There are several differences between IS-IS Hello packets used on broadcast interfaces and on point-to-point interfaces.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
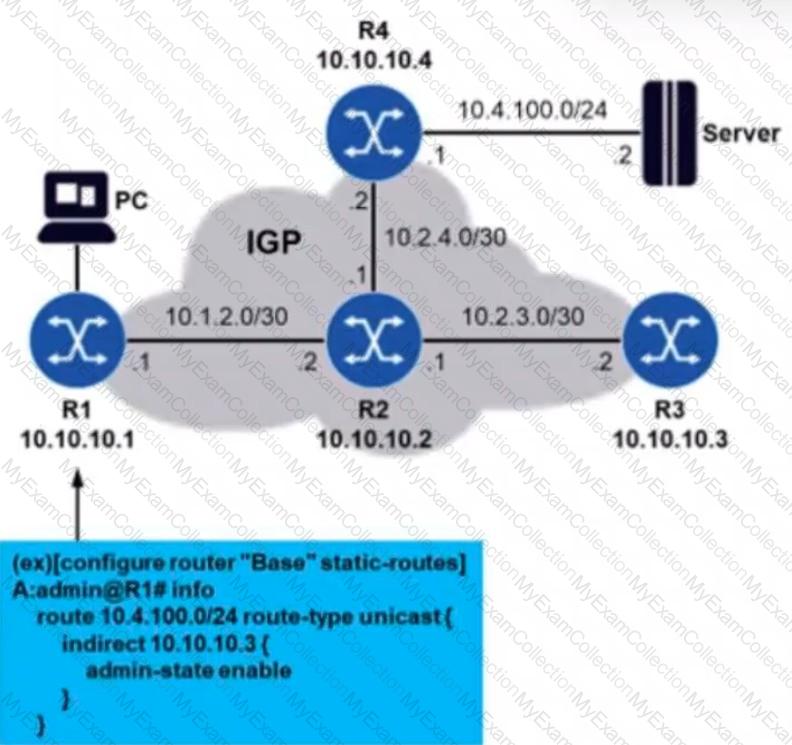
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other’s system IP addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails. What may be the problem in this case?
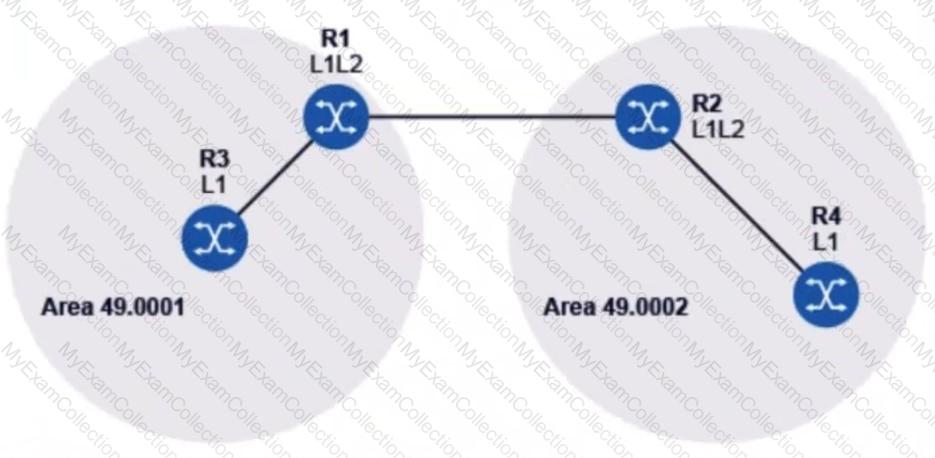
Routers R1 through R4 in the diagram have established IS-IS adjacencies. Router R1 is L1/L2 and is the DIS of its two broadcast interfaces. How many LSPs will it generate?
A series of actions are triggered on a router as a result of enabling both loopfree-alternate for a link-state routing protocol and ip-fast-reroute. Which of the following is NOT one of those actions?
What do the address resolution protocol (ARP) for IPv4 and the neighbor discovery procedures for IPv6 have in common?
On a broadcast interface, an IS-IS router receives an LSP that is newer than the one on its database. Which of the following statements best describes the actions taken by the router as a consequence?
A router running a link-state routing protocol detects that one of its neighbors is no longer connected to it. The router generates a new link-state advertisement to inform other routers of the topology change. Which of the following is NOT an action that is triggered by this event?
A router is trying to establish an IS-IS adjacency with the DIS on a broadcast link. What event causes the adjacency to change from “Initializing†to “UP�

