Based on the data below, what can be concluded about outsourcing print job?
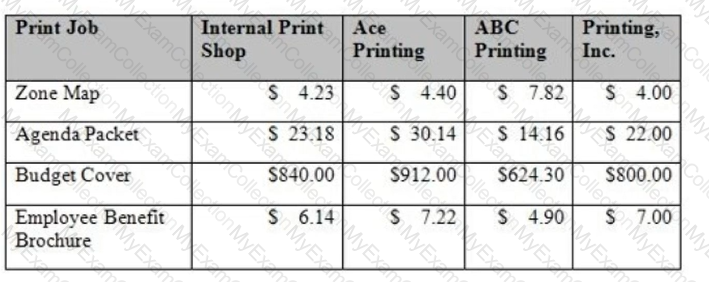
It is better to keep the printing in-house.
Outsourcing printing is feasible.
Outsourcing printing is necessary.
ABC Printing should be awarded the outsourcing contract.
Answer:
Explanation:
Understanding the Scenario:The table compares the costs of four printing jobs performed by an "Internal Print Shop" versus three external vendors (Ace Printing, ABC Printing, and Printing, Inc.). Eachvendor's pricing varies by print job type. The task is to evaluate whether outsourcing (hiring external vendors) is a reasonable alternative to keeping the work in-house.
Key Considerations in Outsourcing:According to governmental accounting principles and budgeting practices outlined by theAssociation of Government Accountants (AGA), the decision to outsource should consider:
Cost-effectiveness: Does outsourcing reduce costs without compromising quality or service delivery?
Operational efficiency: Can outsourcing free up internal resources for other priorities?
Comparative pricing: How do external vendor rates compare to internal costs for identical services?
Analysis of the Print Jobs:Let’s break down the cost comparison for each print job:
Zone Map:Internal cost = $4.23.Cheapest vendor = Printing, Inc., at $4.00.Outsourcing is cheaper for this job.
Agenda Packet:Internal cost = $23.18.Cheapest vendor = Printing, Inc., at $22.00.Outsourcing is cheaper for this job.
Budget Cover:Internal cost = $840.00.Cheapest vendor = ABC Printing, at $624.30.Outsourcing is significantly cheaper for this job.
Employee Benefit Brochure:Internal cost = $6.14.Cheapest vendor = ABC Printing, at $4.90.Outsourcing is cheaper for this job.
Conclusion Based on Analysis:
Across all four print jobs, the lowest-cost external vendor always beats the Internal Print Shop's costs.
From abudgetary perspective, outsourcing is feasible as it offers cost savings across all jobs.
Why Not A, C, or D?:
Option A(Keep printing in-house): Incorrect, as in-house costs are consistently higher than the cheapest external vendor.
Option C(Outsourcing is necessary): Incorrect, as feasibility doesn’t mean necessity; internal printing is still an option if other factors (like quality or control) outweigh costs.
Option D(Award contract to ABC Printing): Incorrect, since the best vendor depends on the job (e.g., Printing, Inc. is cheaper for Zone Map and Agenda Packet).
References:
Association of Government Accountants (AGA),Government Financial Manager Certification Study Guide: Budgeting, Cost Accounting, and Auditing Principles.
Government Finance Officers Association (GFOA),Best Practices in Outsourcing and Procurement.
Federal Accounting Standards Advisory Board (FASAB),Cost Accounting Standards for Governmental Operations.
In an attestation engagement, which party would make an assertion about a subject matter?
management
auditor
practitioner
user
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Is an Attestation Engagement?An attestation engagement is a type of professional service where an independent practitioner (typically an auditor or CPA) evaluates and provides a report on assertions made by another party about a specific subject matter. These engagements follow standards set by organizations like the AICPA or GAO.
ï‚·Who Makes the Assertion?
Management's Role:Management is the party responsible for making an assertion about the subject matter under review. For example, management might assert that internal controls are effective or that financial statements are fairly presented.
Auditor/Practitioner’s Role:The auditor or practitioner examines the evidence related to the assertion and provides an opinion or conclusion based on that examination.
User’s Role:The users are the stakeholders (e.g., investors, regulators) who rely on the practitioner’s report, but they do not make assertions.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Auditor/Practitioner:The auditor or practitioner evaluates the assertion made by management, not the other way around.
C. Practitioner:See above—practitioners don’t make assertions.
D. User:Users are the intended audience of the attestation report, not the party making assertions.
ï‚·References and Documents:
AICPA Attestation Standards (SSAEs):Clarifies the role of management in making assertions during attestation engagements.
GAO’s Government Auditing Standards (Yellow Book):Provides additional guidance on the roles of parties in attestation engagements.
