The family of a patient with trauma believes that the patient is in pain and requests that a neighbor, a therapeutic touch practitioner, be allowed to see the patient. Unit policy allows visits by immediate family only. Which of the following is the most important consideration in a nurse's decision about facilitating the visit?
The nurse is caring for a patient with neutropenia secondary to chemotherapy. When communicating dietary needs to the provider, the nurse should request which of the following to improve the patient's immune function?
Which of the following should the nurse expect in a patient with papillary muscle dysfunction?
A patient is experiencing lower left quadrant pain with guarding, as well as abdominal distention and rigidity. KUB reveals free air in the abdominal
cavity. Vital signs are:
BP76/40
HR130
RR32
T101.7° F (38.7°C)
A nurse would suspect
Family members have been complaining about limited visiting hours. To facilitate a potential change in practice, a nurse should first
The spouse of a critically ill patient is indecisive, withdrawn, and tells the nurse, "I feel so helpless." Appropriate nursing interventions include
There is an increase in catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) following a change in urinary catheter insertion trays. After conducting a literature review of evidence-based practices regarding indwelling catheter insertion and care, the nurse should
A patient lying on the left side in Trendelenburg position is in the correct position for postural drainage of which of the following lobes of the lungs?
A patient is admitted for hypertensive crisis. As a nurse is starting a peripheral IV, the patient appears increasingly anxious as the catheter is about to be inserted. The patient threatens to harm the nurse if the catheter insertion causes pain. Which of the following is the nurse's best action?
A patient reported to have smoked crack cocaine is brought to the hospital by paramedics and admitted in an agitated state. On the way to the hospital, the patient had a generalized seizure. The toxicology screen is positive for cocaine. Which of the following is most appropriate to administer?
A patient is admitted with an acute anterior wall MI. Initial hemodynamic readings are:

The nurse anticipates initiating a plan of care for
An unconscious patient presents with the following laboratory values:
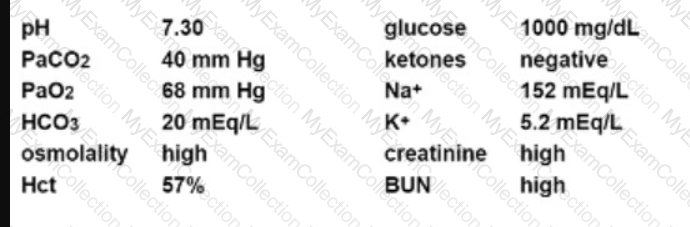
Appropriate management of this patient should include
When assessing a patient who has acute pancreatitis, which of the following findings require immediate notification to the provider?
Postoperatively, symptoms that may indicate hemothorax or internal bleeding in a video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) patient include
Examination of a patient exhibiting Kernig's and Brudzinski's signs indicates which of the following?
A nurse has responded to a rapid response call on a medical-surgical floor in the hospital. The nurse finds the patient with the following data:
BP72/30
HR132
RR24
T102.3° F (39.0° C)
SpO295%
Ph7.13
PaCO234 mm Hg
PaO288 mm Hg
HCO3 14 mEq/L
Na+ 142 mEq/L
The nurse should anticipate an order to administer which of the following?
A patient who was admitted after an open aortofemoral bypass for claudication at rest has a hemoglobin A1C of 8.9. The patient admits having poor control of blood glucose levels and is scared to use insulin as directed because of a few episodes of hypoglycemia. Which of the following should the nurse initially request to be consulted?
The nurse who is caring for a patient following an esophagectomy notes new subcutaneous emphysema in the upper chest and neck. The nurse should expect an order for
A patient with acute renal failure has a serum potassium level of 7.2 mEq/L. The most appropriate immediate intervention for this patient is
A patient with hypertension received tPA for an acute embolic stroke with complete resolution of symptoms. Twenty-four hours after tPA administration, the nurse should anticipate an order for
A patient with unilateral facial droop and slurred speech has a history of hyperlipidemia and hypertension. The nurse should anticipate an order for a
During the monthly code team review, it is noted that regulators have been consistently missing from the O2 tanks. Which of the following is a nurse's best action?
An older adult patient reports an inability to sleep due to staff waking the patient for frequent neurological assessments. In order to minimize sleep disruptions, the nurse should
A unit council is requesting to change a documentation screen of the electronic health record (EHR) at a large health system. The change was not discussed with the department prior to the request and was denied by the EHR committee. Which of the following strategies will most likely lead to accomplishing the team's goals?
The primary pathophysiology underlying acute respiratory failure in a patient with head trauma involves
A patient in septic shock is treated with a dopamine (Intropin) infusion of 10 mcg/kg/min. Which of the following indicates that this intervention has been effective?
A patient who survives near-drowning develops hypoxia-induced cerebral edema. Interventions should include
After observing an increase in the occurrence of oral pressure injuries in intubated patients on the unit, the nurse should
A patient is receiving continuous enteral feedings via jejunostomy tube. The patient develops mild, intermittent diarrhea. Which of the following actions is most appropriate?
Potentially life-threatening consequences of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) include
Which of the following ECG changes is expected in a patient with a potassium concentration of 3.0 mEq/L?
A nurse is performing medication reconciliation during a patient's admission. To determine the patient's current understanding of the medication furosemide (Lasix), which of the following is the best statement by the nurse?
The underlying pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is best explained as
A patient is admitted with hypotension, tachycardia, and intermittent confusion. Upon arrival, the patient asks to walk to the bathroom. Which of the
following is a nurse's best action?
A patient was admitted 3 days ago for an overdose of acetaminophen (Tylenol). The patient is developing a decreasing level of consciousness. Which the following is the most likely finding?
 Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis
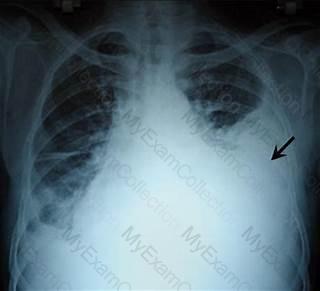 Hemothorax
Hemothorax Hypovolemic shock
Hypovolemic shock A bag of food on a hook
Description automatically generated
A bag of food on a hook
Description automatically generated
 Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia
