-date risk register, because it does not summarize or represent the organization’s exposure or level of risk, and it may not be feasible or realistic for the organization.
Quantifying the organization’s risk appetite means measuring and expressing the amount and type of risk that the organization is willing and able to accept or take, in pursuit of its objectives and goals. Quantifying the organization’s risk appetite can help to establish and communicate the boundaries and expectations for the organization’s risk management function, but it is not the primary benefit of maintaining an up-to-date risk register, because it does not summarize or represent the organization’s exposure or level of risk, and it may not be consistent or compatible with the organization’s strategy and culture. References =
ISACA, CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, 2022, pp. 19-20, 23-24, 27-28, 31-32, 40-41, 47-48, 54-55, 58-59, 62-63
ISACA, CRISC Review Questions, Answers & Explanations Database, 2022, QID 201
CRISC Practice Quiz and Exam Prep
What is senior management's role in the RACI model when tasked with reviewing monthly status reports provided by risk owners?
Accountable
Informed
Responsible
Consulted
Answer:
Explanation:
Senior management’s role in the RACI model when tasked with reviewing monthly status reports provided by risk owners is accountable, as it means that they have the ultimate authority and responsibility to approve or reject the risk management decisions and actions, and to oversee the risk management performance and outcomes. The other options are not the correct roles, as they imply different levels or types of involvement or participation in the risk management process, such as being informed, responsible, or consulted, respectively. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 101.
Which of the following roles should be assigned accountability for monitoring risk levels?
Risk practitioner
Business manager
Risk owner
Control owner
Answer:
Explanation:
 The risk owner should be assigned accountability for monitoring risk levels, as they have the authority and responsibility to manage the risk and its associated controls, and to report on the risk status and performance. The risk practitioner, the business manager, and the control owner are not the best choices, as they have different roles and responsibilities related to risk identification, assessment, response, and reporting, but they are not accountable for the risk and its monitoring. References = CRISC Review Manual, 7th Edition, page 101.
Which of the following situations would cause the GREATEST concern around the integrity of application logs?
Weak privileged access management controls
Lack of a security information and event management (SIEM) system
Lack of data classification policies
Use of hashing algorithms
Answer:
Which of the following is the MOST effective key performance indicator (KPI) for change management?
Percentage of changes with a fallback plan
Number of changes implemented
Percentage of successful changes
Average time required to implement a change
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), the percentage of successful changes is the most effective key performance indicator (KPI) for change management, as it measures thequality and effectiveness of the change management process and its alignment with the organization’s objectives and requirements. The percentage of successful changes helps to:
Evaluate the extent to which the changes have met the expected outcomes and benefits
Identify and analyze the root causes of any failed or problematic changes and implement corrective actions or improvement measures
Monitor and report the performance and progress of the change management process and its impact on the organization
Enhance the confidence and satisfaction of the stakeholders and customers with the change management process and its results
References = CRISC Review Manual (Digital Version), Chapter 2: IT Risk Assessment, Section 2.4: IT Risk Scenarios, pp. 107-1081
The MOST important consideration when selecting a control to mitigate an identified risk is whether:
the cost of control exceeds the mitigation value
there are sufficient internal resources to implement the control
the mitigation measures create compounding effects
the control eliminates the risk
Answer:
Explanation:
The most important consideration when selecting a control to mitigate an identified risk is whether the cost of control exceeds the mitigation value, because this determines the cost-benefit ratio of the control. A control should not be implemented if the cost of implementing and maintaining it is higher than the expected benefit of reducing the risk exposure. The other options are not the most important considerations, although they may also influence the control selection process. The availability of internal resources, the potential compounding effects, and the possibility of eliminating the risk are secondary factors that depend on the cost and value of the control. References = CRISC: Certified in Risk & Information Systems Control Sample Questions
Which of the following is the MOST significant risk related to an organization's use of AI technology?
The AI system's contract does not include a right-to-audit clause
The AI system is being used beyond its intended purpose
The AI system is on unsupported infrastructure
The AI system results have not been validated
Answer:
Explanation:
Unvalidated AI outputs pose considerable integrity and operational risks, potentially leading to erroneous decisions or compliance lapses. ISACA CRISC guidance underscores that ensuring results validity is a highest-priority control for new technologies such as AI.
An organization has outsourced its customer management database to an external service provider. Of the following, who should be accountable for ensuring customer data privacy?
The organization's business process owner
The organization's information security manager
The organization's vendor management officer
The vendor's risk manager
Answer:
Which of the following is the MOST critical consideration when awarding a project to a third-party service provider whose servers are located offshore?
Difficulty of monitoring compliance due to geographical distance
Cost implications due to installation of network intrusion detection systems (IDSs)
Delays in incident communication
Potential impact on data governance
Answer:
Which of the following would be the BEST senior management action to influence a strong risk-aware culture within an organization?
Initiating disciplinary actions against individuals causing incidents
Identifying the root cause of incidents
Sponsoring changes to prevent recurrence of incidents
Reviewing the risk register and preparing incident reports
Answer:
A risk practitioner observes that hardware failure incidents have been increasing over the last few months. However, due to built-in redundancy and fault-tolerant architecture, there have been no interruptions to business operations. The risk practitioner should conclude that:
a root cause analysis is required
controls are effective for ensuring continuity
hardware needs to be upgraded
no action is required as there was no impact
Answer:
Explanation:
According to the Risk and Information Systems Control documents, the risk practitioner should conclude that no action is required as there was no impact. The fact that there have been no interruptions to business operations despite the increasing hardware failure incidents indicates that the built-in redundancy and fault-tolerant architecture are effective in ensuring continuity.
Options A and C are not necessary in this scenario. A root cause analysis (Option A) might be considered if there were actual interruptions or impact on business operations. However, since there were no interruptions, a root cause analysis may not be immediately required. Similarly, upgrading hardware (Option C) may not be necessary if the existing controls are effectively preventing business disruptions.
References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual
The risk associated with an asset before controls are applied can be expressed as:
a function of the likelihood and impact
the magnitude of an impact
a function of the cost and effectiveness of control.
the likelihood of a given threat
Answer:
Explanation:
The risk associated with an asset before controls are applied is also known as the inherent risk. It is the level of risk that exists in the absence of any mitigating actions or measures. To express the inherent risk, one needs to consider two factors: the likelihood and the impact of a potential threat. The likelihood is the probability or frequency of a threat occurring, while the impact is the magnitude or severity of the consequences if the threat materializes. The inherent risk can be calculated by multiplying the likelihood and the impact, or by using a risk matrix that assigns a risk rating based on the combination of these two factors. The other options are not correct ways of expressing the inherent risk, as they do not account for both the likelihood and the impact of a threat. The magnitude of an impact is only one component of the risk, and it does not reflect how likely the threat is to happen. The function of the cost and effectiveness of control is related to the residual risk, which is the risk that remains after controls are applied. The likelihood of a given threat is also only one component of the risk, and it does not indicate how severe the impact would be if the threat occurs. References = Risk and Information Systems Control Study Manual, 7th Edition, Chapter 2, Section 2.1.1, Page 47.