The four general government auditing standards are
compliance, timeliness, qualifications and due professional care.
supervision, planning, management controls and evidence.
planning, internal controls, independence and irregularities.
qualifications, independence, due professional care and quality control.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Are the Four General Government Auditing Standards?
These standards, as defined in theGAO Yellow Book (Government Auditing Standards):
Qualifications:Auditors must have the necessary professional skills and competence to perform their work.
Independence:Auditors must remain free from personal, external, and organizational impairments to maintain objectivity.
Due Professional Care:Auditors must exercise care and diligence, adhering to professional standards and ethical requirements.
Quality Control:Auditors must establish and maintain a system of quality control to ensure audit work meets professional standards.
ï‚·Why Is Option D Correct?
These four elements are explicitly outlined in the GAO Yellow Book as the core principles of government auditing standards.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Compliance, timeliness, qualifications, and due professional care:Timeliness and compliance are not part of the four general standards; they are components of audit objectives.
B. Supervision, planning, management controls, and evidence:These are aspects of audit performance, not general standards.
C. Planning, internal controls, independence, and irregularities:Planning and internal controls are part of the audit process, not general standards.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Yellow Book (Generally Accepted Government Auditing Standards - GAGAS):Lists qualifications, independence, due professional care, and quality control as the four general standards.
AICPA Audit Standards:Aligns with GAGAS in emphasizing these four principles.
Under the control environment component of internal control, management should
demonstrate a commitment to integrity and ethical values.
implement control activities through policies.
communicate quality information to achieve the entity's objectives.
establish and operate activities to monitor the internal control system.
Answer:
Explanation:
Control Environment Component:
The control environment is the foundation of an internal control system, setting the tone at the top.
Demonstrating integrity and ethical values is the first principle of the control environment, as outlined in theCOSO Internal Control Framework.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Demonstrate a commitment to integrity and ethical values: Correct. This is a foundational principle of the control environment.
B. Implement control activities through policies: This relates to the "Control Activities" component, not the control environment.
C. Communicate quality information to achieve the entity's objectives: This relates to the "Information and Communication" component.
D. Establish and operate activities to monitor the internal control system: This relates to the "Monitoring Activities" component.
References:
COSO,Internal Control - Integrated Framework.
GAO,Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government (Green Book).
Cloud computing includes which of the following services?
satellite-to-satellite
hosted
gateway transmission
mainframe computing
Answer:
Explanation:
Definition of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services (e.g., servers, storage, databases, networking, software) over the internet.
A common feature of cloud computing is the "hosted" service model, where applications, storage, or infrastructure are hosted and managed by a cloud service provider.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Satellite-to-satellite: This involves communication between satellites, unrelated to cloud computing.
B. Hosted: Correct. Hosted services are a fundamental aspect of cloud computing, where applications or data are stored and accessed on remote servers.
C. Gateway transmission: Refers to communication gateways, unrelated to cloud computing services.
D. Mainframe computing: Mainframes are large on-premises computers, not part of the cloud model.
References:
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST),Cloud Computing Reference Architecture.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP),Cloud Service Providers Guidance.
A program manager at a local agency needs to understand if program participation varies significantly from enrollment. The information changes daily. The best way to quickly analyze this would be to use
crosstab.
portable document format.
text file.
dashboard.
Answer:
Explanation:
Analyzing Participation and Enrollment Trends:
Dashboards are tools that provide real-time visualizations of data, making them ideal for quickly analyzing trends such as program participation versus enrollment.
They allow program managers to view up-to-date metrics and identify variances without manual data processing.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Crosstab: While useful for comparing categorical data, crosstabs are static and less effective for real-time analysis.
B. Portable document format (PDF): A PDF is a static file format, unsuitable for dynamic data analysis.
C. Text file: Text files provide raw data but require additional processing, making them inefficient for quick analysis.
D. Dashboard: Correct. Dashboards provide dynamic, real-time analytics, perfect for monitoring daily changes in participation and enrollment.
References:
Association of Government Accountants (AGA),Data Visualization in Public Sector Management.
Government Performance Lab,Using Dashboards for Real-Time Program Management.
The basic steps in fraud audits include all of the following EXCEPT
consulting legal counsel.
reporting the results.
follow-up on control weaknesses.
considering political ramifications.
Answer:
Explanation:
Fraud Audit Objective:Fraud audits aim to detect and investigate fraudulent activities, strengthen internal controls, and report findings to stakeholders.
Basic Steps in Fraud Audits:
Consulting Legal Counsel: Ensures compliance with legal requirements and protects the organization.
Reporting the Results: Essential to inform stakeholders of findings and corrective actions.
Follow-up on Control Weaknesses: Addresses identified vulnerabilities to prevent future fraud.
Explanation of Incorrect Answer:
D. Considering political ramifications: Irrelevant to fraud audits, as these audits focus on financial and legal matters rather than political considerations.
References:
Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE),Fraud Examination Manual.
Government Accountability Office (GAO),Fraud Risk Management Framework.
Who holds primary responsibility for establishing internal controls?
ccountants
internal auditors
management
audit committee
Answer:
Explanation:
Responsibility for Internal Controls:
Managementholds the primary responsibility for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an organization’s internal control system.
This responsibility is outlined in frameworks such as COSO’sInternal Control - Integrated Frameworkand the GAO’sGreen Book.
Roles of Other Parties:
A. Accountants: While accountants may assist in designing or assessing controls, they are not primarily responsible.
B. Internal auditors: Their role is to evaluate the effectiveness of controls, not establish them.
D. Audit committee: Provides oversight but does not implement or design controls.
References:
COSO,Internal Control - Integrated Framework.
GAO,Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government (Green Book).
To support optimal cash management vendor payment procedures, invoices with discount terms should be paid
after the due date to increase cash flow.
prior to the due date to improve credit rating.
on the due date, unless a charge is assessed for late payment.
on the discount date.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·Why Pay on the Discount Date?
Discount termsare offered by vendors to encourage early payment, such as "2/10, net 30" (2% discount if paid within 10 days). Paying on the discount date ensures the organization takes advantage of cost savings while still making timely payments.
This approach optimizes cash management by reducing payment obligations while maintaining good vendor relationships.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. After the due date:Late payments can damage vendor relationships and incur penalties.
B. Prior to the due date:Paying too early does not provide additional benefits and can unnecessarily deplete cash reserves.
C. On the due date:If a discount is offered, waiting until the due date means missing the opportunity to save money.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Financial Management Guide:Recommends paying invoices with discounts on the discount date to maximize cost savings.
Best Practices in Governmental Cash Management (AGA):Highlights the importance of managing vendor payments to take advantage of discounts.
One of the minimum components of a government financial system is
automated transaction processing.
debt-reduction analysis.
performance management reporting.
general ledger account definition.
Answer:
Explanation:
Minimum Components of a Government Financial System:
A general ledger is the foundation of any financial system, providing a complete record of all financial transactions.
The definition ofgeneral ledger accountsensures proper classification, tracking, and reporting of financial activities.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Automated transaction processing: Incorrect. While automation is beneficial, it is not a "minimum" requirement. Manual systems can still exist.
B. Debt-reduction analysis: Incorrect. This is a financial management activity, not a core component of the financial system.
C. Performance management reporting: Incorrect. Performance reporting is separate from the foundational financial system.
D. General ledger account definition: Correct. This is a fundamental element of any government financial system.
References:
GAO,Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government (Green Book).
GASB,Codification of Governmental Accounting and Financial Reporting Standards.
Earned value management is preferred over traditional project management because
earned value management is used to monitor progress and deliverables of smaller projects.
earned value management provides information about status of deliverables, funds and time expended.
traditional project management is used to monitor progress and deliverables of larger projects.
traditional project management provides information about status of deliverables, funds and time expended.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Is Earned Value Management (EVM)?
EVMis a project management methodology that integrates scope, cost, and schedule to measure project performance. It provides a comprehensive view of progress by combining information about deliverables (work completed), funds (budget spent), and time (schedule adherence).
ï‚·Why Is EVM Preferred Over Traditional Project Management?
EVM offers a holistic view of project performance by quantifying progress and comparing it to planned performance, allowing for proactive decision-making.
Traditional project management often focuses on individual aspects (e.g., timelines or budgets) without integrating them as effectively as EVM.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. EVM monitors smaller projects:EVM is not restricted to small projects; it is widely used for complex, large-scale projects.
C. Traditional project management is used for larger projects:This is incorrect—both methodologies can be used for projects of any size.
D. Traditional project management provides status on deliverables, funds, and time:This is inaccurate; traditional methods often lack the integrated performance tracking provided by EVM.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Guide to Project Management:Recommends EVM for comprehensive performance tracking.
PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge):Details the advantages of EVM over traditional project management.
Which of the following is a forensic technique used to quantify the impact of fraud?
test of controls
computer-assisted audit techniques
data integrity
benchmarking
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Are Computer-Assisted Audit Techniques (CAATs)?
CAATsare specialized tools used in forensic accounting and auditing to analyze large volumes of data for patterns, anomalies, and irregularities that may indicate fraud.
These techniques help quantify the impact of fraud by identifying discrepancies, overpayments, or unaccounted transactions.
ï‚·Why Are CAATs Used for Quantifying Fraud?
CAATs can efficiently analyze transactional data, calculate losses, and determine the extent of financial damage caused by fraud.
Examples include using software to detect duplicate payments, inflated invoices, or unauthorized transactions.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Test of controls:Tests of controls evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls but do not quantify the impact of fraud.
C. Data integrity:Ensuring data integrity is important, but it does not specifically address quantifying fraud.
D. Benchmarking:Benchmarking compares performance metrics but does not analyze or quantify fraud.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Fraud Prevention Framework:Highlights the use of CAATs in forensic accounting.
AICPA Forensic Accounting Guidelines:Recommends CAATs for fraud detection and quantification.
The Federal Credit Reform Act requires complex calculations, which are likely to include errors. This is an example of
audit risk.
control risk.
detection risk.
inherent risk.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·Definition of Inherent Risk:Inherent risk refers to the risk of material misstatement in financial statements or other reports due to the nature of the subject matter, without considering any controls in place. It arises from the complexity, judgment, or uncertainty involved in the underlying transactions or calculations.
ï‚·Why This Is Inherent Risk:
TheFederal Credit Reform Actrequires complex calculations to estimate loan subsidies, interest rates, and cash flows. These calculations inherently involve significant judgment and estimation, making them prone to errors. This is a classic example of inherent risk because the complexity exists regardless of controls.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Audit Risk:This refers to the overall risk that the auditor may issue an incorrect opinion. In this case, the issue is about the inherent complexity of the calculations, not the auditor’s procedures.
B. Control Risk:This is the risk that errors will not be prevented or detected due to weak internal controls. While control risk could contribute to misstatements, it is not the primary issue in this example.
C. Detection Risk:This is the risk that auditors will not detect a misstatement. This risk relates to audit procedures, not the inherent complexity of the calculations.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Yellow Book on Risk Assessment:Explains inherent risk in the context of government financial reporting.
AICPA Standards on Audit Risk (AU-C 315):Highlights inherent risk as arising from the nature of transactions or subject matter.
In a performance aygit, due professional care is used to
obtain sufficient and competent evidence.
determine scope.
set materiality of financial statements.
present the findings in accordance with GAAP.
Answer:
Explanation:
Performance Audit Overview:
A performance audit focuses on evaluating the economy, efficiency, and effectiveness of government programs or activities.
Due professional care is a requirement inGovernment Auditing Standards (Yellow Book), ensuring auditors perform their duties responsibly and with professional judgment.
Key Requirement: Sufficient and Competent Evidence:
Auditors must collect sufficient and reliable evidence to support their findings, conclusions, and recommendations. This is the cornerstone of "due professional care."
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Obtain sufficient and competent evidence: Correct. This ensures audit findings are supported by reliable, documented evidence.
B. Determine scope: While part of audit planning, it is not directly related to due professional care.
C. Set materiality of financial statements: This applies to financial audits, not performance audits.
D. Present the findings in accordance with GAAP: GAAP is not a requirement for performance audits.
References:
GAO,Government Auditing Standards (Yellow Book).
Association of Government Accountants (AGA),Performance Auditing Practices.
The National Performance Management Advisory Commission established a comprehensive framework that
incorporates performance measurement into the
internal control plan.
financial statements.
audit procedures.
budget process.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·National Performance Management Advisory Commission Framework:
TheNational Performance Management Advisory Commissiondeveloped a comprehensive framework to integrateperformance measurementinto government operations.
One of its primary goals was to incorporate performance metrics into thebudget processto align resource allocation with program outcomes.
This ensures that budgeting decisions are informed by program performance, improving efficiency and accountability.
ï‚·Why the Budget Process?
By linking performance to budgeting, governments can prioritize funding for programs that demonstrate effectiveness and reduce funding for underperforming initiatives.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Internal control plan:Internal controls focus on risk management, not incorporating performance measurement.
B. Financial statements:Performance metrics are not reported in financial statements, which focus on financial position and results.
C. Audit procedures:Audits verify financial accuracy and compliance but do not incorporate performance measurement.
ï‚·References and Documents:
National Performance Management Advisory Commission Report (2010):Recommends integrating performance measurement into the budget process.
GAO Guide on Performance Budgeting:Explains how performance metrics inform budget decisions.
The main objective of the Cash Management Improvement Act is to require
states to pay invoices within 30 days of receipt of a proper invoice.
states to minimize the time elapsing between funds drawn and their final disposition.
federal agencies to take discounts when available and cost-effective.
federal agencies to disburse payments via electronic funds transfer.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Is the Cash Management Improvement Act (CMIA)?
CMIA requires states and federal agencies to minimize the time between when federal funds are drawn (transferred to the state) and when those funds are spent (final disposition).
The goal is to reduce idle funds, ensure efficient use of federal funds, and reduce interest liabilities for both parties.
ï‚·Key Objective:
By minimizing the time between fund transfers and usage, the act ensures that federal funds are used promptly for their intended purposes, preventing excess cash from sitting idle in state accounts.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. States to pay invoices within 30 days:This is unrelated to CMIA; it is part of general payment practices.
C. Federal agencies to take discounts:This relates to payment terms, not the timing of fund transfers.
D. Federal agencies to disburse payments via EFT:While electronic funds transfers are a common practice, CMIA focuses on minimizing idle funds, not payment methods.
ï‚·References and Documents:
Cash Management Improvement Act (1990):Mandates reducing the time between fund transfer and usage.
Treasury Financial Manual:Provides specific guidelines for implementing CMIA.
In the context of audit risk, which type of risk is primarily influenced by the effectiveness of an organization's internal
controls?
inherent risk
control risk
detection risk
audit risk
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Is Control Risk?
Control riskrefers to the risk that an organization’s internal controls will fail to prevent or detect material misstatements in a timely manner.
The effectiveness of internal controls directly influences control risk. If controls are weak or poorly designed, the risk increases.
ï‚·Why Is Option B Correct?
The primary focus of control risk is the adequacy and effectiveness of an entity’s internal controls. Effective controls reduce the likelihood of material misstatements, while deficiencies increase control risk.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Inherent Risk:This is the risk of material misstatements due to the nature of the business or transactions, independent of controls.
C. Detection Risk:This refers to the risk that auditors will fail to detect material misstatements. It is influenced by the nature and extent of audit procedures, not internal controls.
D. Audit Risk:This is the overall risk that an auditor will issue an incorrect opinion. It combines inherent, control, and detection risks.
ï‚·References and Documents:
AICPA Standards on Audit Risk (AU-C 315):Explains control risk and its relationship to the effectiveness of internal controls.
GAO Yellow Book:Emphasizes assessing control risk when evaluating internal controls in audits.
A state agency has begun a pilot program with a community action agency for a community-based approach to provide services to underserved areas. A review after the first year compared the number of families served by both agencies and identified efficiencies reached by having community involvement. What type of engagement was used to review the pilot program?
financial audit
single audit
performance audit
attestation
Answer:
Explanation:
Type of Engagement for Reviewing Pilot Programs:
A performance audit evaluates theeffectiveness, efficiency, and economyof programs or operations.
In this case, the review of the pilot program assessed the number of families served and the efficiencies achieved through community involvement, which aligns with performance auditing objectives.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Financial audit: Focuses on the accuracy of financial statements, not program effectiveness or efficiency.
B. Single audit: Focuses on compliance with federal grant requirements, not program evaluation.
C. Performance audit: Correct. This type of audit reviews program outcomes and operational efficiencies.
D. Attestation: Provides assurance on specific subject matter but does not evaluate program performance.
References:
GAO,Government Auditing Standards (Yellow Book).
Association of Government Accountants (AGA),Performance Auditing Best Practices.
A federal government agency that expends beyond its appropriation is in violation of the
Federal Managers’ Financial Integrity Act.
Federal Financial Management Improvement Act.
Antideficiency Act.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
Answer:
Explanation:
Antideficiency Act Overview:
TheAntideficiency Act (31 U.S.C. §§ 1341, 1342, 1517)prohibits federal agencies from:
Obligating or expending funds in excess of their appropriations.
Entering into contracts without sufficient appropriated funds.
Violating the Act is a serious matter, and agencies are required to report such violations to Congress and the President.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Federal Managers’ Financial Integrity Act: Incorrect. This Act requires agencies to assess internal controls, not monitor appropriations.
B. Federal Financial Management Improvement Act: Incorrect. This Act focuses on improving financial systems, not budgetary compliance.
C. Antideficiency Act: Correct. This Act directly prohibits expenditures beyond appropriations.
D. Sarbanes-Oxley Act: Incorrect. This Act applies to corporate financial reporting, not federal appropriations.
References:
Antideficiency Act (31 U.S.C. §§ 1341, 1342, 1517).
GAO,Principles of Federal Appropriations Law.
The first step in investment management is to
ensure all employees understand their investment options.
develop a consensus among managers of the investment objectives.
develop an investment policy manual.
establish criteria for divesting.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·Investment Management Basics:The first step in investment management is establishing theobjectivesof the investment program. This requires consensus among key stakeholders, such as managers, on what the investment goals are (e.g., risk tolerance, return expectations, liquidity needs).
Without clear objectives, subsequent steps like developing policies or selecting investments cannot be effectively carried out.
ï‚·Why Consensus Is Important:
Investment objectives must align with the organization’s mission, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
Consensus ensures that all managers are on the same page before developing specific strategies or policies.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Ensure employees understand their investment options:Employee understanding is not the first step; it comes later when the investment strategy is implemented.
C. Develop an investment policy manual:This happens after the objectives have been established.
D. Establish criteria for divesting:Divestment criteria are part of the investment policy and are determined later.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Financial Management Guide:Highlights setting objectives as the first step in investment management.
COSO Framework for Investment Risk Management:Stresses the importance of aligning objectives before policy development.
According to OMB Circular A-11, what analytical method should be used to measure the cost, schedule and performance goals of a capital asset acquisition project?
earned value management
net present value
future value
regression analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
OMB Circular A-11 and Capital Asset Acquisition:
OMB Circular A-11 mandates the use ofearned value management (EVM)for measuring cost, schedule, and performance goals in capital asset acquisition projects.
EVM integrates project scope, schedule, and cost data to assess project performance and forecast outcomes.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Earned value management: Correct. EVM is the prescribed method for tracking progress on capital projects under OMB Circular A-11.
B. Net present value: Used for financial analysis, such as determining the economic value of future cash flows, but not for tracking project progress.
C. Future value: Measures the value of an investment at a future point, not applicable to project tracking.
D. Regression analysis: A statistical method for identifying relationships between variables, not for measuring project performance.
References:
OMB Circular A-11,Capital Programming Guide.
U.S. General Services Administration (GSA),Earned Value Management Implementation.
The Federal Credit Reform Act of 1990 prescribes a special budget treatment for direct loans and loan guarantees
that measures cash flows to and from the government using which financial analytical technique?
future value
net present value
current value
regression analysis
Answer:
Explanation:
Federal Credit Reform Act of 1990:This Act established a new accounting framework for federal credit programs, such as direct loans and loan guarantees. It requires using thenet present value (NPV)method to measure the costs of loans and guarantees by discounting future cash flows (e.g., loan repayments, defaults) to their present value.
Explanation of Financial Analytical Technique:
Net Present Value (NPV): Accounts for the time value of money by discounting future cash flows to the present. It provides an accurate measure of the economic cost to the government.
Other options:
A. Future value: Focuses on future cash flows, not their present cost.
C. Current value: Not a recognized technique for analyzing long-term cash flows.
D. Regression analysis: A statistical method, unrelated to calculating loan program costs.
References:
Federal Credit Reform Act of 1990, Section 502.
Congressional Budget Office (CBO),Federal Credit Program Cost Analysis.
Office of Management and Budget (OMB),Circular A-11: Credit Reform Accounting.
Auditors may limit their public reporting in attestation engagements when the
auditors detect material fraud.
audit report would compromise ongoing legal proceedings.
auditor detects non-compliance with provisions of law.
entity management fails to satisfy legal requirements.
Answer:
Explanation:
Limiting Public Reporting in Attestation Engagements:
Government auditing standards allow auditors to limit public reporting in rare cases, such as when disclosing certain information could compromise sensitive or ongoing legal proceedings.
The goal is to protect the integrity of investigations or legal actions while maintaining transparency where possible.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Auditors detect material fraud: Auditors are required to report material fraud to appropriate authorities, not limit reporting unless legal proceedings are affected.
B. Audit report would compromise ongoing legal proceedings: Correct. This is a valid reason to limit public reporting under auditing standards.
C. Auditor detects non-compliance with provisions of law: Non-compliance must be disclosed unless legal considerations warrant confidentiality.
D. Entity management fails to satisfy legal requirements: This would typically be reported, not withheld.
References:
GAO,Government Auditing Standards (Yellow Book).
AICPA,Attestation Standards and Public Reporting Guidance.
A variable that would influence management's decision to hire contractors to perform management control
evaluations is
lack of management expertise.
availability of qualified contractors.
suspicion of internal fraud.
knowledge of systemic deficiencies.
Answer:
Explanation:
Why Hire Contractors for Management Control Evaluations?Management may decide to bring in external contractors when there are gaps in the organization’s capacity to perform evaluations internally. One key factor is thelack of management expertise—if management lacks the necessary knowledge or experience to evaluate controls effectively, it may outsource this task to qualified contractors.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Availability of Qualified Contractors:While availability is a factor, it’s not a variable that influences the decision to outsource. Instead, it’s a logistical consideration once the decision has been made.
C. Suspicion of Internal Fraud:Suspicion of fraud may lead to investigations, but hiring contractors to evaluate controls is driven by expertise gaps rather than fraud concerns.
D. Knowledge of Systemic Deficiencies:If management already has knowledge of systemic deficiencies, they may focus on remediation rather than outsourcing evaluations.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Standards for Internal Control in the Federal Government (Green Book):Emphasizes the need for knowledgeable personnel to evaluate controls.
GAGAS (Yellow Book):Highlights the role of external expertise in cases where internal expertise is insufficient.
Given the information below, which control would be the lowest priority?
Asset$Amount at RiskCost of Control
AssetA $ 150,000$15,000
Asset B$6,000$ 2,500
Asset C$2,000,000$50,000
Asset D$500,000$20,000
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·How to Prioritize Controls Based on Cost and Risk:
The priority of a control is based on its cost-effectiveness. Controls that protect assets with higher risk exposure relative to the cost of the control should be prioritized. The formula to calculate cost-effectiveness is: Cost-Effectiveness=Cost of ControlAsset Amount at Risk\text{Cost-Effectiveness} = \frac{\text{Cost of Control}}{\text{Asset Amount at Risk}}Cost-Effectiveness=Asset Amount at RiskCost of Control​
Lower ratios indicate more cost-effective controls.
ï‚·Calculations:
Asset A:$15,000 / $150,000 = 0.10 (10%)
Asset B:$2,500 / $6,000 = 0.42 (42%)
Asset C:$50,000 / $2,000,000 = 0.025 (2.5%)
Asset D:$20,000 / $500,000 = 0.04 (4%)
ï‚·Lowest Priority:
Asset Bhas the highest ratio (42%), meaning it is the least cost-effective and should be the lowest priority for controls.
ï‚·References and Documents:
COSO Internal Control Framework:Discusses cost-benefit analysis for prioritizing controls.
GAO Risk Management Guide:Emphasizes evaluating control cost-effectiveness relative to asset risk.
Government performance measurement promotes
responsibility.
profitability.
accountability.
cash availability.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Is Government Performance Measurement?Government performance measurement is the process of setting goals, tracking progress, and evaluating outcomes for government programs and services. This system ensures that public funds are used effectively and that programs achieve intended results.
ï‚·How Does It Promote Accountability?
Accountability is the primary goal of performance measurement. It holds government officials and agencies responsible for managing public resources efficiently and achieving measurable outcomes.
By measuring performance, governments can transparently demonstrate how resources are being used and whether programs are meeting their objectives.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Responsibility:While responsibility is important, it refers more to the assignment of duties, not the system of holding entities accountable.
B. Profitability:Governments are not profit-driven organizations; their focus is on service delivery, not profits.
D. Cash Availability:Performance measurement focuses on outcomes, not managing cash flows.
ï‚·References and Documents:
Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA):Promotes accountability through performance measurement and reporting.
GAO Report on Performance Accountability:Emphasizes the role of performance measurement in achieving government accountability.
An employee is set to receive a lumpsum payment of $500,000 in ten years. The agency uses an opportunity rate of 12% for its investments. If inflation is 3%, how much must the agency invest today to cover the future lumpsum payment?
$160,986
$186,023
$440,000
$485,000
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Are We Solving For?
We are determining the present value (PV) of a $500,000 lump sum payment to be received in 10 years, using anopportunity rate of 12%. Inflation is not relevant here because the opportunity rate already reflects the expected return, including inflation adjustments.
ï‚·Formula for Present Value:The present value (PV) is calculated using the formula:
PV=FV(1+r)nPV = \frac{FV}{(1 + r)^n}PV=(1+r)nFV​
Where:
FVFVFV = Future Value = $500,000
rrr = Opportunity rate = 12% or 0.12
nnn = Number of years = 10
ï‚·Calculation:
PV=500,000(1+0.12)10PV = \frac{500,000}{(1 + 0.12)^{10}}PV=(1+0.12)10500,000​ PV=500,000(1.12)10PV = \frac{500,000}{(1.12)^{10}}PV=(1.12)10500,000​ PV=500,0003.10585PV = \frac{500,000}{3.10585}PV=3.10585500,000​ PV≈160,986PV ≈ 160,986PV≈160,986
ï‚·Why Inflation Is Not Included:
The opportunity rate already incorporates the expected inflation. Using it ensures the PV reflects the real purchasing power of the future lump sum payment.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. $186,023, C. $440,000, D. $485,000:These values result from incorrect calculations or the misuse of inflation in the formula.
ï‚·References and Documents:
GAO Financial Analysis Guide:Recommends using present value calculations with opportunity rates for investment decision-making.
AICPA Financial Management Guide:Provides detailed examples of calculating present value for lump sum payments.
A governmental attestation engagement may include a requirement to
monitor a subgrantee for compliance to the grant restrictions.
establish a policy concerning fraud prevention.
monitor purchasing card charges for compliance with travel policies.
review the revenue coverage requirements on outstanding bonds.
Answer:
Explanation:
Governmental Attestation Engagements:
These engagements involve providing assurance on specific elements of financial or non-financial information, such as compliance with laws, contracts, or bond covenants.
Reviewing revenue coverage requirements for outstanding bonds fits the scope of attestation engagements, which focus on confirming adherence to specific requirements.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Monitor a subgrantee for compliance to the grant restrictions: Monitoring is a management responsibility, not typically part of an attestation engagement.
B. Establish a policy concerning fraud prevention: Establishing policies is a management duty, not a task for auditors.
C. Monitor purchasing card charges for compliance with travel policies: Monitoring is operational, not attestation-related.
D. Review the revenue coverage requirements on outstanding bonds: Correct. This falls within the scope of attestation engagements.
References:
GAO,Government Auditing Standards (Yellow Book).
AICPA,Attestation Standards for Government Engagements.
The goal of shared gervices is to
reduce current staffing levels.
transfer responsibilities to another entity.
efficiently aggregate resources.
provide private business opportunities.
Answer:
Explanation:
Understanding Shared Services:Shared services involve consolidating and centralizing resources, personnel, or processes to achieve efficiency and cost savings. This is common in government organizations looking to optimize operations.
Explanation of Answer Choices:
A. Reduce current staffing levels: While staff reductions may occur as a result, this is not the primary goal.
B. Transfer responsibilities to another entity: This describes outsourcing, not shared services.
C. Efficiently aggregate resources: Correct, as shared services aim to centralize resources for improved efficiency.
D. Provide private business opportunities: This is unrelated to shared services, which focus on internal government operations.
References:
Association of Government Accountants (AGA),Shared Services in Government.
Management shoulg consider the cost of internal controls in relationship to
the available budget.
inherent risks.
benefits provided.
risk of collusion.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·Why Should Management Consider the Cost of Internal Controls in Relation to Benefits?
Thecost-benefit principlestates that the cost of implementing and maintaining internal controls should not exceed the benefits derived from those controls. Effective internal controls help mitigate risks, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance, but their implementation comes with costs (e.g., time, resources, systems).
Management must evaluate whether the benefits of preventing or detecting potential issues (e.g., fraud, errors) justify the associated costs.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. The available budget:While the budget is important, internal controls are not solely dictated by budget constraints; their effectiveness and benefit-to-cost ratio are key considerations.
B. Inherent risks:While inherent risks are a factor in determining control needs, the relationship between cost and benefit remains the primary consideration.
D. Risk of collusion:Controls address collusion risks, but management does not prioritize collusion specifically when assessing cost versus benefit.
ï‚·References and Documents:
COSO Internal Control Framework:Highlights the cost-benefit principle when implementing controls.
GAO Standards for Internal Control (Green Book):Emphasizes balancing costs with benefits when designing internal control systems.
Pay.gov is an example of
a zero-balance account.
a concentration system.
an electronic lockbox.
a data warehouse system.
Answer:
Explanation:
ï‚·What Is Pay.gov?
Pay.govis anelectronic lockbox systemmanaged by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. It allows federal agencies to collect payments electronically, improving efficiency and reducing the time and cost associated with manual payment processing.
It supports online payments for taxes, fees, and other government-related obligations.
ï‚·Why Is It an Electronic Lockbox?
Pay.gov consolidates and processes payments on behalf of federal agencies, similar to how a lockbox service processes payments for private businesses.
ï‚·Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Zero-balance account:This refers to a type of bank account that maintains a balance of zero by automatically transferring funds as needed, unrelated to Pay.gov’s purpose.
B. Concentration system:Refers to pooling funds from multiple accounts into one central account, not payment processing.
D. Data warehouse system:A data warehouse stores and organizes large amounts of data for analysis, unrelated to payment collection.
ï‚·References and Documents:
U.S. Treasury Pay.gov Website:Describes Pay.gov as an electronic lockbox for federal payment processing.
GAO Financial Management Systems Guide:Highlights the role of electronic lockboxes like Pay.gov in improving efficiency.

